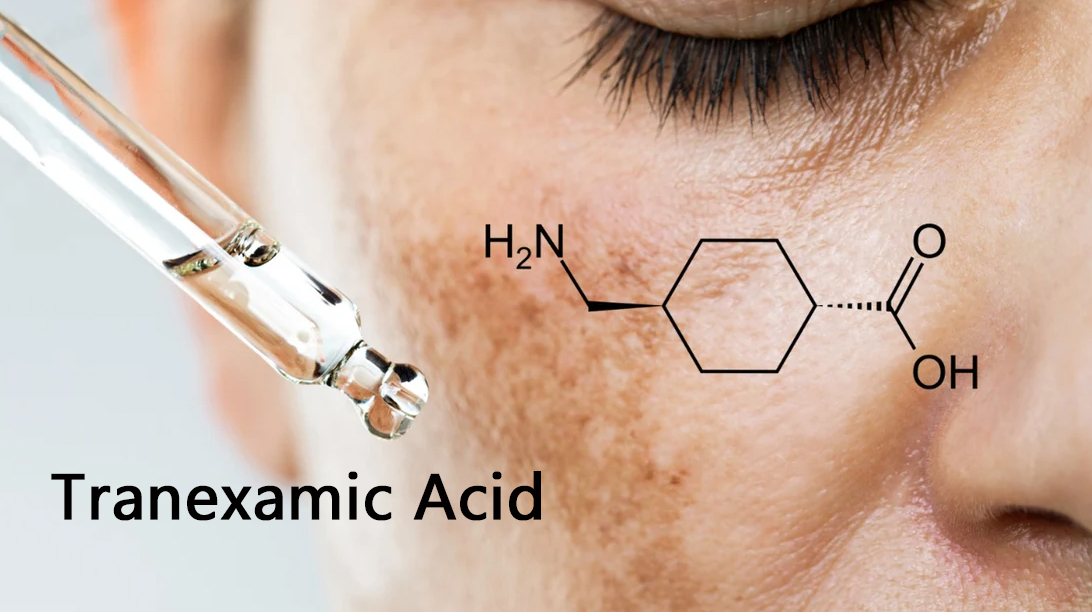
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is an antifibrinolytic medication that helps prevent excessive bleeding by inhibiting the breakdown of blood clots. It is used in various medical conditions, including:
1. Surgical and Trauma-Related Uses:
- Major surgeries (e.g., cardiac, orthopedic, liver transplantation, and C-section) – Reduces blood loss and the need for transfusions.
- Trauma patients – Used in emergency settings to prevent excessive bleeding (e.g., in cases of severe injury or hemorrhage).
- Dental procedures in hemophiliacs – Prevents excessive bleeding after tooth extraction.
2. Obstetric and Gynecological Uses:
- Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) – Helps control severe bleeding after childbirth.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (Menorrhagia) – Reduces menstrual blood loss in women with excessive bleeding.
3. Hematologic and Medical Conditions:
- Hemophilia – Used as adjunct therapy to reduce bleeding episodes.
- Hereditary angioedema – Helps prevent swelling attacks by reducing fibrinolysis.
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis) – Applied as a topical treatment or taken orally to control frequent nosebleeds.
4. Dermatological and Cosmetic Uses:
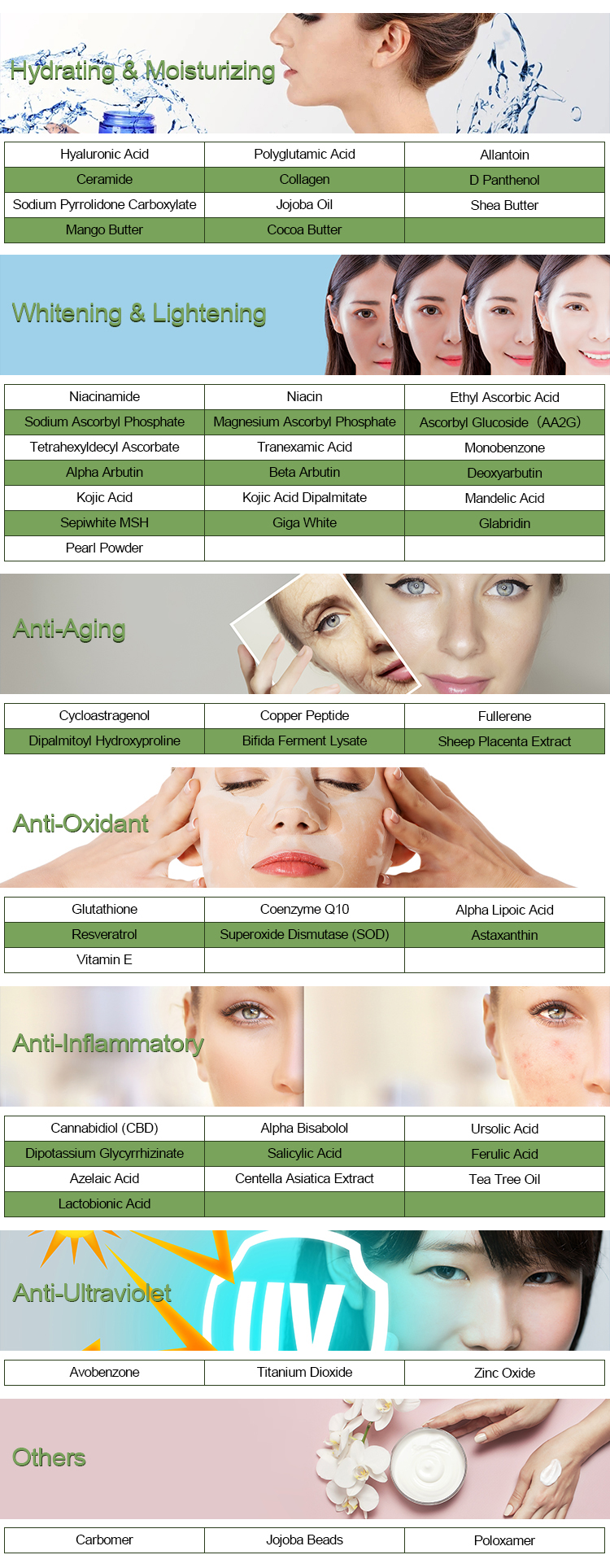
- Hyperpigmentation & Melasma – Used orally or topically to lighten dark patches on the skin.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) – Helps reduce skin discoloration.
5. Miscellaneous Uses:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding – Used in cases of upper GI bleeding to control blood loss.
- Intracranial hemorrhage (limited evidence) – Investigated for its potential role in reducing bleeding in stroke patients.
Note: Tranexamic acid should be used with caution in individuals at risk of thrombosis (e.g., history of deep vein thrombosis or stroke). It should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional.
Would you like details on dosing or side effects?
