Melatonin is a hormone that is primarily produced by the pineal gland in the brain, and it plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle and circadian rhythms in humans and other animals. Over the years, comprehensive studies have been conducted to understand the various aspects of melatonin, including its production, functions, effects on health, and potential therapeutic uses. Here is an overview of some of the key areas of research on melatonin:
1.Production and Regulation of Melatonin:
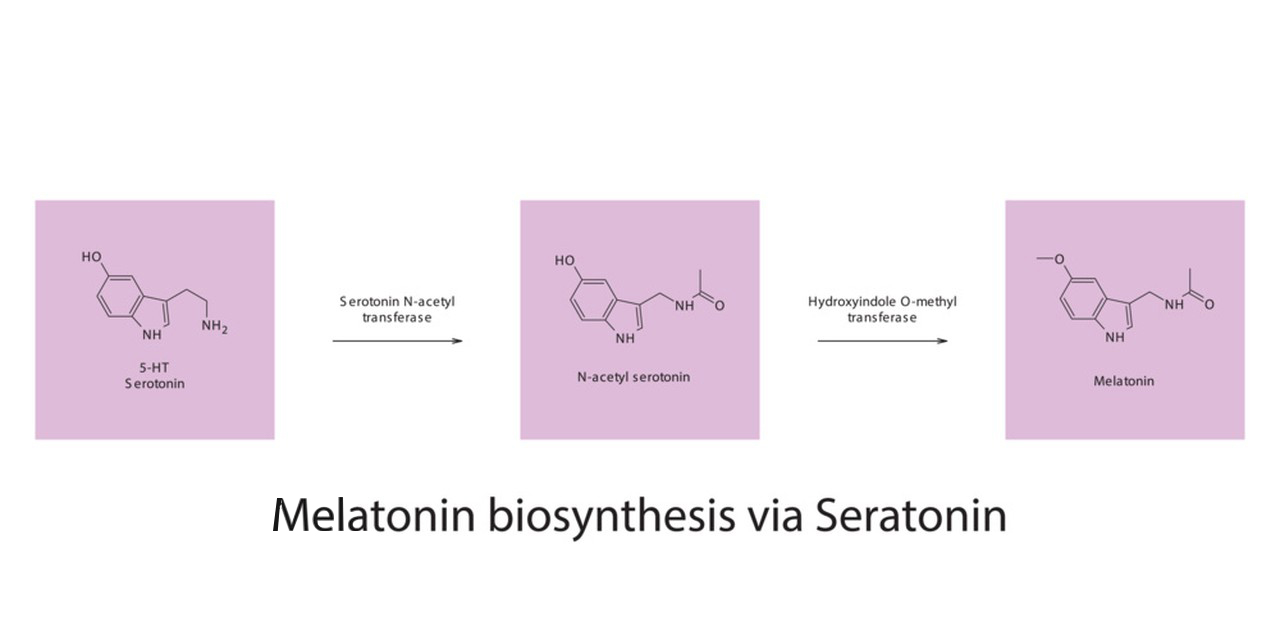
Melatonin is produced in the pineal gland, and its production is influenced by the light-dark cycle. The hormone is typically released at night, helping to signal the body that it’s time to sleep.
Research has focused on understanding the molecular mechanisms that regulate melatonin synthesis and secretion.

2.Circadian Rhythms:
Melatonin plays a central role in regulating circadian rhythms, which are the body’s internal clock. Research has explored how melatonin levels vary throughout the day and night and how disruptions in these rhythms can affect health.
3.Sleep and Insomnia:
Numerous studies have investigated melatonin’s role in promoting sleep and its potential use in treating insomnia. Melatonin supplements are often used as a sleep aid.
4.Jet Lag and Shift Work:
Research has examined the effectiveness of melatonin in mitigating the symptoms of jet lag and helping shift workers adjust to changing schedules.
5.Antioxidant Properties:
Melatonin has antioxidant properties and can help protect cells from oxidative damage. Studies have explored its potential role in reducing the risk of various diseases associated with oxidative stress.
6.Immune System Regulation:
Some research suggests that melatonin may modulate the immune system and help the body fight infections and diseases. This has led to investigations into its potential role in enhancing immunity.
7.Cancer:
There is ongoing research into melatonin’s potential role in cancer prevention and treatment. Some studies have suggested that it may inhibit the growth of cancer cells and reduce the side effects of cancer treatments.
8.Neuroprotective Effects:
Melatonin has been studied for its potential neuroprotective properties and its role in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
9.Cardiovascular Health:
Some studies have explored the impact of melatonin on cardiovascular health, including its potential to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
10.Aging and Longevity:
Melatonin’s role in aging and longevity has also been investigated. It may have protective effects on the aging process, but the results are mixed.
11.Potential Side Effects and Safety:
Research has examined the safety and potential side effects of melatonin supplements, particularly when used in high doses or for extended periods.
It’s important to note that while melatonin has shown promise in various areas of research, further studies are needed to establish its efficacy and safety for specific uses. As with any supplement or medication, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using melatonin for any particular purpose, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
