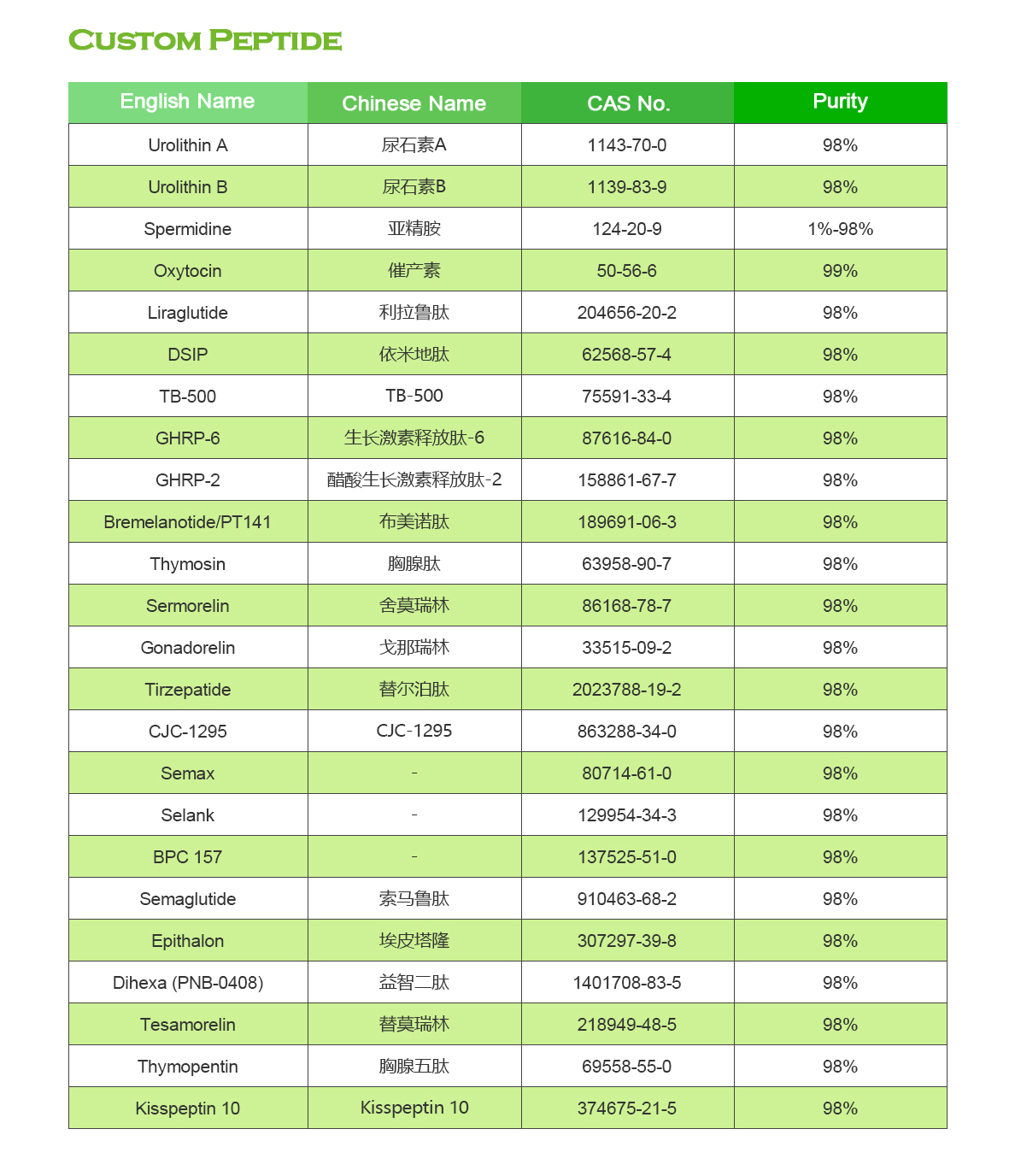
Semaglutide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. The primary mechanism of action of semaglutide is to stimulate the release of insulin and reduce the production of glucagon in response to elevated blood sugar levels. This helps lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, semaglutide has been shown to be effective in managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Clinical trials and studies have demonstrated its ability to improve glycemic control, reduce HbA1c levels, and contribute to weight loss.
One of the notable formulations of semaglutide is a once-weekly injection, which offers a convenient dosing schedule compared to some other medications. This can contribute to better adherence to the treatment plan.
It’s important to note that individual responses to medications can vary, and the overall efficacy of semaglutide may depend on factors such as the patient’s specific health condition, adherence to the prescribed treatment plan, and lifestyle factors.

Evaluation of the efficacy of Semaglutide
As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, semaglutide is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs known as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. Semaglutide works by mimicking the effects of GLP-1, a hormone that stimulates insulin secretion and reduces glucagon production.
Evaluating the efficacy of semaglutide involves assessing its impact on various parameters, including glycemic control, weight loss, and cardiovascular outcomes. Clinical trials and real-world studies provide valuable information in this regard. Here are some key aspects of evaluating the efficacy of semaglutide:
1.Glycemic Control:
Semaglutide is primarily used to improve glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Clinical trials typically assess its effectiveness in reducing HbA1c levels, which reflect average blood glucose levels over a few months.
Evaluation of fasting and postprandial glucose levels is also crucial in understanding how well semaglutide controls blood sugar throughout the day.
2.Weight Loss:
Many GLP-1 receptor agonists, including semaglutide, are associated with weight loss. Evaluating the extent of weight loss in clinical trials and its maintenance over time is an important aspect of efficacy.
Understanding the impact of weight loss on overall health, including cardiovascular risk factors, is essential.
3.Cardiovascular Outcomes:
Cardiovascular safety is a critical consideration for diabetes medications. Clinical trials may assess the impact of semaglutide on major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), such as heart attack and stroke.
Real-world studies contribute additional insights into the long-term cardiovascular safety and outcomes associated with semaglutide.
4.Adverse Events:
Evaluating the safety profile of semaglutide is essential. This includes assessing adverse events such as hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal side effects, and any other potential concerns.
5.Patient-reported Outcomes:
Understanding the impact of treatment on the quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and adherence is crucial. Patient-reported outcomes provide insights into how well individuals tolerate and accept the medication.
It’s important to note that the evaluation of efficacy may vary depending on individual patient characteristics, comorbidities, and specific study designs. Additionally, new research and clinical data may have emerged since my last update in January 2022. Therefore, for the most current and comprehensive information on the efficacy of semaglutide, it’s advisable to consult the latest medical literature, guidelines, and regulatory agency reports.
