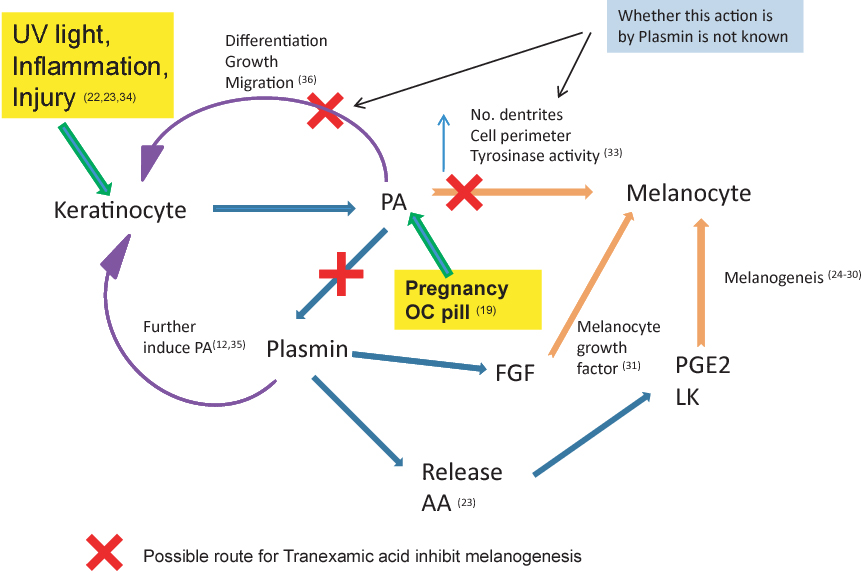
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a synthetic antifibrinolytic agent used to prevent or reduce excessive bleeding by inhibiting plasminogen activation, thereby stabilizing blood clots.
General Information of Tranexamic Acid
- Name: Tranexamic Acid
- Chemical Formula: C₈H₁₅NO₂
- Molecular Weight: 157.21 g/mol
- Drug Class: Antifibrinolytic agent
Mechanism of Action
Tranexamic acid works by inhibiting plasminogen activation, preventing the breakdown of fibrin clots. This helps reduce excessive bleeding.

Uses of Tranexamic Acid
- Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Prevention and treatment of bleeding in hemophilia patients
- Postoperative bleeding prevention (e.g., after dental extraction in hemophilia patients)
- Control of bleeding in trauma and surgery
- Treatment of hereditary angioedema
Dosage
- Oral: Typically 1-1.5 g, 2-3 times daily for a few days (varies by condition)
- IV: Dose varies depending on indication (e.g., 10 mg/kg for surgical use)
- Topical: Used in some formulations for skin discoloration treatment
Side Effects of Tranexamic Acid
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Headache and dizziness
- Risk of blood clots in some cases
- Allergic reactions (rare)
Contraindications
- History of blood clots (deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism)
- Active intravascular clotting conditions
- Severe kidney disease without dose adjustment
Precautions
- Use cautiously in patients with a history of thromboembolic disorders
- Adjust dosage in renal impairment
- Not recommended for use with certain clot-promoting conditions
Would you like more details on a specific aspect?
