Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up about 30% of the body’s total protein content. It plays a crucial role in providing structure, strength, and elasticity to various tissues and organs, including the skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, and even the cornea of the eyes.
Types of Collagen
There are at least 28 types of collagen, but the most common types are:
- Type I: The most abundant form, found in skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
- Type II: Found in cartilage and helps provide joint support.
- Type III: Found in the skin, muscles, and blood vessels, often present alongside type I collagen.
- Type IV: Found in the layers of the skin and the kidneys.
- Type V: Found in the cornea of the eye, hair, and placenta.

Structure of Collagen
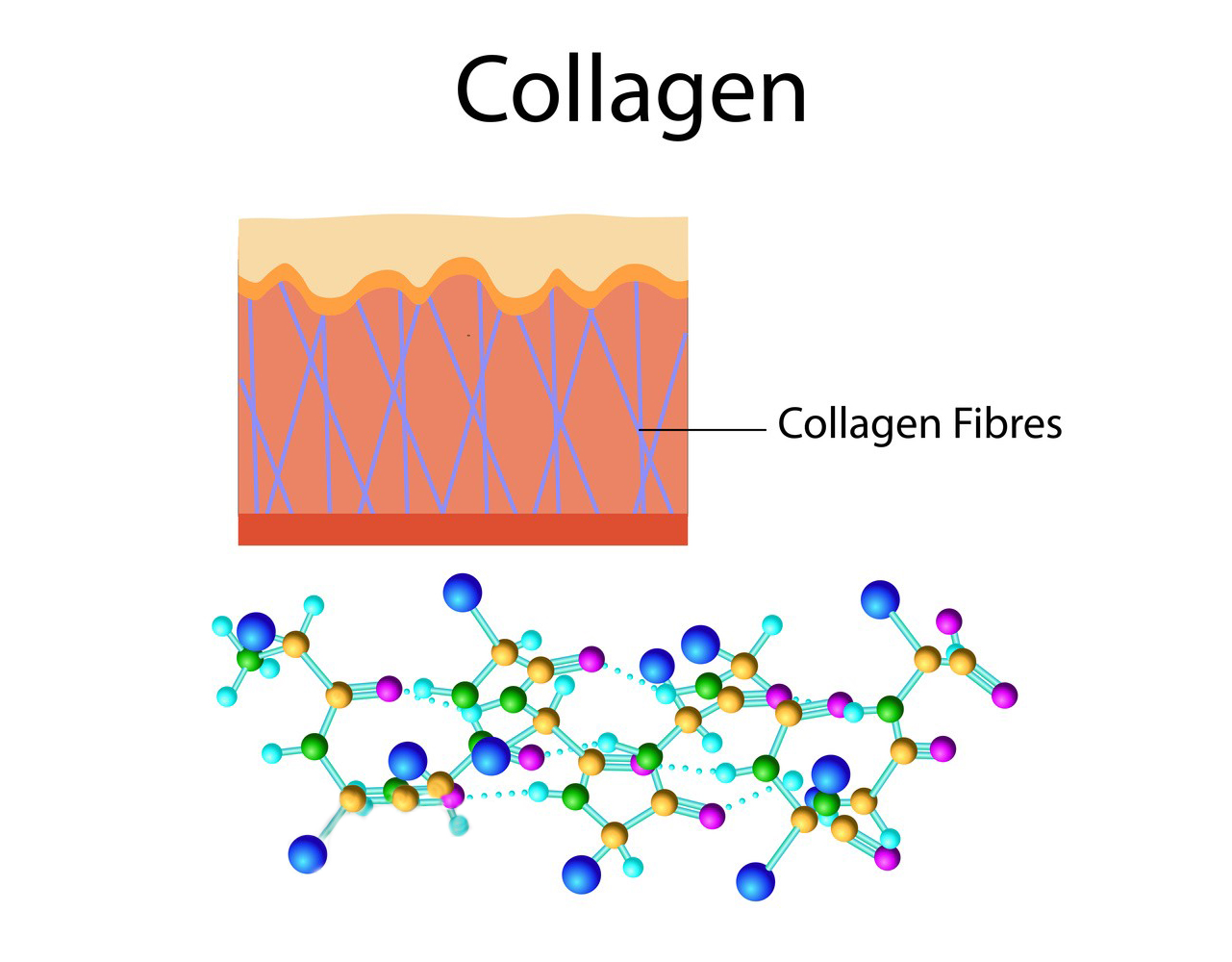
Collagen is made up of amino acids, primarily glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids form a triple-helix structure, which provides the tensile strength and flexibility characteristic of collagen fibers.
Functions of Collagen
- Structural Support: Collagen provides strength and structure to tissues.
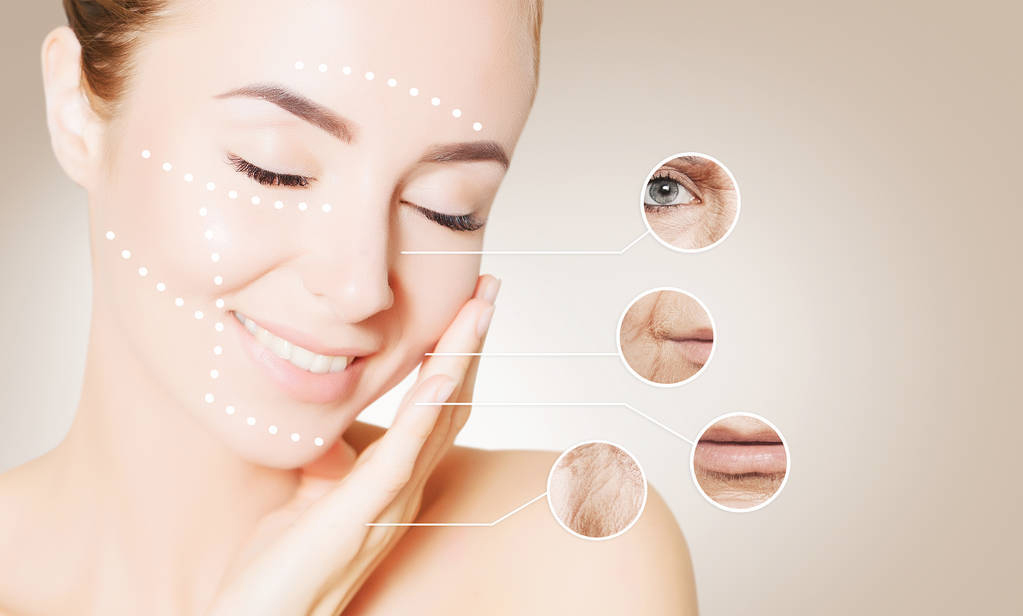
- Skin Health: It contributes to the skin’s elasticity and firmness, which is why collagen is a key factor in reducing wrinkles and maintaining youthful skin.
- Joint Health: Collagen in cartilage helps to cushion joints, reducing friction and wear.
- Bone Strength: Collagen fibers form a scaffold to support the mineralization of bones, making them strong but also slightly flexible.
- Wound Healing: Collagen is vital in the formation of new tissue during the healing process.

Collagen Synthesis
The body naturally produces collagen, but its production declines with age, typically after the age of 25. Factors such as excessive sun exposure, smoking, poor diet (lack of vitamin C), and other lifestyle choices can accelerate collagen breakdown.
Sources of Collagen
- Animal-based sources: Bone broth, chicken skin, fish skin, and pork skin.
- Supplements: Collagen peptides, usually derived from bovine (cow) or marine (fish) collagen, are commonly available as powders, capsules, or liquid supplements.
- Plant-based alternatives: While plants don’t contain collagen, certain plant-based foods (like those rich in vitamin C) support the body’s collagen production. Examples include citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens.
Collagen and Aging
As we age, the body produces less collagen, leading to common signs of aging like wrinkles, sagging skin, and weaker joints. Collagen supplements, particularly hydrolyzed collagen (which is broken down into smaller peptides for easier absorption), are often used to help combat these effects.
Potential Benefits of Collagen Supplements:
- Improved skin elasticity and hydration
- Reduced appearance of wrinkles and fine lines
- Joint pain relief
- Stronger nails and hair
Collagen is integral to maintaining health and youthfulness, and as research continues, we may uncover even more benefits related to its supplementation.
