Curcumin, the active compound found in turmeric, is widely studied for its potential health benefits. It has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer properties, among others. The applicable population for curcumin includes:
- Individuals with Chronic Inflammation: Curcumin has been studied for its ability to reduce inflammation, making it useful for people with conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and other inflammatory disorders.
- People at Risk of Heart Disease: Curcumin may help reduce cardiovascular risk factors, including high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and inflammation, potentially benefiting people at risk of heart disease.
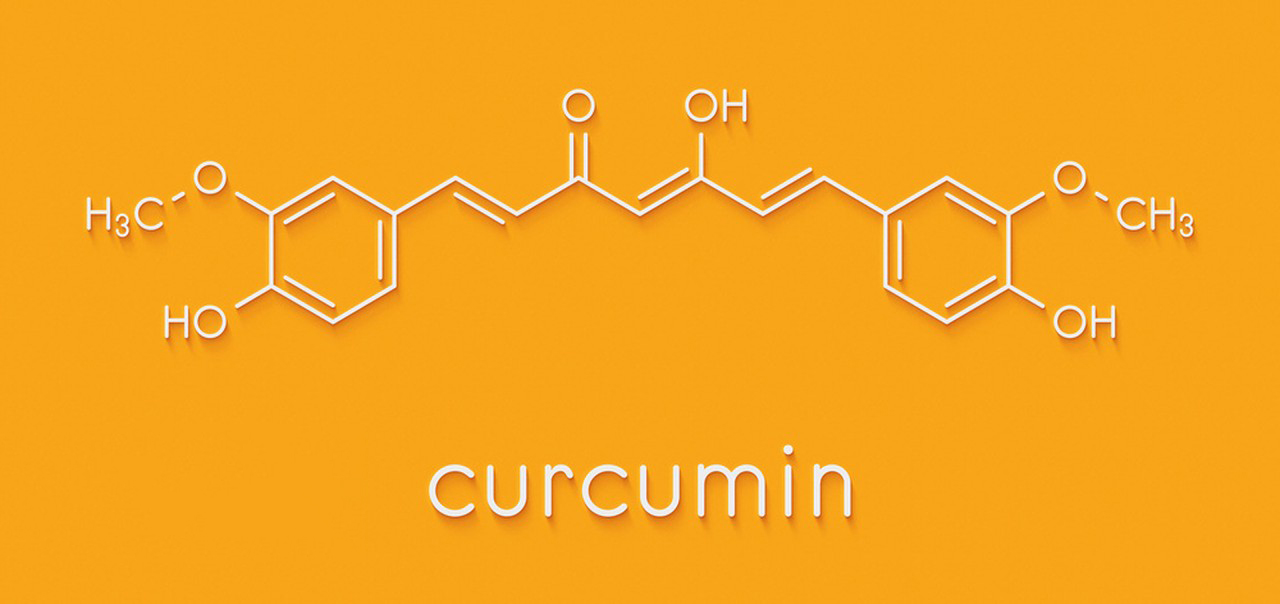
- Cancer Patients or High-Risk Individuals: Some studies suggest curcumin has anti-cancer effects, helping to slow the growth of cancer cells or enhancing the effectiveness of chemotherapy. It may be applicable to people undergoing cancer treatment or those at high risk.
- Individuals with Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like type 2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome may benefit from curcumin due to its potential effects on insulin sensitivity, blood sugar regulation, and fat metabolism.
- Neurological Health: Curcumin has been studied for its potential to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Gut Health: Individuals with digestive issues, such as IBD, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or general gut discomfort, may find curcumin helpful for reducing inflammation and promoting gut health.
Caution
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Should consult a healthcare provider before using curcumin supplements due to limited evidence on its safety during pregnancy.
- Individuals with certain health conditions: People with gallstones, bleeding disorders, or those taking blood thinners should consult their healthcare provider before using curcumin, as it may have blood-thinning effects or interfere with other medications.
Curcumin’s bioavailability (how well it is absorbed by the body) is often low, so supplements with enhanced bioavailability, such as those combined with black pepper extract (piperine), are typically recommended for better absorption. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements, especially for people with underlying conditions or who are on medication.
