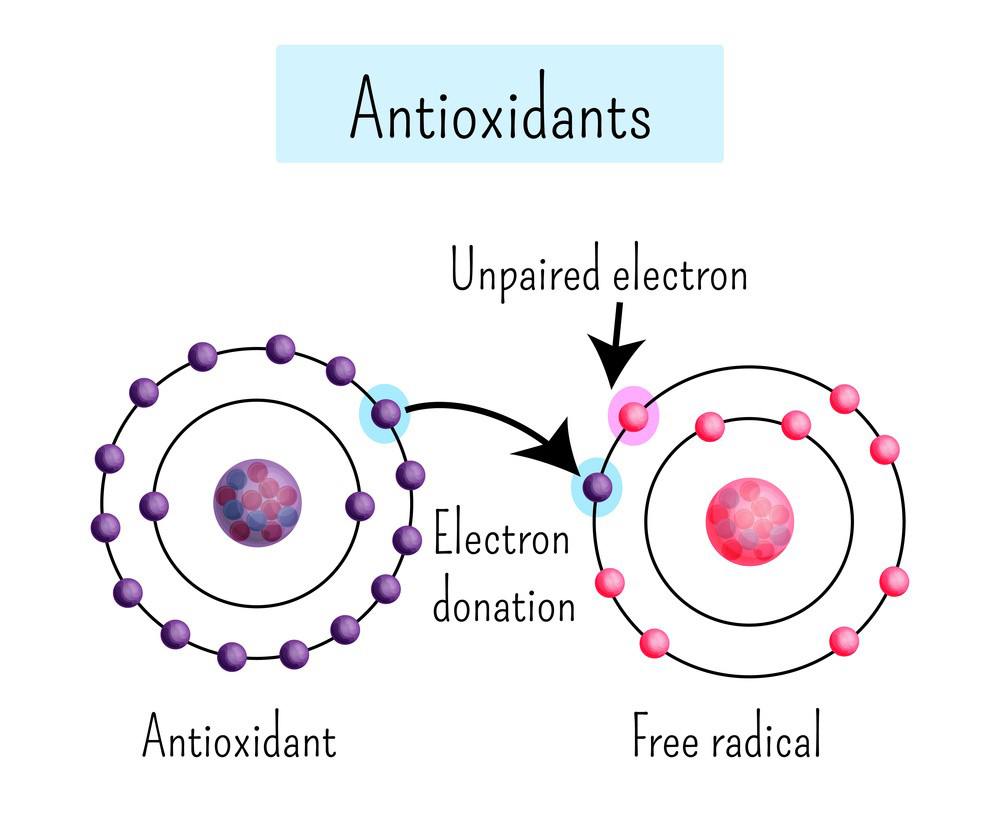
Ferulic acid is a plant-derived antioxidant commonly found in various foods and skincare products. Its chemical structure makes it a potent free-radical scavenger. The basic components that define ferulic acid include:
1.Hydroxycinnamic Acid Backbone:
Ferulic acid belongs to the class of hydroxycinnamic acids, characterized by a cinnamic acid core (a benzene ring with a carboxylic acid and a vinyl group).
2.Phenolic Group (-OH):
This hydroxyl group attached to the aromatic ring is responsible for its antioxidant properties, allowing it to neutralize free radicals.
3.Methoxy Group (-OCH₃):
Ferulic acid has a methoxy group attached to its aromatic ring, enhancing its stability and antioxidative efficiency.
4.Carboxylic Acid (-COOH):
The carboxylic acid group at the end of the molecule provides acidity and solubility characteristics.

Sources in Nature
Ferulic acid is commonly found in:
- Grains: Rice, wheat, and oats (especially in their bran layers)
- Fruits: Apples, oranges, and tomatoes
- Vegetables: Spinach, eggplant, and beets
- Seeds: Flaxseeds and sunflower seeds
It is widely used in skincare for its ability to boost the stability and efficacy of other antioxidants like Vitamin C and E.
Adverse effects of Ferulic Acid
Ferulic acid is a natural antioxidant commonly found in plants like rice bran, oats, and coffee. It is widely used in skincare products and supplements for its anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, and UV-protective properties. While ferulic acid is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience adverse effects. These include:
1. Skin Irritation
- Symptoms: Redness, itching, rash, or dryness.
- Cause: Often due to individual skin sensitivity or the presence of other active ingredients in the product.
- Risk Groups: Those with sensitive skin or a history of allergic reactions to skincare products.
2. Allergic Reactions
- Symptoms: Swelling, hives, or more severe reactions like difficulty breathing (rare).
- Cause: Allergy to ferulic acid or other compounds in the formulation.
- What to Do: Discontinue use and seek medical advice.
3. Photosensitivity
- Symptoms: Increased sensitivity to sunlight, leading to sunburn or skin discoloration.
- Cause: Although ferulic acid is often combined with UV-protective agents, improper use or overuse can make the skin sensitive to the sun.
- Preventive Measures: Always pair ferulic acid products with broad-spectrum sunscreen during daytime use.
4. Stinging or Burning Sensation
- Symptoms: Tingling or burning, especially when applied to broken or freshly exfoliated skin.
- Cause: High concentration of ferulic acid or interaction with other active ingredients like vitamin C or retinol.
- Management: Opt for lower concentrations or products formulated for sensitive skin.
5. Discoloration or Staining
- Symptoms: Temporary staining of the skin or clothing.
- Cause: Oxidation of the product when exposed to air or light.
- Solution: Store ferulic acid products in airtight, opaque containers.
6. Systemic Reactions (with Oral Supplements)
- Symptoms: Digestive issues, headaches, or dizziness (rare).
- Cause: Overuse of ferulic acid supplements or interactions with other medications.
- Precautions: Consult a healthcare provider before taking ferulic acid orally, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are on medication.
Precautions
- Always do a patch test before applying ferulic acid products to your face.
- Use as directed by a dermatologist or product instructions.
- Store products properly to maintain efficacy and reduce the risk of irritation.
If you experience persistent or severe side effects, consult a healthcare professional.
