Vitamin U is not a well-recognized or established vitamin in the same way that vitamins like vitamin C or vitamin D are. In fact, there is no official vitamin U included in the standard list of essential vitamins for humans. Instead, “vitamin U” is a term that has been used historically to refer to a compound called S-methylmethionine, which is also known as methylmethionine sulfonium chloride or simply “methylmethionine.”
Here’s what we know about S-methylmethionine (vitamin U):
Historical Context: The term “vitamin U” was coined in the early 20th century by a Romanian doctor named Dr. Garnett Cheney. He used it to describe a substance found in cabbage juice that seemed to have potential therapeutic benefits for certain digestive ailments.
Role in Health: S-methylmethionine, while not officially recognized as a vitamin, is a naturally occurring compound in various foods, including cabbage, broccoli, and other vegetables. It has been suggested to have potential health benefits, particularly in the context of digestive health and gastrointestinal disorders. Some proponents claim that it can help with conditions like gastritis and peptic ulcers.

Limited Scientific Research: Despite some historical interest, there is relatively limited scientific research on S-methylmethionine compared to well-established vitamins. Many of the claims surrounding its health benefits are anecdotal or based on older, less rigorous studies.
Controversy and Skepticism: The concept of “vitamin U” and its supposed health benefits have been met with skepticism in the scientific community. Many researchers consider it more of a dietary component than an essential vitamin, and they question the validity of some of the claims made about its therapeutic properties.
Dietary Sources: If you are interested in increasing your intake of S-methylmethionine, you can do so by consuming vegetables like cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli. These foods are natural sources of this compound.
In summary, vitamin U is not a well-established essential vitamin, and its health benefits remain a subject of debate and limited scientific research. If you are interested in its potential benefits, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have specific health concerns. Additionally, a balanced and varied diet that includes a wide range of fruits and vegetables can provide essential vitamins and nutrients to support overall health.
Application of Vitamin U
Vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine or methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, is not actually a true vitamin, as it is not considered essential for human health. However, it has been studied for its potential health benefits in various applications. Here are some of the potential applications of Vitamin U:
Gastric Health: Vitamin U has been studied for its potential to promote gastric health. It is believed to have a protective effect on the stomach lining and may help in reducing the risk of gastric ulcers and gastritis. Some dietary supplements and over-the-counter products containing Vitamin U have been marketed for digestive health.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Vitamin U has shown anti-inflammatory properties in some studies, which may be beneficial for reducing inflammation in the stomach and other tissues. This could potentially be helpful in conditions where inflammation plays a role.
Skin Health: Some topical creams and ointments containing Vitamin U are available and are promoted for skin health. It is believed to help with wound healing and may have anti-inflammatory effects when applied to the skin.
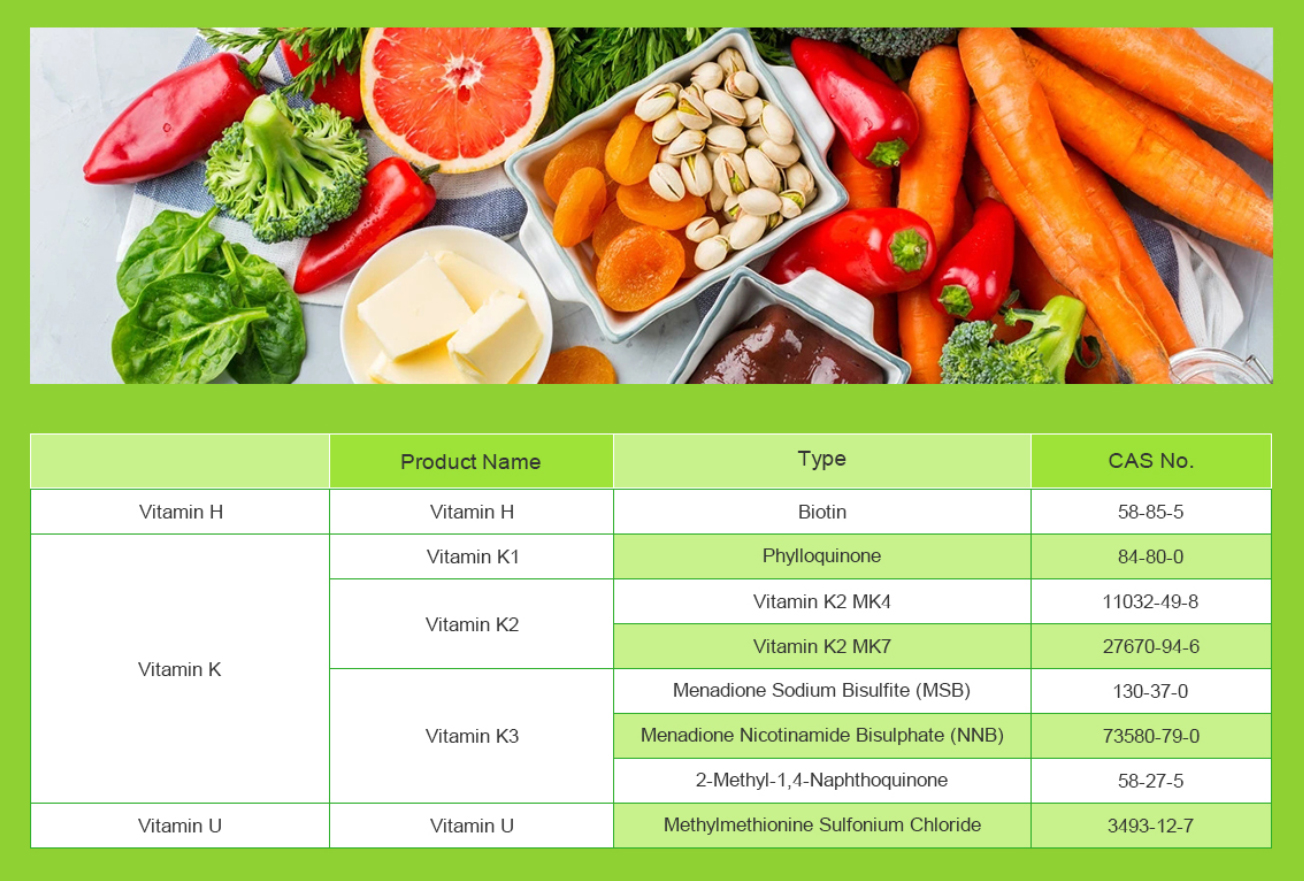
Allergies: Vitamin U has been investigated for its potential to alleviate allergy symptoms, particularly those related to respiratory allergies. It may help reduce the severity of symptoms like sneezing and nasal congestion.
Detoxification: Some supplements and alternative medicine practices suggest that Vitamin U can aid in detoxifying the body. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited.
It’s important to note that research on Vitamin U is relatively limited compared to well-established vitamins and nutrients. Furthermore, the safety and effectiveness of Vitamin U supplements have not been widely studied, and there may be potential side effects or interactions with other medications. Before using Vitamin U supplements or products for specific health purposes, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.
As with any dietary supplement or alternative treatment, it’s crucial to approach it with caution and ensure it aligns with your individual health needs and goals.
