Riboflavin, also known as Vitamin B2, is an essential nutrient that plays a key role in the body’s energy production and overall health. Here are the details regarding its effectiveness, side effects, and special precautions:
Effectiveness of Riboflavin:
1.Energy Production: Riboflavin is crucial for converting carbohydrates into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main form of energy used by cells.
2.Antioxidant Function: It acts as an antioxidant, helping to neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress.
3.Supports Growth and Development: Riboflavin is important for growth, red blood cell production, and the maintenance of skin and mucous membranes.
4.Eye Health: It may contribute to maintaining healthy vision, particularly in preventing cataracts.

Side Effects of Riboflavin:
Riboflavin is generally considered safe when taken within recommended doses. However, excessive intake can lead to some side effects:
1.Urine Discoloration: High doses of riboflavin can turn urine bright yellow-orange, which is harmless but can be alarming to some individuals.
2.Diarrhea: In rare cases of very high doses, riboflavin may cause diarrhea.
Special Precautions of Riboflavin:
1.Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Riboflavin requirements increase during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it’s generally safe when taken in normal amounts from food sources or supplements.
2.Medical Conditions: People with certain medical conditions may need to monitor their riboflavin intake:
Migraine Headaches: Riboflavin has been studied for its potential to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
Certain Genetic Disorders: Conditions like riboflavin transporter deficiency may require higher doses under medical supervision.
3.Interactions: Riboflavin can interact with some medications. For example, it may reduce the effectiveness of certain antibiotics like tetracyclines when taken together.
4.Allergies and Sensitivities: Individuals with known allergies or sensitivities to riboflavin should avoid supplements containing this vitamin.
Dosage:
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for riboflavin varies by age and gender. For adults, typical doses are around 1.1 to 1.3 mg per day for women and slightly higher for men (1.3 to 1.6 mg/day).
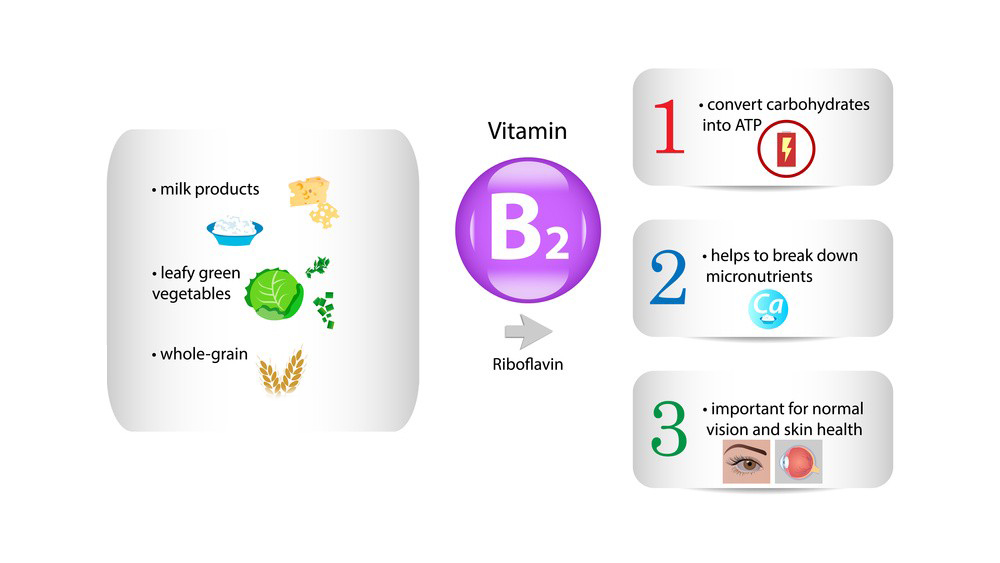
Food Sources:
Riboflavin is found naturally in various foods, including:
Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
Meat (especially liver and kidney)
Eggs
Green vegetables (like broccoli and spinach)
Nuts and seeds
Fortified cereals and grains
Conclusion:
Riboflavin is essential for energy production, growth, and antioxidant function in the body. It’s generally safe when consumed in recommended amounts, but excessive intake may cause minor side effects. For individuals with specific medical conditions or those taking medications, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure appropriate supplementation and avoid potential interactions.
