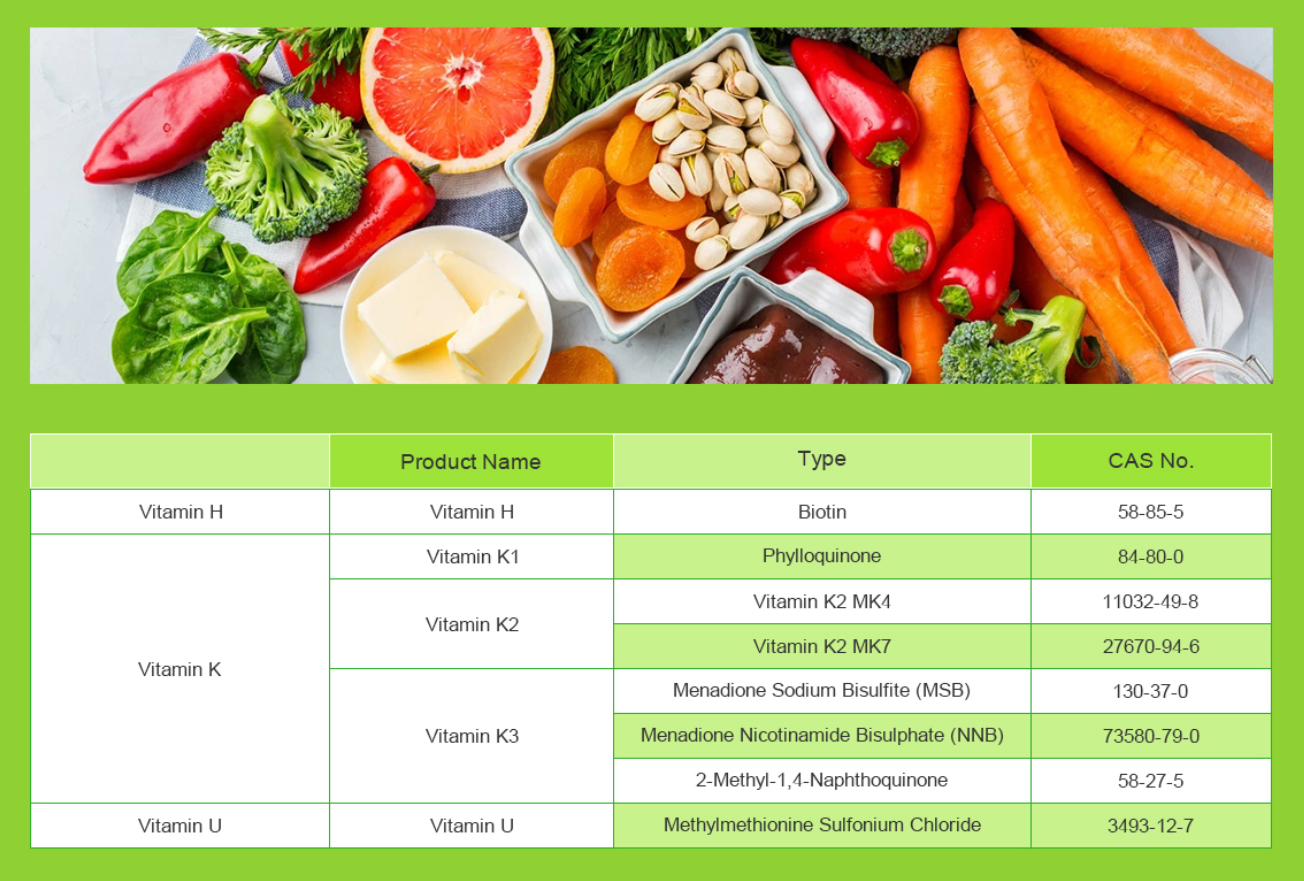
Vitamin U is not actually a true vitamin but rather a historical term that was used to refer to a compound called S-methylmethionine, also known as methylmethionine sulfonium chloride. This compound is found in certain vegetables, particularly in cabbage. It was initially thought to have potential therapeutic effects on stomach health.
Some of the potential benefits associated with S-methylmethionine (Vitamin U) for the stomach include:
Gastric Ulcers: Historically, Vitamin U was believed to help heal gastric ulcers and promote overall gastric health. It was thought to have protective properties for the stomach lining, which could potentially aid in the healing of ulcers.
Anti-Inflammatory: S-methylmethionine is believed to have anti-inflammatory properties, which might help reduce inflammation in the stomach and alleviate symptoms associated with gastritis.
Gastrointestinal Health: Some proponents of Vitamin U suggest that it can contribute to overall gastrointestinal health by promoting a balanced gut environment.
It’s important to note that the term “Vitamin U” is not widely recognized in modern scientific literature, and it has fallen out of common usage. Additionally, the therapeutic effects of S-methylmethionine are not well-established through extensive scientific research, and it is not considered a standard treatment for stomach conditions.

If you have concerns about your stomach health or are dealing with specific gastrointestinal issues, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can provide guidance on dietary and lifestyle changes, as well as recommend evidence-based treatments that may be more effective in addressing stomach-related problems.
Effect evaluation of Vitamin U in the treatment of gastric diseases
Vitamin U is not actually a recognized vitamin, but rather a term that was historically used to refer to a substance called S-methylmethionine (SMM). SMM is found in various foods, including cabbage, and was once thought to have potential therapeutic effects on gastric diseases. However, it’s important to note that the concept of Vitamin U has largely fallen out of favor in modern medicine, and there is limited scientific evidence to support its use in the treatment of gastric diseases.
Historical Background:
The term “Vitamin U” was coined by Dr. Garnett Cheney in the 1950s to describe a substance that he believed had anti-ulcer properties, primarily found in cabbage juice. At the time, it was suggested that SMM, found in cabbage, could help protect the stomach lining and potentially aid in the treatment of peptic ulcers and other gastric issues.
Current Understanding:
Since the introduction of the concept of Vitamin U, the field of gastroenterology and nutrition has advanced significantly. Today, the understanding of gastric diseases and their treatment is based on a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes and risk factors, as well as evidence-based therapies. While cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables are considered healthy and may offer some general health benefits, they are not considered a specific treatment for gastric diseases.
The treatment of gastric diseases typically involves a combination of medical approaches, including:
1.Medications: Depending on the specific condition, medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2-receptor antagonists, antibiotics, and others may be prescribed to manage symptoms or treat underlying causes.
2.Lifestyle and Dietary Changes: Dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, and lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, can play a role in managing gastric diseases.
3.Endoscopy and Surgery: In some cases, endoscopy or surgery may be necessary to diagnose and treat certain gastric conditions, such as gastric ulcers, tumors, or severe cases of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
4.Management of Underlying Causes: Gastric diseases can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection with Helicobacter pylori, excessive use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), smoking, and alcohol consumption. Identifying and addressing these underlying causes is an important part of treatment.
In summary, while S-methylmethionine (SMM) was once referred to as “Vitamin U” and was thought to have potential benefits for gastric diseases, the concept of Vitamin U has largely been abandoned in modern medicine. Treatment for gastric diseases is now based on a more evidence-based and comprehensive approach, taking into consideration the underlying causes, symptoms, and individual patient factors. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options for gastric diseases.
