UDCA stands for Ursodeoxycholic Acid, which is a bile acid naturally produced by the human body and also available as a medication. It is commonly used to treat certain liver and gallbladder conditions, particularly primary biliary cholangitis and certain types of gallstones. The basic components of UDCA are as follows:
Chemical Structure: UDCA is a bile acid, and its chemical structure consists of a steroid nucleus with four rings and a side chain containing hydroxyl (-OH) groups. Its systematic name is 3α,7β-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid.
Active Ingredient: The active pharmaceutical ingredient in UDCA medication is ursodeoxycholic acid itself.
Formulation: UDCA is available in various pharmaceutical formulations, including tablets, capsules, and liquid suspensions. These formulations may contain additional inactive ingredients to aid in drug delivery, stability, and absorption.
Mode of Action: UDCA works by reducing the concentration of toxic bile acids in the liver and improving bile flow. It also has anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective properties. By doing so, it can help protect liver cells and improve liver function in certain diseases.
Therapeutic Uses: UDCA is primarily used to treat specific liver and gallbladder disorders, such as primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), where it can slow down the progression of the disease. It can also be used to dissolve cholesterol gallstones in the gallbladder.
Dosage: The recommended dosage of UDCA can vary depending on the specific medical condition being treated. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage for your individual case.

Side Effects: Common side effects of UDCA may include diarrhea, stomach discomfort, and changes in liver enzyme levels. It is essential to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare professional.
Precautions: UDCA should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, especially in pregnant or nursing women and individuals with certain preexisting medical conditions. It may interact with other medications, so a comprehensive medical history should be disclosed to the healthcare provider.
Administration: UDCA is usually taken orally, and the dosage regimen is determined by the specific medical condition and the healthcare provider’s recommendations.
It’s important to note that UDCA is a medication and should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. This information is provided for general understanding, and specific dosages and recommendations should be obtained from a healthcare provider based on an individual’s medical needs.
Efficacy and Function of UDCA
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a naturally occurring bile acid that is used for various medical purposes, primarily in the treatment of liver and gallbladder-related conditions. Its efficacy and function depend on the specific medical condition it is being used to treat. Here are some of the primary functions and efficacy of UDCA in different contexts:
1.Treatment of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC): UDCA is most commonly prescribed for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis (formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis). PBC is a chronic autoimmune liver disease that can lead to progressive liver damage. UDCA is effective in slowing the progression of PBC, reducing the levels of liver enzymes, and improving liver function in many patients. It is considered the first-line therapy for PBC.
2.Dissolution of Gallstones: UDCA is sometimes used to dissolve cholesterol gallstones in individuals who are not suitable candidates for surgery. It can take several months of treatment for this purpose and is typically more effective for small, radiolucent (cholesterol-based) gallstones.
3.Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Some studies suggest that UDCA may have a role in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. While the results are not definitive, UDCA has been investigated for its potential to improve liver enzyme levels and reduce liver inflammation in NAFLD patients.
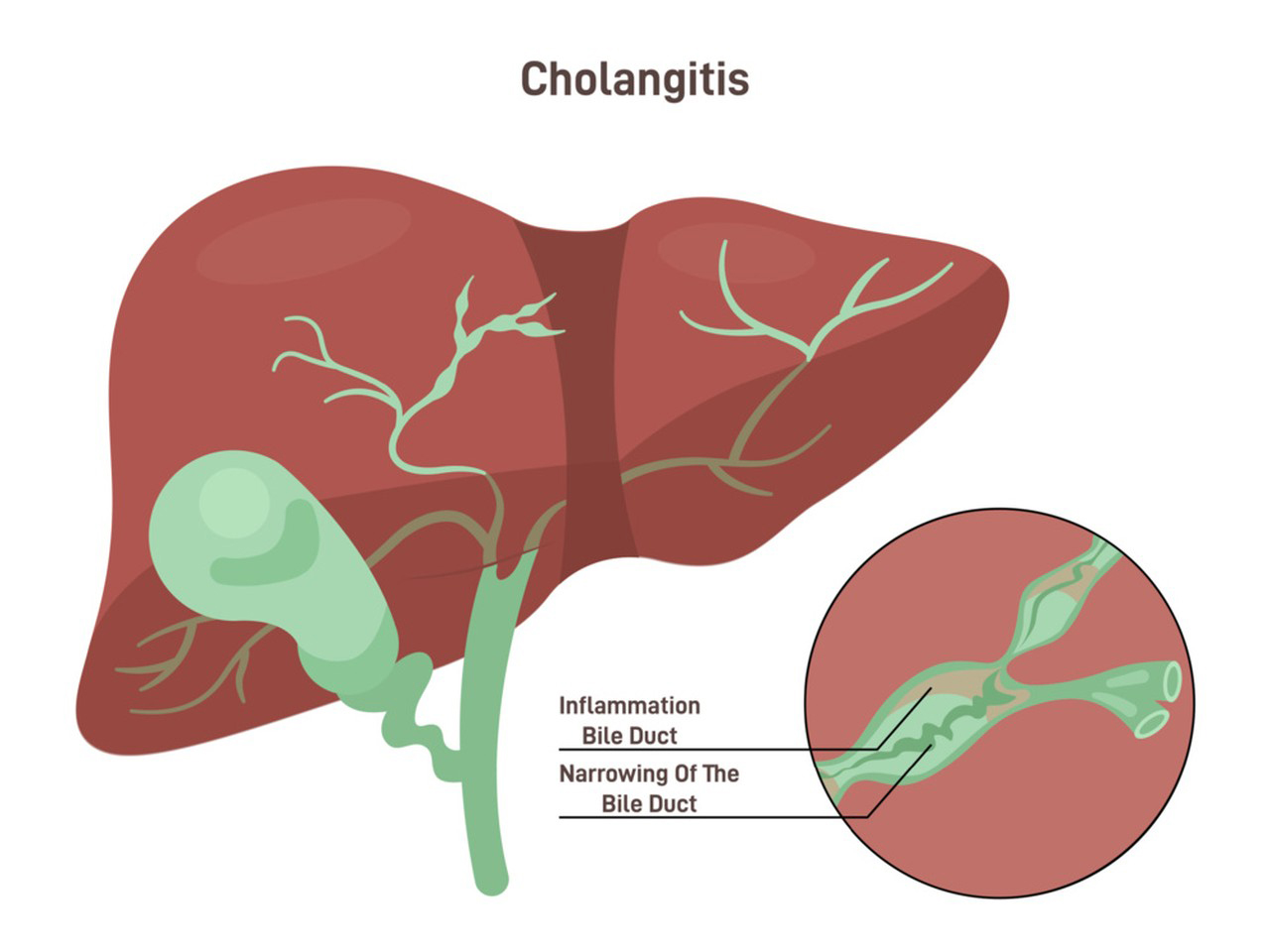
4.Prevention of Bile Duct Complications: UDCA is used to reduce the risk of complications in patients who have undergone liver transplantation, particularly in the context of bile duct complications and graft rejection.
5.Cholestatic Liver Diseases: UDCA is used in the management of various cholestatic liver diseases, where there is impaired bile flow. It can help reduce itching and improve liver function in these conditions.
6.Other Potential Uses: UDCA has also been studied for potential benefits in other conditions, such as certain autoimmune disorders and cystic fibrosis-related liver disease. Research is ongoing in these areas.
UDCA works by several mechanisms, including:
Reducing the toxic effects of certain bile acids.
Increasing the secretion of bicarbonate in the bile, which can reduce the acidity of bile and protect the liver and bile ducts.
Improving the flow of bile in the liver and gallbladder, which can be especially beneficial in cholestatic conditions.
It’s important to note that UDCA may not be effective for all individuals or all conditions. Its use should be determined by a healthcare professional after a thorough evaluation of the patient’s specific condition and needs. Additionally, like any medication, UDCA can have side effects, and patients should be monitored regularly while taking it. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations when using UDCA or any other medication.
