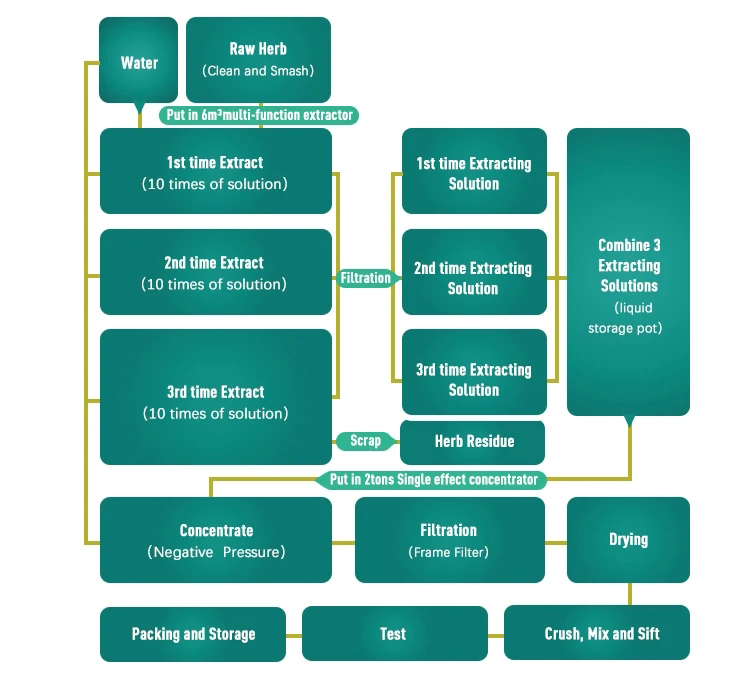
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in antioxidant defense by catalyzing the dismutation of superoxide radicals into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. This enzyme is essential for protecting cells from oxidative stress, which is associated with various health conditions, including aging and certain diseases.
The treatment of superoxide dismutase deficiency or imbalance typically involves approaches to enhance its activity or availability. Here are some ways in which the treatment of superoxide dismutase is approached:
Diet and Nutrition: Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, including foods that support the production of Superoxide dismutase, can be beneficial. These include fruits and vegetables such as berries, spinach, kale, and broccoli.
Supplements: Superoxide dismutase supplements are available, but their effectiveness is a subject of ongoing research. Some studies suggest that oral administration of Superoxide dismutase may face challenges in terms of absorption and stability.

Exercise: Regular physical activity has been linked to increased Superoxide dismutase activity. Exercise induces the production of antioxidant enzymes, including Superoxide dismutase, to help the body cope with the increased oxidative stress during physical exertion.
Environmental Factors: Avoiding exposure to environmental stressors, such as pollution and excessive sunlight, can help reduce oxidative stress and support the natural function of Superoxide dismutase.
Medications: In some cases, medications that have antioxidant properties may be prescribed to mitigate oxidative stress. However, the use of such medications would depend on the specific health condition and needs of the individual.
It’s important to note that while the importance of Superoxide dismutase in cellular defense against oxidative stress is well-established, the direct administration of Superoxide dismutase has faced challenges in terms of practicality and efficacy. Researchers continue to explore ways to enhance the body’s natural antioxidant defenses as a means of addressing conditions related to oxidative stress.
If you have a specific condition or concern related to superoxide dismutase, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
The Potential Benefits of Superoxide Dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in antioxidant defense mechanisms in the body. Here are some potential benefits associated with Superoxide Dismutase:
Antioxidant Properties: Superoxide dismutase helps neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which are byproducts of normal cell processes. Free radicals can cause oxidative stress, leading to cellular damage and various health issues. Superoxide dismutase’s antioxidant properties help protect cells from this damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Superoxide dismutase has been suggested to have anti-inflammatory effects, potentially reducing inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various diseases, and Superoxide dismutase may help mitigate some of these inflammatory processes.
Aging and Skin Health: Some studies propose that Superoxide dismutase could contribute to the prevention of premature aging by protecting the skin from oxidative stress. This may have positive effects on maintaining skin health and elasticity.
Neuroprotection: Superoxide dismutase has been investigated for its potential neuroprotective effects. It may help protect nerve cells from oxidative damage, potentially playing a role in the prevention or management of neurodegenerative diseases.
Cardiovascular Health: Antioxidants, including Superoxide dismutase, may contribute to cardiovascular health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This could have implications for preventing conditions such as atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Immune System Support: Superoxide dismutase is involved in the regulation of the immune system. It may enhance the body’s defense mechanisms by promoting a balanced immune response.
Exercise Recovery: Some studies suggest that Superoxide dismutase may play a role in reducing exercise-induced oxidative stress. Athletes and individuals engaged in strenuous physical activity may benefit from Superoxide dismutase supplementation for faster recovery.
It’s important to note that while there is promising research on the potential benefits of Superoxide dismutase, more studies are needed to fully understand its mechanisms and effectiveness. Additionally, individual responses to Superoxide dismutase supplementation may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional before considering any supplementation is advisable.
