Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including inflammation and cell signaling. Here’s an overview of arachidonic acid oil:
Sources
- Dietary Sources: Arachidonic acid is found in animal products, particularly in meat, eggs, and dairy. It can also be synthesized in the body from linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid found in vegetable oils.
- Supplementation: Arachidonic acid oil is available as a dietary supplement, often marketed for athletes and bodybuilders to support muscle growth and recovery.
Functions
- Inflammation: It is a precursor to eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules that regulate inflammation, immune responses, and other physiological processes.
- Brain Health: Arachidonic acid is important for brain function and development, contributing to neuronal signaling and membrane fluidity.

Health Implications
- Pro-Inflammatory Effects: While necessary for certain bodily functions, excessive arachidonic acid can lead to heightened inflammatory responses, potentially contributing to various health issues such as cardiovascular disease and arthritis.
- Balance with Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Maintaining a balance between omega-6 (like arachidonic acid) and omega-3 fatty acids (like EPA and DHA) is crucial for overall health.
Usage
- Sports Nutrition: Some athletes use arachidonic acid oil to enhance muscle growth and performance, though research on its effectiveness is mixed.
- Dosage: If considering supplementation, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure it aligns with individual health goals.
Conclusion
Arachidonic acid oil can be beneficial in moderation, but it’s important to maintain a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids to mitigate potential inflammatory effects.
Metabolic pathway of Arachidonic Acid
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid that plays a crucial role in cellular signaling and inflammation. It is derived from membrane phospholipids and can be metabolized through several key pathways:
1.Phospholipase Activation: Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by the action of phospholipase A2.
2.Cyclooxygenase Pathway (COX Pathway):
- Arachidonic acid is converted to prostaglandins and thromboxanes by cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2).
- This pathway is involved in the mediation of inflammation, pain, and fever.
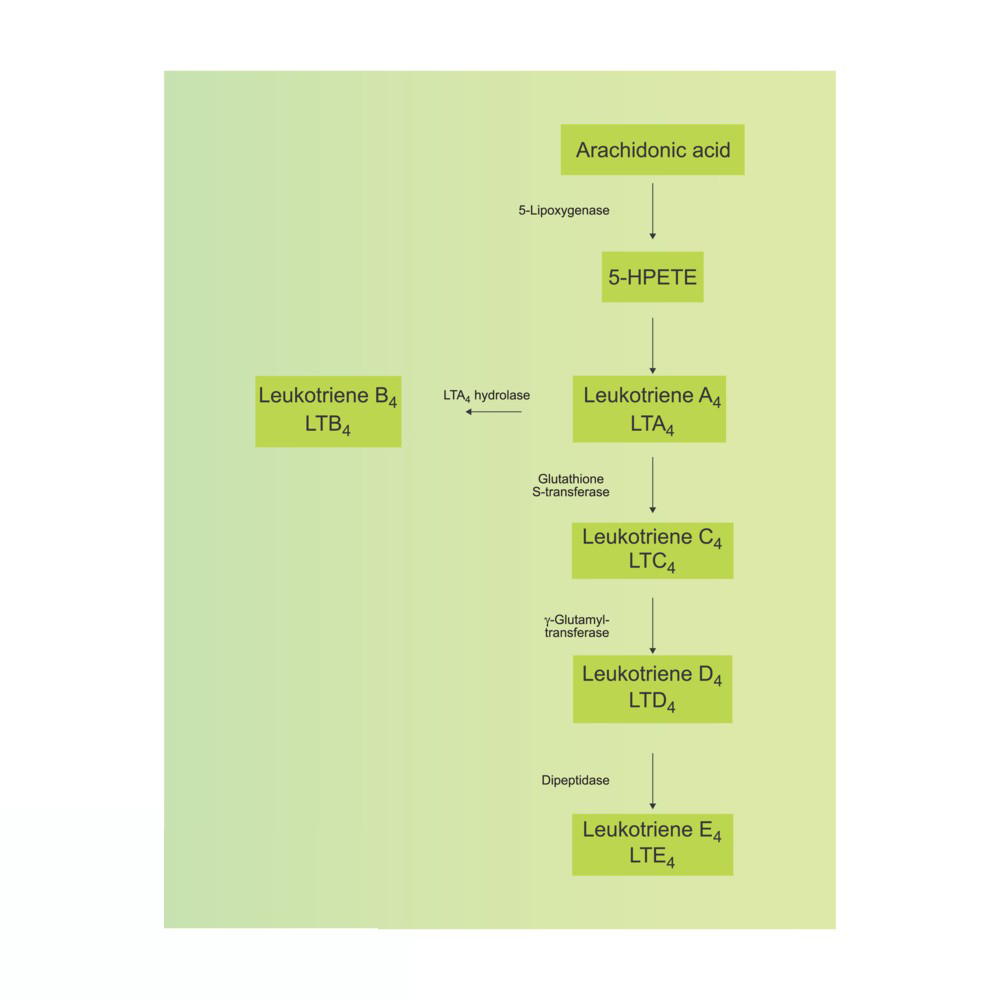
3.Lipoxygenase Pathway:
- Arachidonic acid is converted to leukotrienes by lipoxygenases (LOX).
- Leukotrienes are important in inflammatory responses, especially in asthma and allergic reactions.
4.Cytochrome P450 Pathway:
- Arachidonic acid can also be metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes to produce epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which have various biological effects, including vasodilation and anti-inflammatory properties.
5.Resolvins and Protectins:
- Under certain conditions, Arachidonic acid can be metabolized into specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), such as resolvins and protectins, which help to resolve inflammation.
Each of these pathways highlights the diverse roles of arachidonic acid in health and disease, influencing processes like inflammation, immunity, and cardiovascular function.
