Finasteride is a medication that is primarily used to treat enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) and male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to the growth of the prostate and the shrinking of hair follicles in individuals with male pattern baldness. Here is some information about the chemical structure and physical properties of Finasteride:
Chemical Structure of Finasteride:
Finasteride has the following chemical structure:
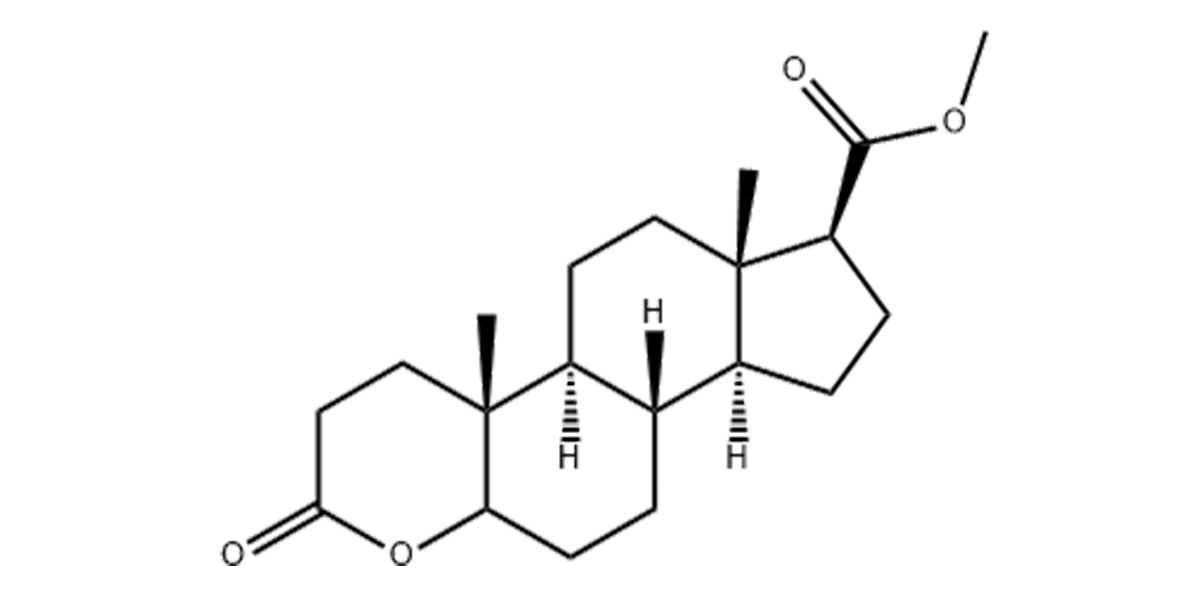
Physical Properties of Finasteride:
- Molecular Formula: C23H36N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 372.55 g/mol
- Melting Point: Approximately 253-255°C
- Solubility: Finasteride is practically insoluble in water, but it is soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and methanol.
Other Information:
- Route of Administration: Finasteride is commonly administered orally in the form of tablets.
- Half-Life: The elimination half-life of Finasteride is around 6 hours in men aged 18-60 years and approximately 8 hours in men over 70 years old.
- Metabolism: Finasteride is metabolized primarily in the liver.
- Excretion: The drug and its metabolites are excreted mainly through urine.
Please note that the information provided here is based on my knowledge as of September 2021, and there may have been new developments or findings since that time. Always consult a medical professional or reliable sources for the most up-to-date and accurate information about medications.
