Vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine or methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, is not a true vitamin, as it is not considered an essential nutrient for humans. Instead, it is a compound found in certain foods and plant extracts, such as raw cabbage, which has been credited with various health benefits, although these claims are often anecdotal and lack strong scientific evidence.
Here are some of the potential benefits that have been associated with Vitamin U:
Gastric Ulcer Treatment: Some early research suggested that Vitamin U might help in the treatment of gastric ulcers and other digestive issues. It was believed to promote the healing of damaged gastric mucosa, which lines the stomach, and reduce inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Vitamin U has been proposed to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may help in reducing inflammation in the body, although the extent of its anti-inflammatory effects is not well-documented.
Detoxification: Some proponents claim that Vitamin U can help the body detoxify harmful substances and protect against environmental toxins. However, there is limited scientific evidence to support this claim.

It’s important to note that the research on Vitamin U is limited and often outdated. Many of the early studies were conducted in the mid-20th century, and more recent research has not confirmed its benefits to the extent that it has become a widely recognized and used supplement.
Furthermore, there is no established recommended dietary allowance (RDA) or daily intake for Vitamin U, as it is not considered an essential nutrient. Its potential benefits are not well-understood, and it is not commonly used in medical practice.
Before taking any dietary supplement, including Vitamin U, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on its safety, potential benefits, and any potential interactions with medications or other supplements. It’s also important to maintain a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle to obtain the necessary nutrients for overall well-being.
Quality and Production of Vitamin U
Vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine or methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, is not actually a true vitamin, as it is not considered essential for human health. It was once believed to be a B-vitamin, but subsequent research has shown that it is not necessary in the diet for humans. However, it does have potential health benefits.
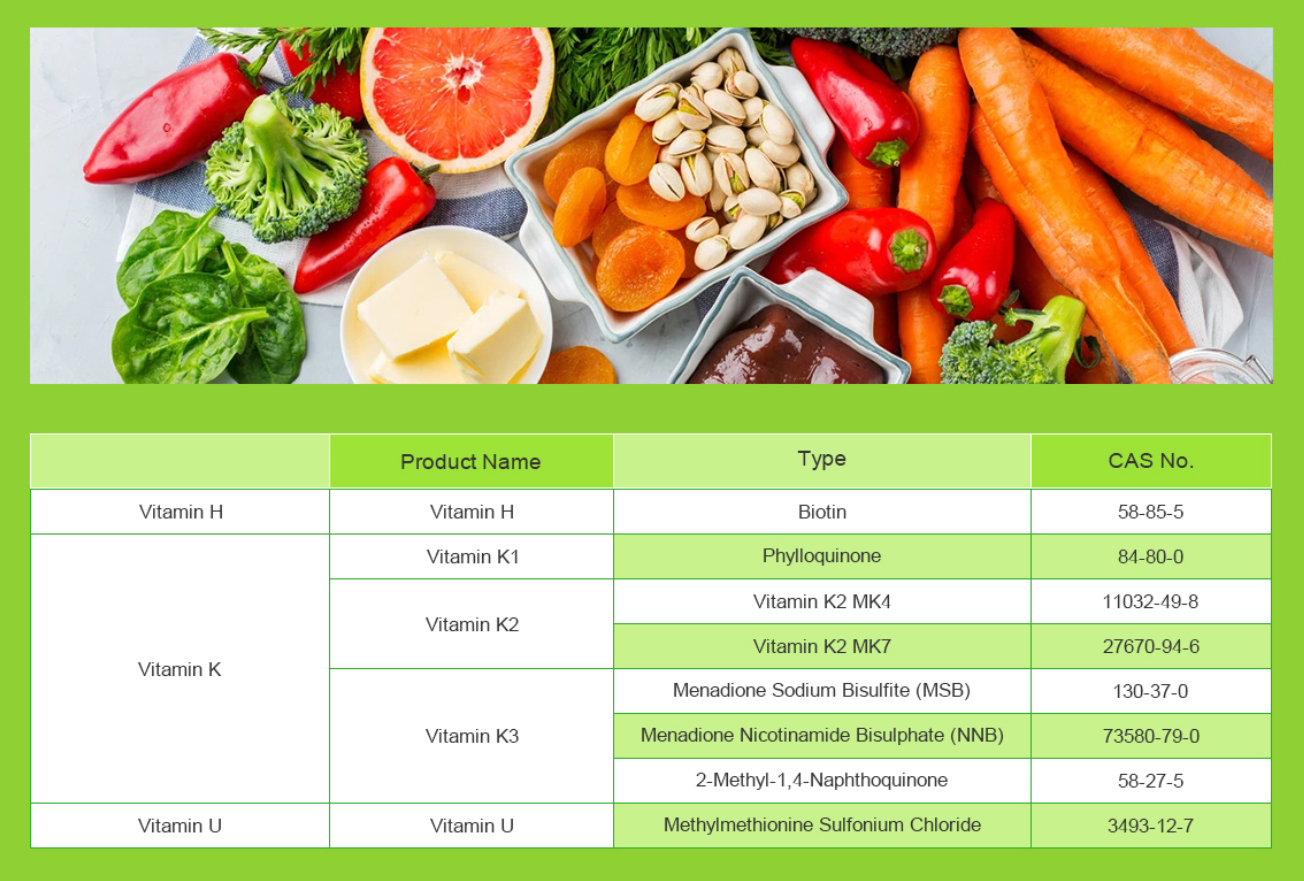
Vitamin U is found in various foods, particularly in green leafy vegetables such as kale, spinach, and cabbage. It is believed to have potential therapeutic effects, particularly in protecting the stomach lining from the damaging effects of alcohol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
In terms of production and quality of Vitamin U in foods, the content of Vitamin U in plant sources can vary based on factors such as the variety of the plant, soil conditions, and farming practices. There are no specific recommended daily allowances or dietary reference intakes for Vitamin U since it is not considered essential. Therefore, there are no established standards for the quality of Vitamin U in foods.
If you are interested in obtaining the potential health benefits of Vitamin U, it’s best to include a variety of green leafy vegetables in your diet. Eating a balanced and diverse diet will help ensure that you receive a wide range of nutrients, including Vitamin U, although you do not need to focus on it specifically.
