L-Glutamic Acid is a naturally occurring amino acid and one of the 20 standard amino acids used by the body to build proteins. It plays an important role in cellular metabolism and functions as a precursor for several bioactive molecules.
Basic information of L-Glutamic Acid
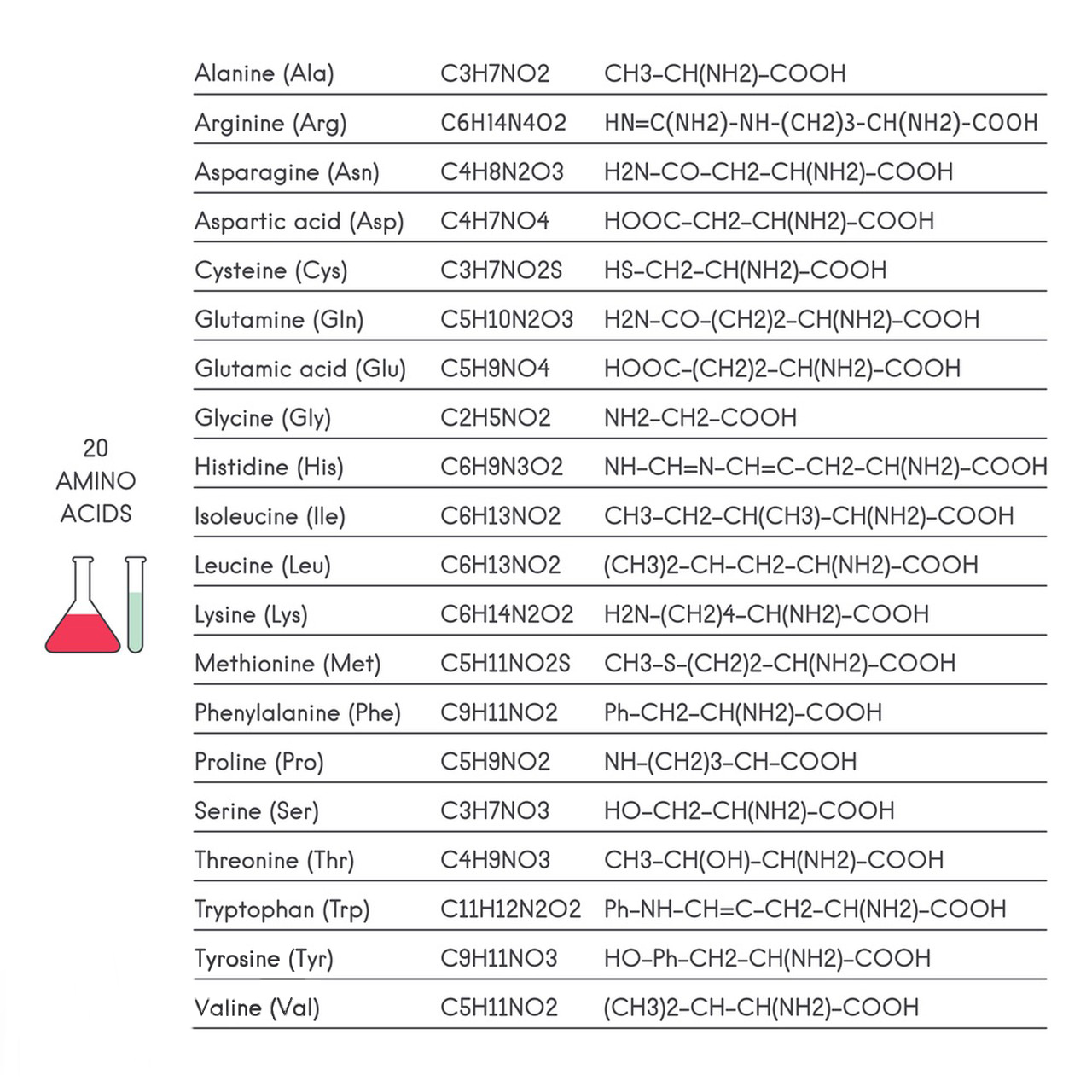
1.Name: L-Glutamic Acid
2.Molecular Formula: C₅H₉NO₄
3.Molecular Weight: 147.13 g/mol
4.Structure:
- Contains an amino group (-NH₂), a carboxylic acid group (-COOH), and a second carboxylic acid group on the side chain.

Physical Properties of L-Glutamic Acid
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether
- Melting Point: 205°C (decomposes)
- pKa Values: ~2.1 (α-carboxylic acid), ~4.1 (side-chain carboxylic acid), ~9.7 (α-amino group)
Biological Significance of L-Glutamic Acid
1.Role in the Body:
- L-Glutamic acid is a non-essential amino acid, meaning the body can synthesize it.
- Functions as a building block of proteins and plays a key role in nitrogen metabolism.
- Serves as a precursor for neurotransmitter glutamate, essential for synaptic transmission in the brain.
2.Pathways: Involved in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and glutamine metabolism.
Uses and Applications of L-Glutamic Acid
1.In Food Industry:
- Found in monosodium glutamate (MSG), a flavor enhancer.
2.In Medicine:
- Used in dietary supplements for its potential role in supporting brain and nervous system health.
- Investigated for use in treatments for neurological conditions.
3.In Research:
- Utilized in studies related to protein synthesis, neurotransmission, and cellular metabolism.
Safety Information
- Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used appropriately in food.
- Overconsumption of MSG (rich in glutamate) may cause sensitivity in some individuals, leading to symptoms like headaches or nausea, often termed “MSG Symptom Complex.”
Let me know if you’d like more detailed information or assistance with specific applications!
