NMN (Nicotinamide mononucleotide) has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential anti-aging and health-promoting properties. To understand the history of NMN, it’s helpful to look at its discovery, its role in cellular metabolism, and its rise in popularity as a supplement.
Early Discovery and Biochemical Role
1.NAD+ and Cellular Metabolism:
The story of NMN starts with NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a crucial coenzyme found in all living cells. NAD+ plays a vital role in energy production by aiding in cellular respiration and metabolism. It also contributes to DNA repair, cell signaling, and the regulation of circadian rhythms. NAD+ levels naturally decline as we age, which has been linked to various age-related diseases and a decline in cellular function.
2.Discovery of NMN:
NMN is a derivative of nicotinamide (a form of vitamin B3) and is a precursor to NAD+. NMN is formed when nicotinamide is combined with a sugar molecule. The discovery of NMN as a component of the NAD+ biosynthesis pathway came about through various biochemical studies in the mid-20th century. In particular, researchers identified NMN as a key intermediate in the pathway through which cells generate NAD+.
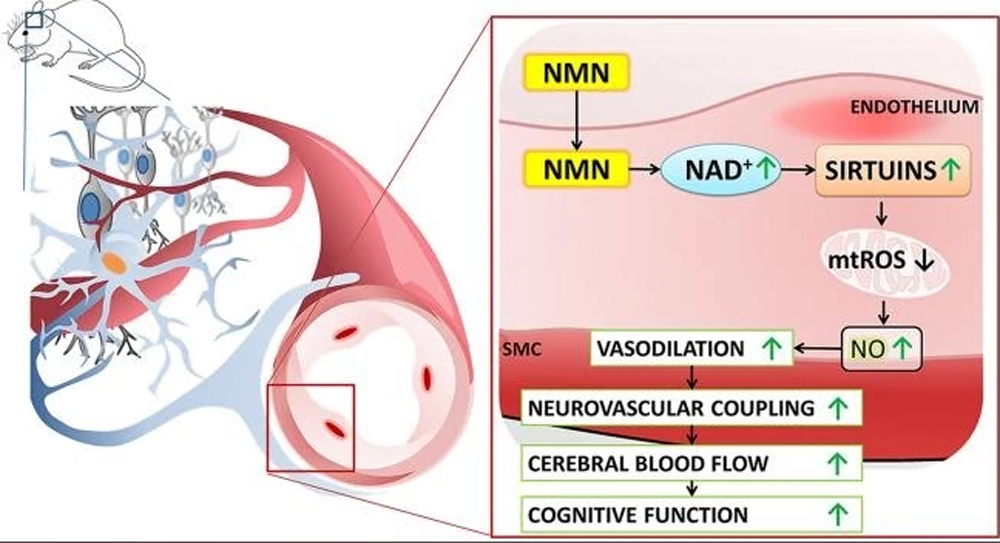
Research and Growing Interest
1.NMN and NAD+ Boosting:
In the early 2000s, scientists began investigating ways to replenish NAD+ levels, especially in relation to aging and age-related diseases. One of the most significant findings came from the work of Dr. David Sinclair, a prominent researcher at Harvard University. Sinclair’s team discovered that NAD+ levels decline with age and that boosting NAD+ could potentially reverse some of the effects of aging. They explored several NAD+ precursors, including NMN, and found that supplementing with NMN could increase NAD+ levels in cells, enhance mitochondrial function, and improve various aspects of health.
2.Dr. David Sinclair’s Pioneering Research:
Sinclair’s research on sirtuins (a family of proteins activated by NAD+) and their role in aging brought NMN to the forefront of anti-aging research. In 2013, Sinclair’s team demonstrated that NMN supplementation in mice led to a significant increase in NAD+ levels, which helped mitigate some of the age-related decline in muscle and metabolic function. The research was published in the journal Cell Metabolism, which generated widespread media interest in NMN and its potential benefits.
3.Human Studies:
While much of the initial research on NMN was conducted in animals, researchers eventually began studying its effects on humans. A 2019 clinical trial conducted in Japan suggested that NMN supplementation could safely increase NAD+ levels in healthy human participants. This study helped establish the foundation for NMN’s growing popularity as a dietary supplement. Other human studies have investigated the potential benefits of NMN for improving insulin sensitivity, exercise performance, and cognitive function, although more extensive trials are needed.
NMN as a Supplement
1.Rise in Popularity:
Following the publication of studies on NMN’s benefits, the compound became widely available as a dietary supplement. NMN supplements are marketed primarily for their potential to combat aging, enhance energy levels, and improve overall health. The growing interest in NMN supplements is also fueled by celebrity endorsements and media coverage of anti-aging research.
2.Controversies and Considerations:
Despite the enthusiasm surrounding NMN, there are still questions and concerns regarding its long-term safety, efficacy, and the optimal dosages for humans. Most of the research to date has been conducted in animal models, with fewer human studies available. Critics caution that the long-term effects of NMN supplementation in humans are not yet fully understood, and more clinical trials are needed to assess its safety and effectiveness over extended periods.

Current and Future Prospects
1.Ongoing Research:
Research on NMN and NAD+ continues to evolve. Studies are being conducted to explore NMN’s potential effects on aging-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Additionally, researchers are exploring whether NMN supplementation can improve physical performance, mental clarity, and longevity.
2.Regulatory Status:
As of now, NMN is considered a dietary supplement in many countries, including the United States. It is not classified as a drug, so its safety and efficacy are not subject to the same regulatory scrutiny as pharmaceutical products. However, the growing body of research may influence future regulations and marketing practices for NMN.
In summary, the history of NMN is intertwined with the broader study of NAD+ and aging. From its discovery as a precursor in the NAD+ biosynthesis pathway to its rise as a popular anti-aging supplement, NMN continues to be an exciting area of research with promising potential benefits for health and longevity. However, as with all supplements, it is important for consumers to stay informed about the latest research and consult healthcare professionals before making significant changes to their supplement regimen.
