Arachidonic Acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid. It is a vital component of the cell membrane phospholipids and serves as a precursor for the synthesis of various important signaling molecules called eicosanoids. Eicosanoids are involved in regulating inflammation, blood clotting, and various other physiological processes in the body.
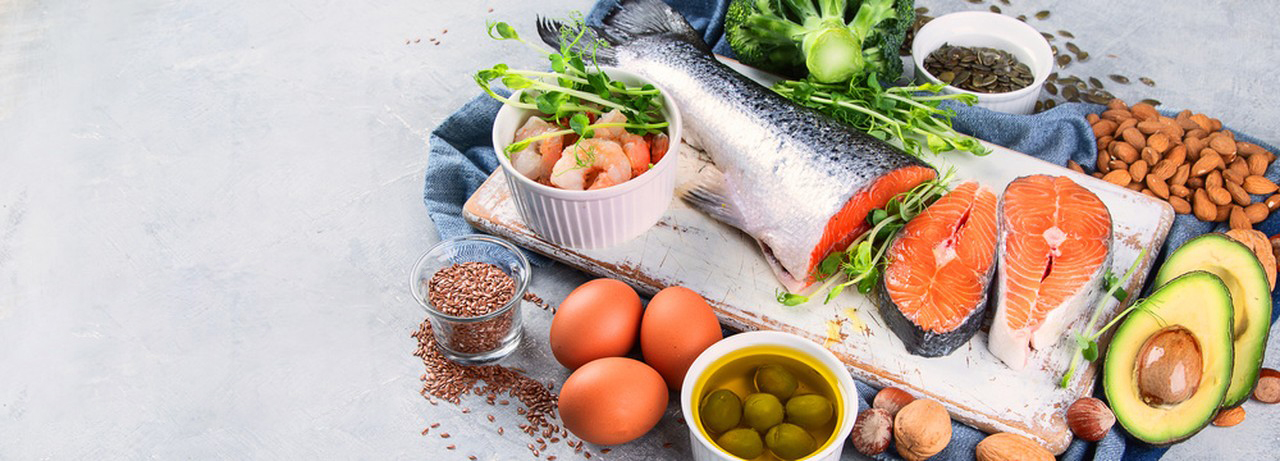
Arachidonic Acid is an essential fatty acid, meaning that the human body cannot synthesize it on its own and must obtain it from dietary sources. It is found in various animal products such as meat, eggs, and dairy, as well as in some plant-based sources like nuts and seeds.

Once Arachidonic Acid is released from cell membranes, it can be metabolized by different enzymes into various eicosanoids, including prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. These eicosanoids play crucial roles in the immune response, inflammation, and the regulation of vascular and smooth muscle tone.
While Arachidonic Acid and eicosanoids are essential for normal physiological functions, excessive production of certain eicosanoids can contribute to inflammation and various diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and inflammatory conditions. As a result, the balance of arachidonic acid and its metabolites is tightly regulated in the body.
Some medical conditions may require specific dietary adjustments to modulate Arachidonic Acid intake and eicosanoid production. For individuals with certain inflammatory conditions, reducing arachidonic acid intake might be beneficial, while it is crucial for others to ensure they have an adequate intake of this essential fatty acid. As always, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice and recommendations.
How to use Arachidonic Acid?
Arachidonic Acid is an essential omega-6 fatty acid that plays important roles in the body, especially in the production of inflammatory and regulatory molecules known as eicosanoids. While the body can produce Arachidonic Acid from dietary sources, it is also available as a dietary supplement in the form of capsules or oils. However, before considering supplementation, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, as excessive intake of Arachidonic Acid may lead to health issues, particularly if not balanced with other fatty acids like omega-3.
Here are some general guidelines for using Arachidonic Acid:
1.Consult with a healthcare professional: Before taking any supplement, including Arachidonic Acid, consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
2.Recommended Dosage: If a healthcare professional determines that supplementation is necessary, they will prescribe the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and health status.
3.Balancing Omega-6 and Omega-3 intake: It’s crucial to maintain a balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in your diet. The Western diet often contains an excess of omega-6 fatty acids, which can lead to an imbalance and promote inflammation. Ensuring an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids (found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, etc.) is essential to counterbalance the effects of omega-6 fatty acids.
4.Dietary Sources: If you prefer to obtain Arachidonic Acid through your diet, it can be found in certain animal-based foods like meat, eggs, and dairy products.

5.Inflammatory Response: Arachidonic Acid is involved in the body’s inflammatory response. While some inflammation is necessary for the immune system to function properly, excessive inflammation can contribute to chronic health conditions. Always be mindful of overall inflammatory factors in your diet and lifestyle.
6.Avoid Self-diagnosis and Treatment: Never attempt to self-diagnose or treat any medical condition with supplements without proper medical guidance. Arachidonic Acid supplementation should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional.
Remember, each person’s health needs are unique, and dietary supplements should be used judiciously and in conjunction with a healthy, balanced diet. Always prioritize a nutrient-rich diet and an active lifestyle for overall well-being.
