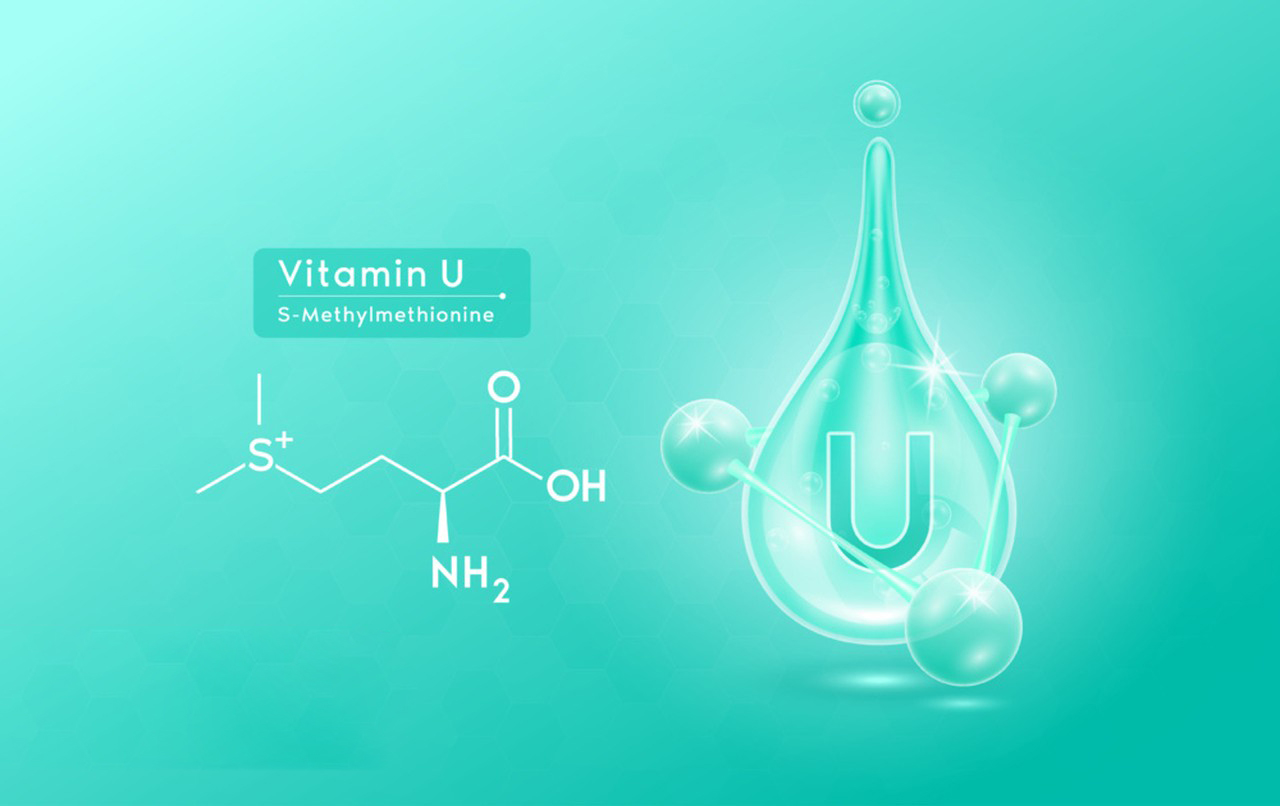
Vitamin U is not a recognized vitamin in the conventional sense, and it is not included in the essential vitamins and minerals that the human body needs for proper functioning. The term “Vitamin U” has been used historically to refer to a compound called S-methylmethionine (SMM), which is found in certain foods like cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables. However, it is not classified as a true vitamin because it is not considered essential for human health.
S-methylmethionine (Vitamin U) has been suggested to have potential health benefits, but the scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness and safety is limited. Some proposed benefits include:
1.Gastric Health: Some early research suggested that S-methylmethionine might have a protective effect on the stomach lining and could potentially help with conditions like gastritis and gastric ulcers.
2.Liver Health: There is some research suggesting that SMM may have a role in supporting liver health and potentially protecting against liver damage.
3.Allergies: There are claims that S-methylmethionine might be beneficial for people with allergies, but the evidence is limited.
It’s important to note that these potential benefits are not well-established, and more research is needed to confirm them.
As for side effects and special attention:
1.Safety: S-methylmethionine (Vitamin U) is generally considered safe when obtained from dietary sources like cabbage. However, there is limited information available regarding its safety in supplement form. If you are considering taking a supplement that contains S-methylmethionine, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your specific health needs.
2.Allergies: Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to certain compounds in cruciferous vegetables, so if you have a known allergy to these foods, you should exercise caution when consuming Vitamin U-rich foods or supplements.
3.Interaction with Medications: Like many dietary supplements, S-methylmethionine may interact with certain medications. If you are taking medications or have underlying medical conditions, consult your healthcare provider before adding this supplement to your regimen.

Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution with supplements and consult a healthcare professional before using them.
In summary, S-methylmethionine, often referred to as Vitamin U, is not considered an essential vitamin, and the scientific evidence supporting its health benefits is limited. If you are interested in using supplements containing S-methylmethionine, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it is suitable for your specific health needs and to discuss potential risks and benefits. It’s generally recommended to obtain essential nutrients from a balanced diet rather than relying on supplements whenever possible.
