L-Arginine is an amino acid, which is one of the building blocks of proteins in the human body. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. Here’s some information about its origin and properties:
1. Origin:
L-Arginine is considered a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid. This means that under normal circumstances, the body can synthesize enough arginine to meet its needs. However, in certain situations, such as during periods of rapid growth, illness, or stress, the body may not produce enough arginine, and it must be obtained through the diet or supplements.
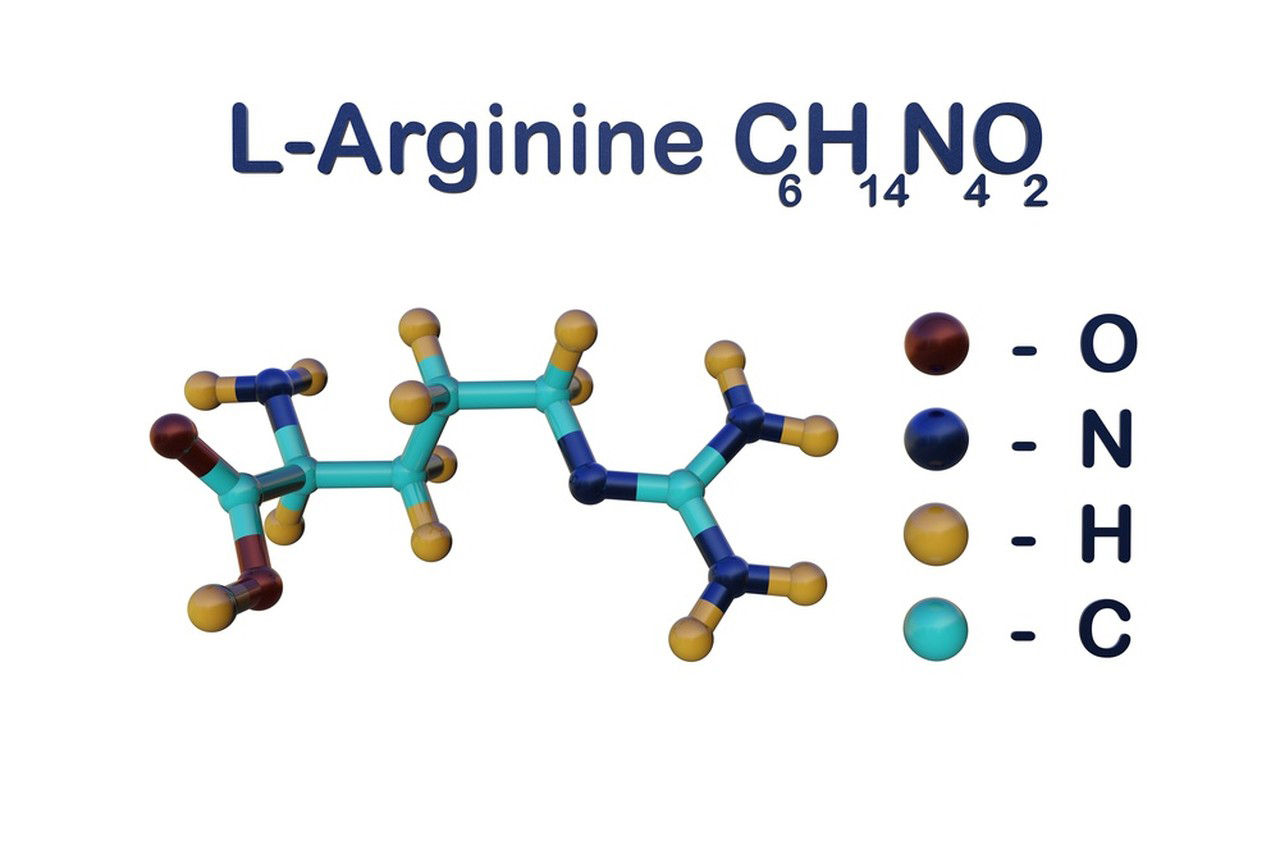
2. Molecular Structure:
L-Arginine is an alpha-amino acid with the chemical formula C6H14N4O2. It has a positively charged guanidino group (NH2-C(NH)NH2) at its side chain, which makes it unique among the 20 common amino acids.
3. Functions and Properties:
- Protein Synthesis: L-Arginine is involved in the synthesis of proteins in the body. It plays a role in the process of translation, where the genetic code in DNA is translated into proteins.
- Nitric Oxide Production: Arginine is a precursor to nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that helps relax and dilate blood vessels, thereby improving blood flow. This property is particularly important for cardiovascular health.
- Immune Function: It plays a role in immune system function, including the production and activation of immune cells.
- Wound Healing: L-Arginine is involved in the wound healing process by promoting collagen production.
- Urea Cycle: It is a key component of the urea cycle, which helps remove excess ammonia from the body.
4. Dietary Sources:
L-Arginine can be obtained through dietary sources, including:
- Meat (especially red meat, poultry, and fish)
- Dairy products
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Whole grains
- Eggs
5. Supplements:
L-Arginine is also available in supplement form, commonly as L-Arginine HCL or L-Arginine AKG (Alpha-Ketoglutarate). Some people take arginine supplements to support athletic performance, cardiovascular health, or for other potential benefits. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, as excessive arginine intake can have side effects and interact with certain medications.
In summary, L-Arginine is an essential amino acid involved in various physiological processes, including protein synthesis, nitric oxide production, and immune function. It can be obtained from dietary sources or taken as a supplement but should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional when used in supplemental form.
