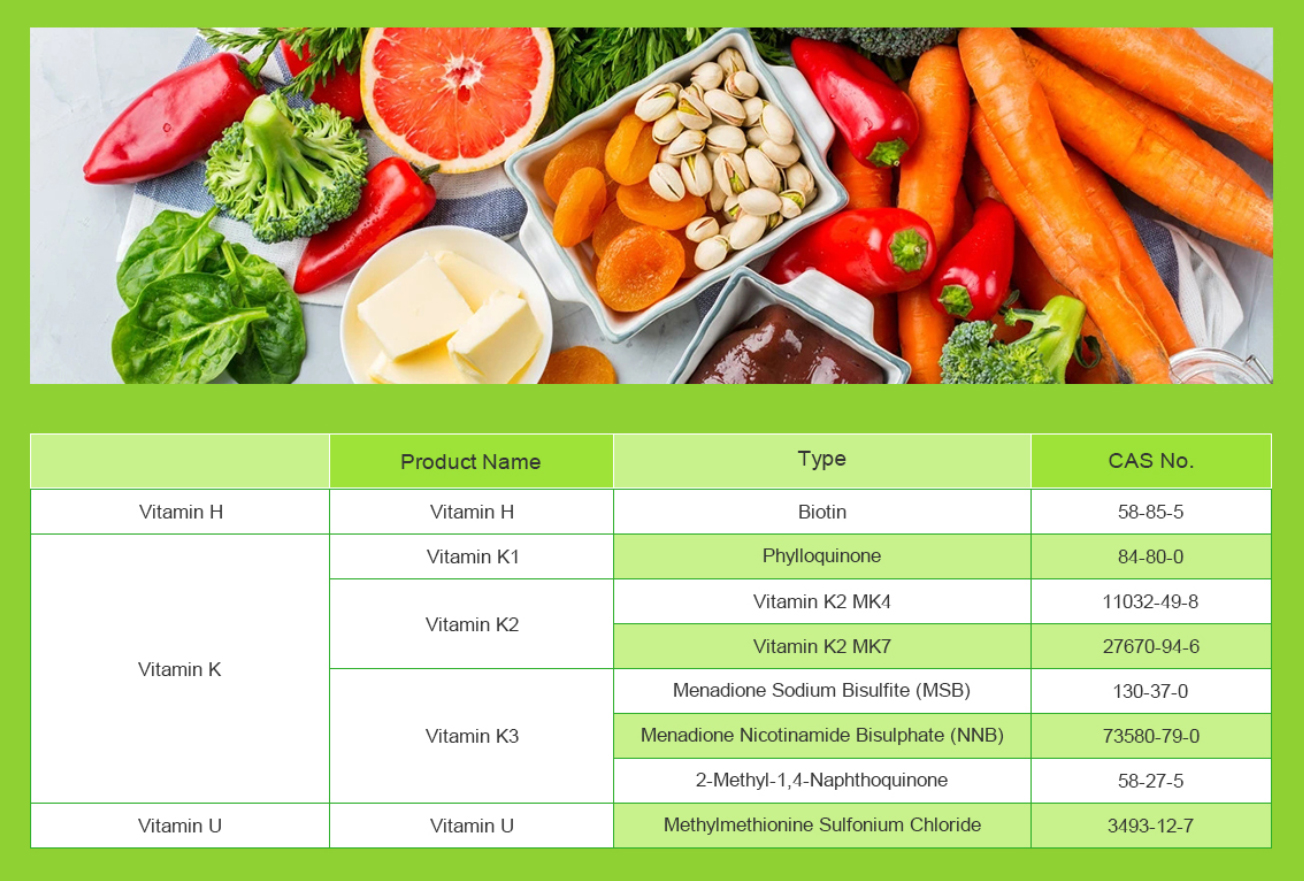
Vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine or methylmethionine, is not a traditional vitamin like vitamin C or vitamin D. Instead, it’s a derivative of the amino acid methionine. While it may have some health benefits, its usage is not as well-established as other vitamins. It’s primarily used as a dietary supplement.

Here are some general guidelines on how to use Vitamin U for potential benefits:
Consult with a healthcare professional: Before starting any new supplement, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can assess your specific health needs and advise you on the appropriate dosage and use.
Dietary sources: Vitamin U can be obtained from various foods, including cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and other cruciferous vegetables. Incorporating these foods into your diet can be an excellent way to naturally increase your intake of Vitamin U.
Supplements: If you and your healthcare provider determine that supplementation is necessary, you can find Vitamin U supplements in various forms, such as capsules or tablets. Follow the recommended dosage on the product label or as advised by your healthcare provider.
Monitor for side effects: While Vitamin U is generally considered safe when used in recommended doses, it’s essential to be aware of any potential side effects or interactions with other medications you may be taking. Side effects are rare but can include gastrointestinal discomfort in some cases.
Be patient: Like many supplements, the effects of Vitamin U may take time to become noticeable, and individual responses may vary. Be patient and consistent with your intake if you are looking to achieve specific health benefits.
Follow a balanced diet: While Vitamin U may offer potential benefits, it’s essential to maintain a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients. It should not be used as a substitute for a healthy diet.
Consider specific health conditions: Some people may consider Vitamin U supplementation for specific health concerns, such as gastric ulcers or gastrointestinal health. In such cases, consult with a healthcare provider for guidance on how to use it effectively.
Track your progress: If you are using Vitamin U to address specific health concerns, keep track of your symptoms and overall well-being to determine if it’s providing the desired results. Share this information with your healthcare provider during follow-up visits.
Remember that Vitamin U is not considered a cure-all or a replacement for a healthy lifestyle. It should be used as part of a broader approach to wellness that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and other health-promoting practices. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.
