Liposomal Glutathione is a form of the antioxidant glutathione encapsulated in liposomes—tiny, spherical vesicles made from phospholipids. Liposomal delivery enhances the bioavailability of glutathione, allowing it to be absorbed more efficiently by the body. This comprehensive study explores its benefits, mechanisms, applications, and limitations.
1.Glutathione Overview
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant naturally present in human cells. It plays a critical role in:
Neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress.
Supporting immune function.
Detoxifying the liver by binding to toxins and making them easier to excrete.
Maintaining cellular health by promoting proper protein function and DNA synthesis.
Protecting against chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative conditions.
However, oral glutathione supplements have low bioavailability due to degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and liver, which is where liposomal technology comes into play.

2.Liposomal Technology and Its Advantages
Liposomal encapsulation involves the use of phospholipid bilayers that resemble cell membranes, enhancing the stability and absorption of nutrients. Liposomes protect the active compound (in this case, glutathione) from being degraded by stomach acids and enzymes, allowing for:
Increased Bioavailability: Liposomes help deliver glutathione directly to the bloodstream and cells, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract’s breakdown processes.
Improved Absorption: Glutathione is absorbed into the bloodstream more efficiently through liposomal delivery, potentially leading to faster and more significant therapeutic effects.
Extended Circulation Time: Liposomes can prolong the half-life of glutathione in the bloodstream, allowing it to be available for a longer period of time.
3.Biological Functions of Glutathione
Detoxification: Glutathione helps detoxify xenobiotics and heavy metals (like mercury and lead), facilitating their elimination from the body.
Antioxidant Defense: It neutralizes free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage that can lead to aging and chronic diseases.
Immune Support: Glutathione supports the immune system by regulating the function of lymphocytes, particularly T cells, which are critical for adaptive immunity.
Mitochondrial Function: It plays a crucial role in maintaining mitochondrial health, which is essential for cellular energy production.
Liver Protection: As glutathione is highly concentrated in the liver, it protects against liver damage from toxins, alcohol, and drugs.
4.Liposomal Glutathione: Mechanism of Action
Absorption: Liposomal glutathione is absorbed through the intestinal lymphatic system or directly through cell membranes due to its phospholipid shell, which is compatible with cell membranes.
Cellular Uptake: The liposome merges with the cell membrane, allowing glutathione to enter the cell where it exerts its antioxidant and detoxifying actions.
Systemic Effects: Once absorbed, glutathione circulates in the bloodstream, protecting tissues from oxidative damage, supporting immune health, and aiding detoxification processes.

5.Potential Benefits
a. Detoxification Support
Liposomal glutathione enhances liver detoxification by binding to toxins and heavy metals and promoting their excretion. This is especially beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental toxins or undergoing detox protocols.
b. Immune Modulation
Studies suggest that glutathione may enhance immune system function by boosting white blood cell count and activity, which is critical in fighting infections and controlling inflammation.
c. Neuroprotection
Glutathione helps protect brain cells from oxidative damage, which is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases. By reducing oxidative stress in neurons, liposomal glutathione may slow the progression of these conditions.
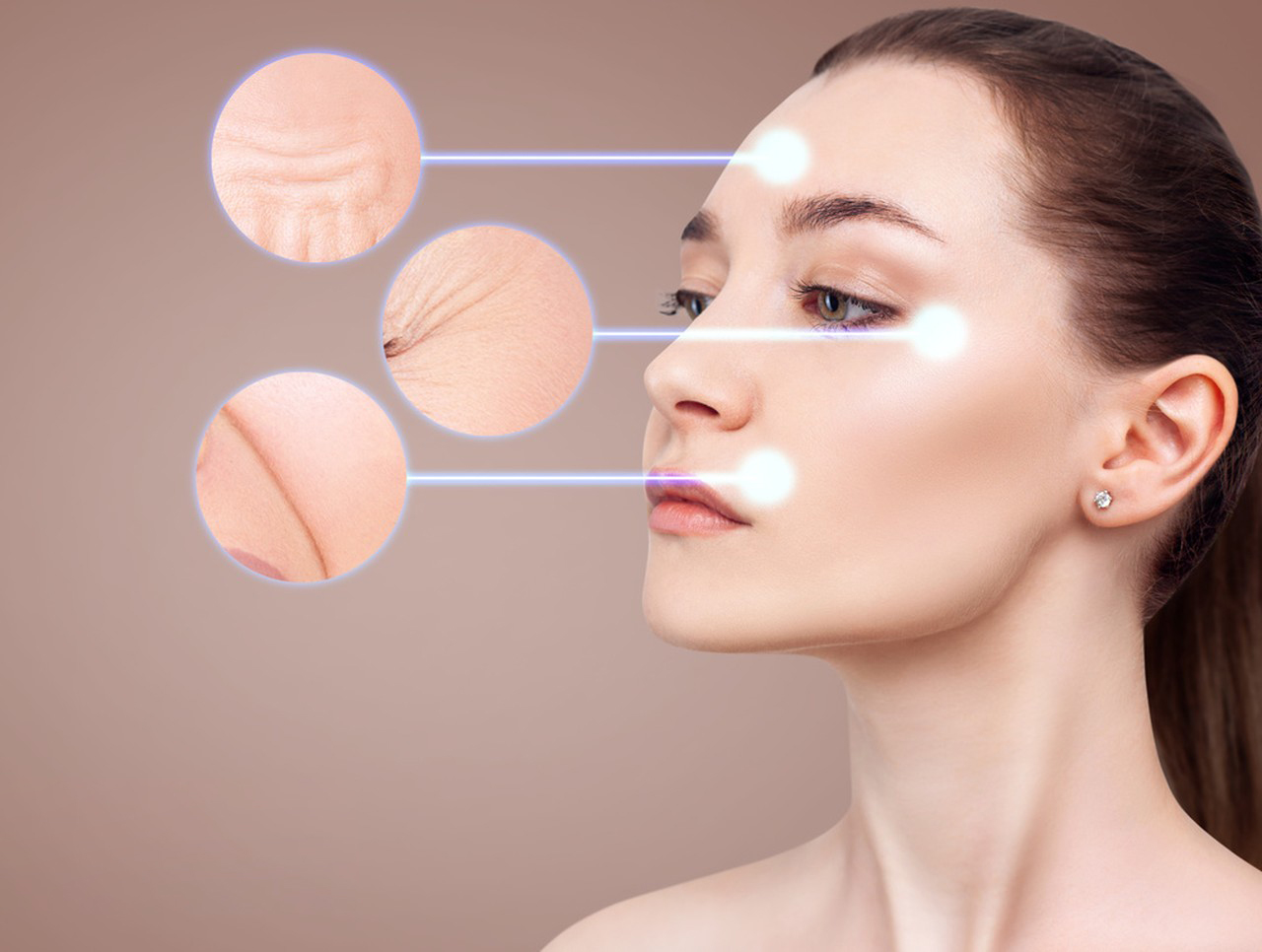
d. Anti-aging and Skin Health
Due to its antioxidant properties, glutathione has been promoted as an anti-aging agent. It reduces oxidative damage that contributes to aging, improves skin tone, and may lighten hyperpigmentation.
e. Cardiovascular Health
Glutathione’s role in neutralizing free radicals can help prevent oxidative stress that contributes to atherosclerosis, hypertension, and other cardiovascular conditions. It may also support healthy blood pressure and reduce cholesterol oxidation.
f. Chronic Disease Management
Because oxidative stress and inflammation are common factors in many chronic diseases, liposomal glutathione has been explored for its potential in managing conditions like diabetes, arthritis, and autoimmune diseases.
6.Clinical Studies and Evidence
Research on liposomal glutathione is still emerging, but early clinical studies and trials have shown promising results:
Oxidative Stress Reduction: Studies have demonstrated that liposomal glutathione reduces oxidative stress markers, such as malondialdehyde, in individuals under oxidative stress.
Improved Liver Function: In trials with patients suffering from liver diseases (like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease), liposomal glutathione supplementation has shown to improve liver enzyme profiles and reduce symptoms.
Support for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): There is some evidence suggesting that glutathione levels are often low in children with ASD. Liposomal glutathione has been explored for improving behavioral outcomes and oxidative stress levels in these individuals.
Parkinson’s Disease: Liposomal glutathione may improve motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients by protecting dopaminergic neurons from oxidative damage.
7.Dosing and Safety
Dosage: The typical dose of liposomal glutathione varies between 200 to 500 mg per day, though higher doses may be used in therapeutic contexts. The dosage should be individualized based on health needs and a healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Safety: Liposomal glutathione is generally considered safe for long-term use. Side effects are rare but can include gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals.
8.Challenges and Limitations
Cost: Liposomal formulations are typically more expensive than regular glutathione supplements due to the manufacturing process.
Limited Research: While liposomal delivery increases absorption, more research is needed to fully understand its long-term efficacy and benefits in various populations.
Storage: Liposomal products may require refrigeration to maintain stability, which can limit convenience and shelf life.
9.Alternative Forms of Glutathione
IV Glutathione: Intravenous administration offers 100% bioavailability but is costly and requires medical supervision.
S-Acetyl Glutathione: A newer form that may also enhance bioavailability but does not rely on liposomal technology.
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): A precursor to glutathione, NAC is often used to raise glutathione levels in the body.
10.Future Research Directions
Long-term Clinical Trials: More research is needed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of liposomal glutathione for chronic diseases.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Focus on the impact of liposomal glutathione in preventing or slowing neurodegenerative conditions.
Comparative Studies: More comparative studies between liposomal, IV, and oral glutathione could help elucidate the most effective delivery methods for various health conditions.
Conclusion
Liposomal glutathione is a promising supplement for enhancing antioxidant defense, detoxification, and immune function due to its superior bioavailability compared to traditional oral glutathione. Although clinical research is still growing, its potential benefits in chronic disease management, anti-aging, and overall health optimization make it an attractive option for individuals looking to improve their wellness. Further studies are needed to confirm its long-term effects and optimal dosing strategies.
