Fullerene C60, also known as Buckminsterfullerene, is a unique allotrope of carbon with a fascinating structure and set of properties. Here is an overview:
Origin of Fullerene C60
- Discovery: Fullerene C60 was discovered in 1985 by scientists Harold Kroto, Richard Smalley, and Robert Curl, who later received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1996) for this work.
- Name Inspiration: It is named after architect Buckminster Fuller because its structure resembles his geodesic domes.
- Production Method: Fullerene C60 was first produced by vaporizing graphite in a helium atmosphere using a laser ablation technique. Later, it was synthesized using arc-discharge and other methods.
Structure of Fullerene C60
- Molecular Geometry: Fullerene C60 is composed of 60 carbon atoms arranged in a hollow, spherical structure. It resembles a soccer ball with a pattern of 12 pentagons and 20 hexagons, following Euler’s rule for polyhedra.
- Symmetry: It has high symmetry and belongs to the icosahedral point group (I_h).
- Bonding: The carbon atoms are sp² hybridized, and each atom is bonded to three others, forming a delocalized π-electron system over the surface.
Properties of Fullerene C60
1.Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Fullerene C60 is a black solid in its bulk form, and it can form crystals.
- Solubility: It is soluble in organic solvents like benzene and toluene, forming a purple-colored solution.
- Thermal Stability: Highly thermally stable but decomposes at temperatures above 600°C.
2.Chemical Properties:
- Reactivity: Fullerene C60 exhibits both aromatic and aliphatic properties. Its double bonds are reactive in reactions like hydrogenation and halogenation.
- Electron Accepting Ability: It can act as an electron acceptor and form charge-transfer complexes.
- Derivatives: Various chemical derivatives of Fullerene C60 are synthesized for specific applications.
3.Electronic Properties:
- Fullerene C60 is a semiconductor with a small bandgap (~1.5-1.9 eV).
- It shows unique electronic properties due to the delocalized π-electrons on its surface.
Applications of Fullerene C60
1.Material Science:
- Used in creating advanced nanomaterials.
- A precursor for carbon nanotubes and graphene production.
2.Electronics:
- Potential use in organic photovoltaics, field-effect transistors, and superconductors.
3.Medicine:
- Studied for drug delivery, imaging agents, and as an antioxidant due to its ability to scavenge free radicals.
4.Catalysis:
- Acts as a catalyst or support in various chemical reactions.
Significance
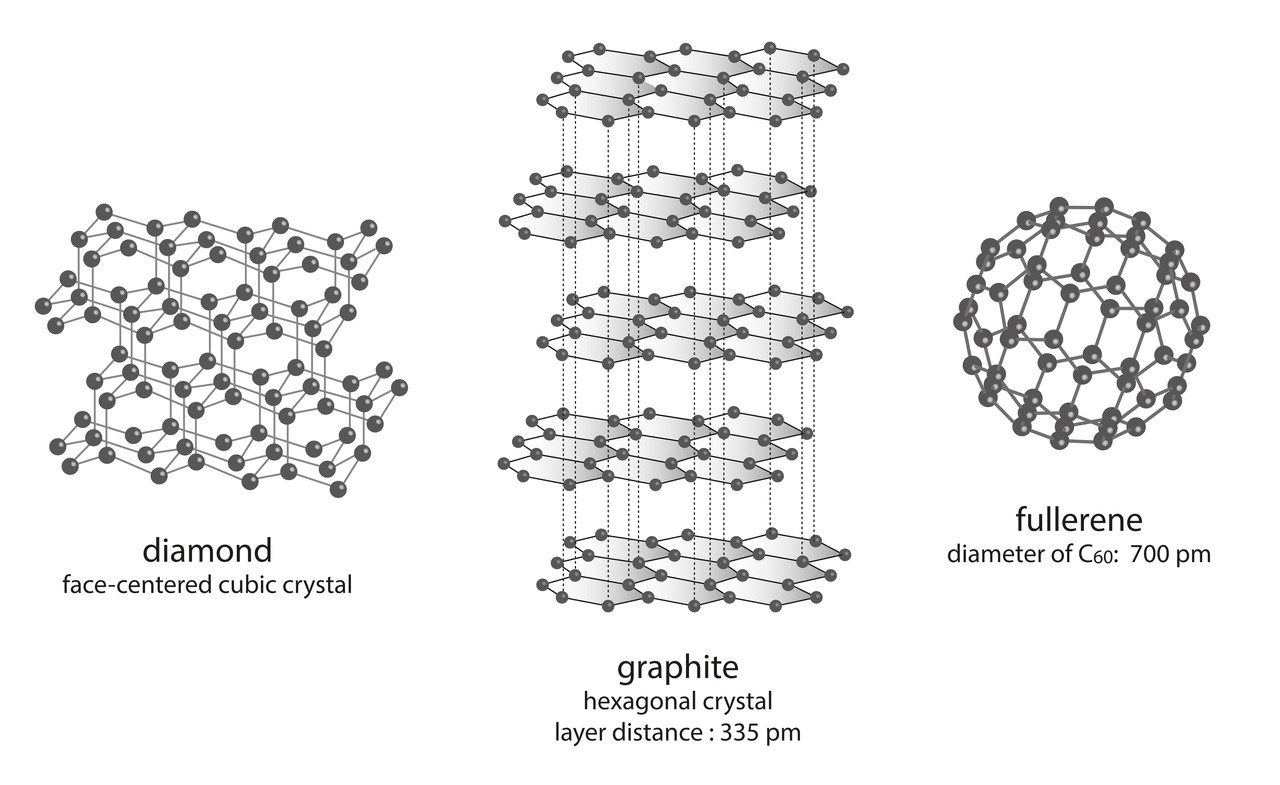
The discovery of fullerene C60 revolutionized carbon chemistry by revealing a new class of carbon allotropes beyond graphite and diamond. Its unique structure and properties have paved the way for innovations in nanotechnology, material science, and biomedicine.
