Ashwagandha Extract (Withania somnifera) is a popular medicinal herb used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. It is known for its adaptogenic properties and is believed to provide various health benefits. The primary method of extracting Ashwagandha’s active compounds is through traditional solvent extraction. However, there are alternative extraction methods that can be used to obtain Ashwagandha extracts. Some of these methods include:

- Steam Distillation: Steam distillation is commonly used for extracting essential oils from plant materials. In the case of Ashwagandha Extract, it can be used to extract volatile compounds and essential oils present in the herb.
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE): Supercritical fluid extraction utilizes supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) as the solvent to extract bioactive compounds from plants. This method is considered safer and more environmentally friendly than traditional solvent extraction.
- Ultrasonic Extraction: Ultrasonic extraction involves the use of ultrasonic waves to break down the cell walls of the plant material, facilitating the release of bioactive compounds. This method can improve the extraction efficiency and reduce extraction time.
- Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE): In microwave-assisted extraction, microwave energy is used to heat the solvent and accelerate the extraction process. It can be a faster method compared to traditional extraction techniques.

- Enzyme-Assisted Extraction (EAE): Enzyme-assisted extraction involves using specific enzymes to help break down cell structures and increase the release of bioactive compounds during extraction.
- Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE): Pressurized liquid extraction, also known as accelerated solvent extraction, involves using elevated temperature and pressure to enhance the solubility of target compounds and improve the extraction efficiency.
- Subcritical Water Extraction: Subcritical water extraction uses water at elevated temperatures and pressures, but below its critical point, to extract bioactive compounds from the plant material.
- Cold Pressing: Cold pressing is a method used to extract oils from seeds or nuts. In the case of Ashwagandha Extract, it can be used to obtain oil-rich extracts.
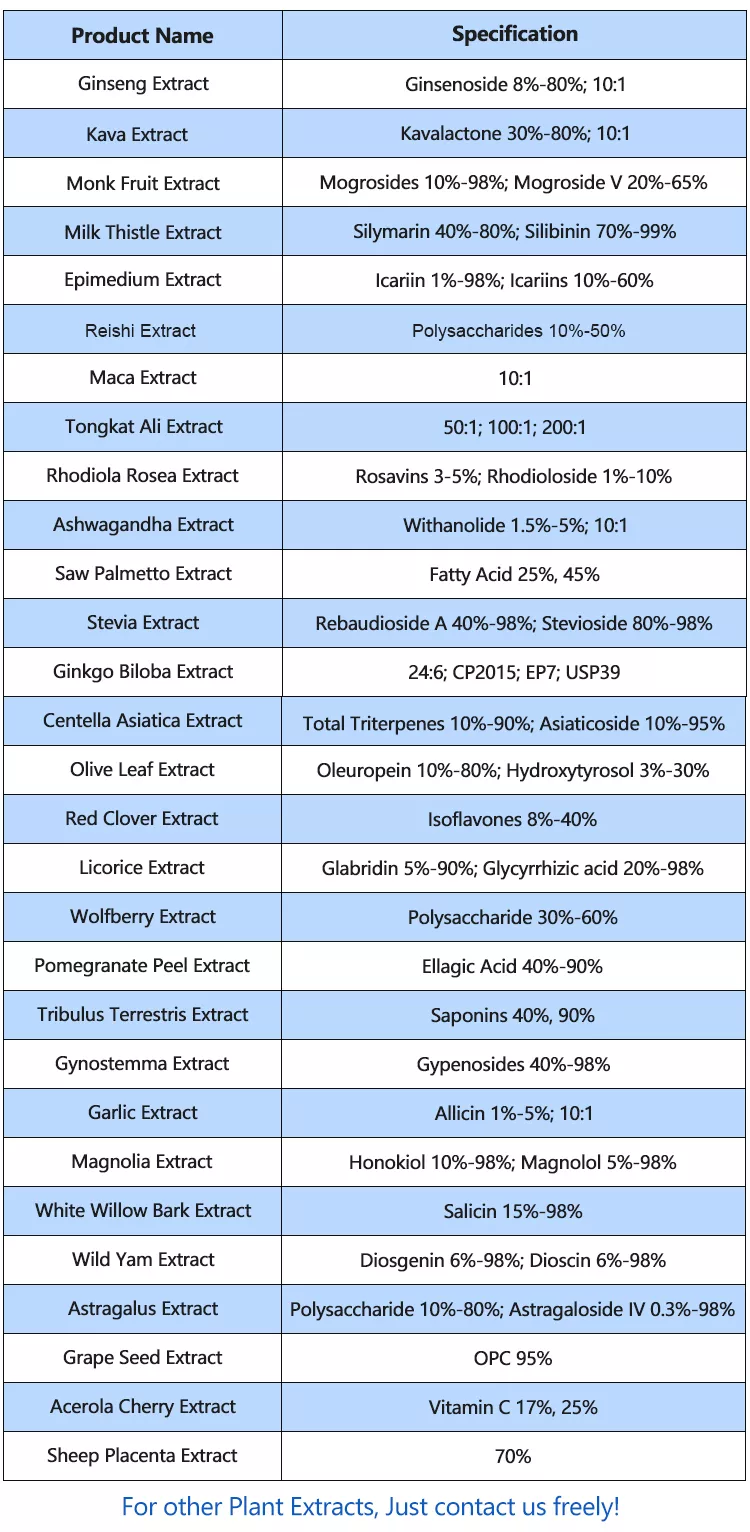
It’s important to note that the choice of extraction method may depend on various factors, including the desired bioactive compounds, the end product’s intended use, efficiency, and cost considerations. Each extraction method may yield different types and concentrations of bioactive compounds, affecting the overall therapeutic properties of the Ashwagandha extract. Therefore, it’s crucial to validate the quality and potency of the extracted compounds through appropriate analytical methods and testing.
