Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B3 (niacin) and a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a critical molecule in cellular metabolism and energy production. NAD+ plays an essential role in many biological processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and the regulation of circadian rhythms. As we age, NAD+ levels decline, and this has been associated with various age-related diseases, so Nicotinamide riboside has gained attention for its potential to boost NAD+ levels and promote health.
Key Points about Nicotinamide Riboside:
1.Structure and Biochemistry:
- Nicotinamide riboside is a nucleotide made up of a nicotinamide group (a form of niacin) attached to a ribose sugar.
- Once inside cells, Nicotinamide riboside is converted into NAD+ through a series of enzymatic steps, which increases cellular NAD+ levels.

2.Health Benefits:
- Boosting NAD+ Levels: Since NAD+ declines with age, Nicotinamide riboside supplementation may help restore NAD+ levels, potentially improving cellular function and overall health.
- Energy Metabolism: NAD+ is involved in the production of ATP, the energy currency of cells. By supporting NAD+ synthesis, NR may improve energy levels and endurance.
- DNA Repair: NAD+ is involved in DNA repair processes through its role in activating sirtuins (proteins that regulate cellular repair mechanisms and metabolism).
- Mitochondrial Health: Nicotinamide riboside has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function and may help in age-related mitochondrial dysfunction, which is linked to conditions like neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders.
- Anti-Aging Potential: Some studies suggest that Nicotinamide riboside could improve markers of aging, but more research is needed to confirm its long-term effects on aging and lifespan.
3.Sources:
- Nicotinamide riboside is found in trace amounts in foods such as milk, yeast, and certain vegetables, but it is typically present in small quantities. As a result, many people turn to supplements to boost Nicotinamide riboside intake.
4.Supplementation:
- Nicotinamide riboside is commonly available as a dietary supplement, and studies have shown that oral Nicotinamide riboside supplementation can increase NAD+ levels in humans and animals.
- Dosing varies, but typical doses range from 250 mg to 500 mg per day, though higher doses are sometimes used in clinical trials.
5.Safety and Side Effects:
- Nicotinamide riboside appears to be generally well-tolerated, with few reported side effects. However, since the long-term effects are not yet fully understood, it is advised to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning supplementation, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions or who are taking other medications.
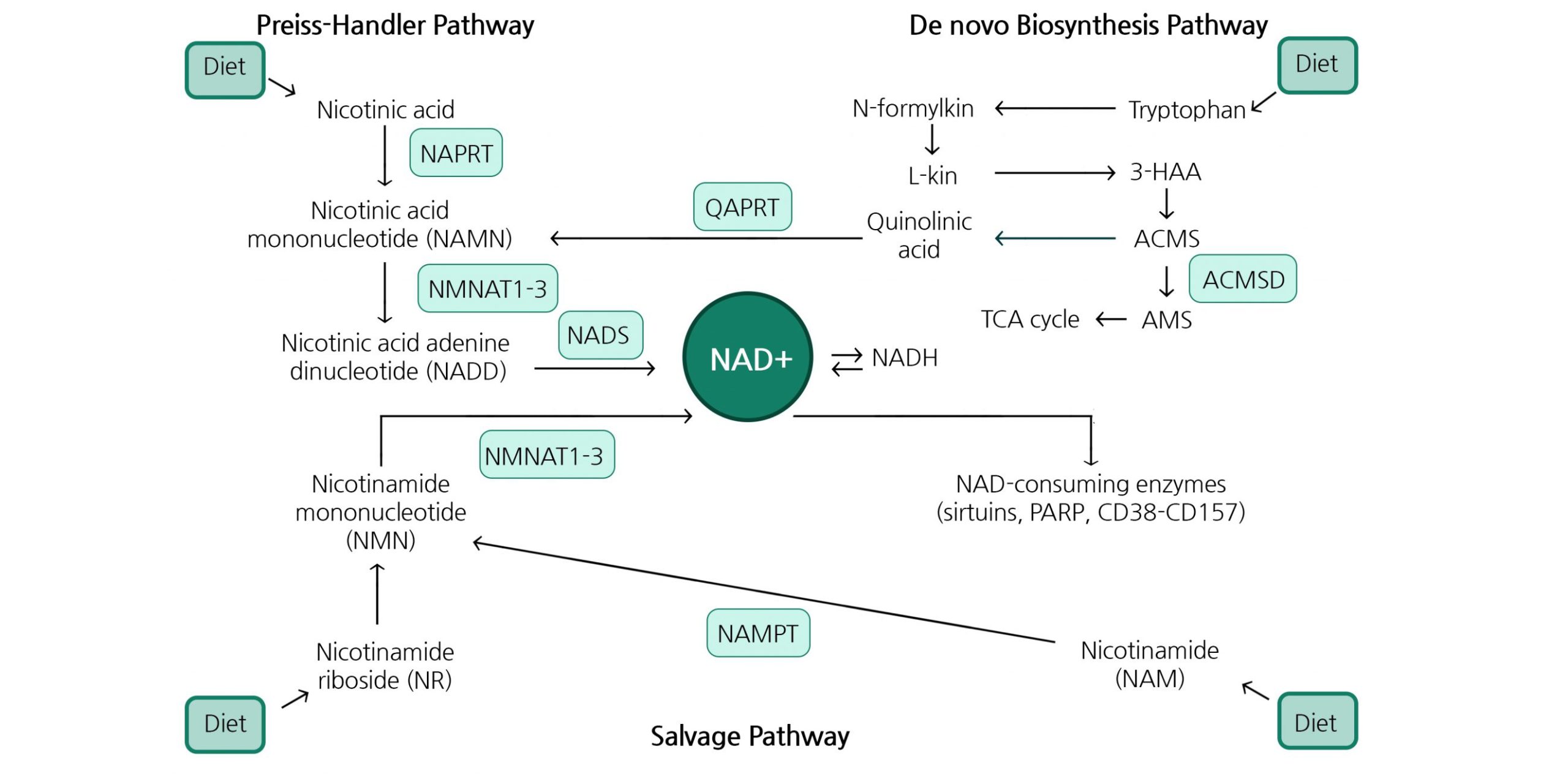
6.Other Related Compounds:
- Other compounds that can boost NAD+ levels include nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), niacin (nicotinic acid), and nicotinamide (NAM). NMN, like Nicotinamide riboside, is also a precursor to NAD+ and has garnered attention for its potential benefits on aging and metabolism.
Ongoing Research:
Research is still ongoing to fully understand the therapeutic potential of Nicotinamide riboside, including its effects on aging, metabolic disorders, and age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cardiovascular conditions. Some clinical trials have shown promising results, but more large-scale studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety over the long term.
Would you like more information on any specific aspect of Nicotinamide Riboside?
