Natamycin is an antifungal agent used to prevent and treat fungal infections. It is a naturally occurring polyene macrolide antibiotic, derived from Streptomyces natalensis, a species of soil bacteria. Here are some key points about natamycin:
1. Chemical Classification
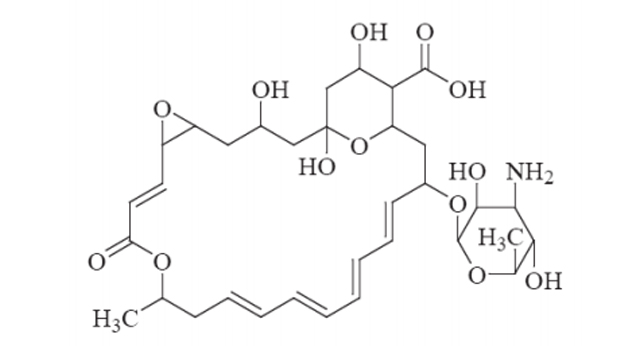
- Class: Polyene macrolides (like nystatin and amphotericin B).
- Chemical Structure: It consists of a large lactone ring with multiple conjugated double bonds, giving it antifungal properties.
2. Mechanism of Action
- Natamycin works by binding to ergosterol, a component of fungal cell membranes, and disrupting their integrity. This results in the leakage of cellular contents and ultimately the death of the fungus.
- It has a selective toxicity for fungi due to the presence of ergosterol in fungal membranes, which is absent in human cells.

3. Uses
- Topical Treatment: Primarily used to treat superficial fungal infections, such as those affecting the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
- Commonly used in eye drops for the treatment of ocular fungal infections (e.g., conjunctivitis, keratitis).
- Food Preservative: Natamycin is also used as a food preservative (E235) to prevent fungal growth on cheese and other dairy products. It is particularly effective against molds.
4. Forms and Dosage
Available in several forms, including:
- Topical ointments or creams for skin infections.
- Eye drops for ocular fungal infections.
- Oral tablets (less common for internal infections).
5. Side Effects
- Generally considered safe for topical and ophthalmic use.
- Localized irritation or allergic reactions (e.g., itching, redness) may occur.
- Systemic absorption is minimal when used topically or ophthalmically, so side effects are usually mild.
6. Resistance
- Fungal resistance to natamycin is rare, but as with any antifungal, misuse or overuse could potentially lead to reduced efficacy.
7. Regulation
- Natamycin is approved for medical use in many countries, including the United States and Europe.
- It is generally regarded as safe for use in food products when used at approved concentrations.
8. Other Considerations
- Contraindications: People with known hypersensitivity to natamycin should avoid using it.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Use with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as safety data are limited, especially for oral forms.
Natamycin is a versatile and relatively safe antifungal agent with both medical and food preservation applications.
