Arachidonic Acid (AA) is a polyunsaturated fatty acid that plays several important roles in the body, including:
- Cell Membrane Composition: Arachidonic Acid is a key component of phospholipids in cell membranes, influencing membrane fluidity and function.
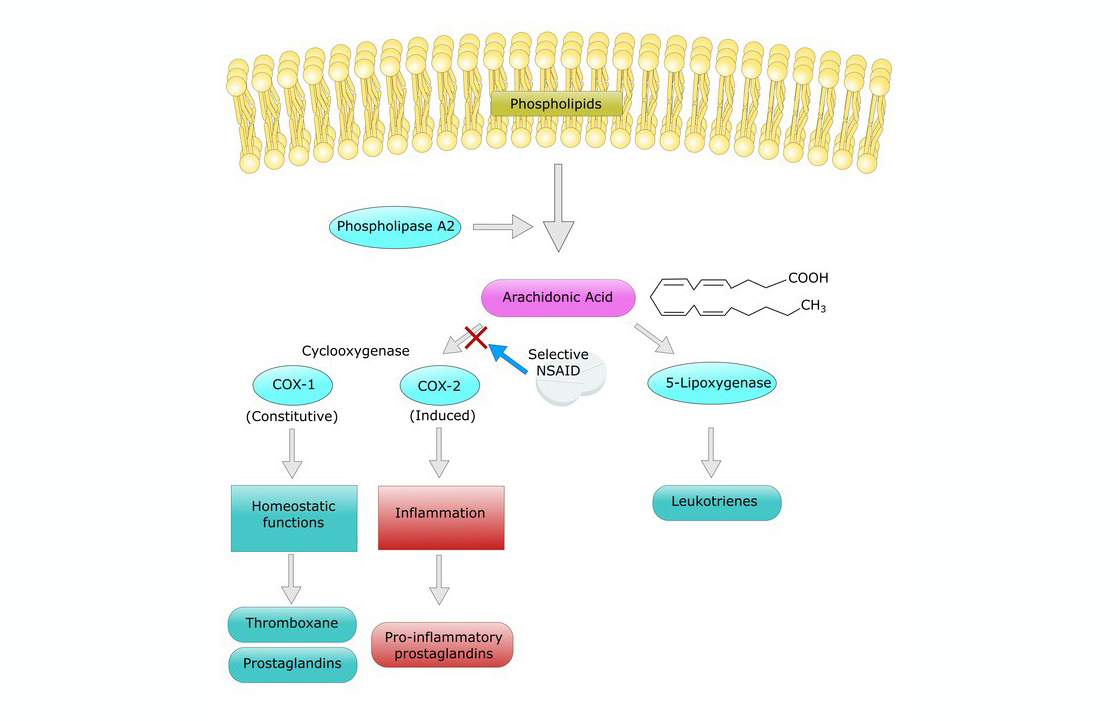
- Eicosanoid Production: Arachidonic Acid is a precursor for the synthesis of eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules that include prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. These molecules are involved in various physiological processes, such as inflammation, immune response, and regulation of blood flow.
- Inflammation and Immune Response: Eicosanoids derived from Arachidonic Acid are critical in mediating inflammation and immune responses. They can promote or resolve inflammation, depending on the context.
- Brain Function: Arachidonic Acid is important for brain health and is involved in neurotransmission and the development of neural connections.
- Reproductive Health: Arachidonic Acid plays a role in reproductive processes, including ovulation and implantation.
- Nutritional Role: It can be obtained through the diet, particularly from animal products, and is essential for certain physiological functions.
Understanding these functions helps in exploring the potential therapeutic roles of arachidonic acid in conditions like inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders.
Properties of Arachidonic Acid
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid with several important properties:
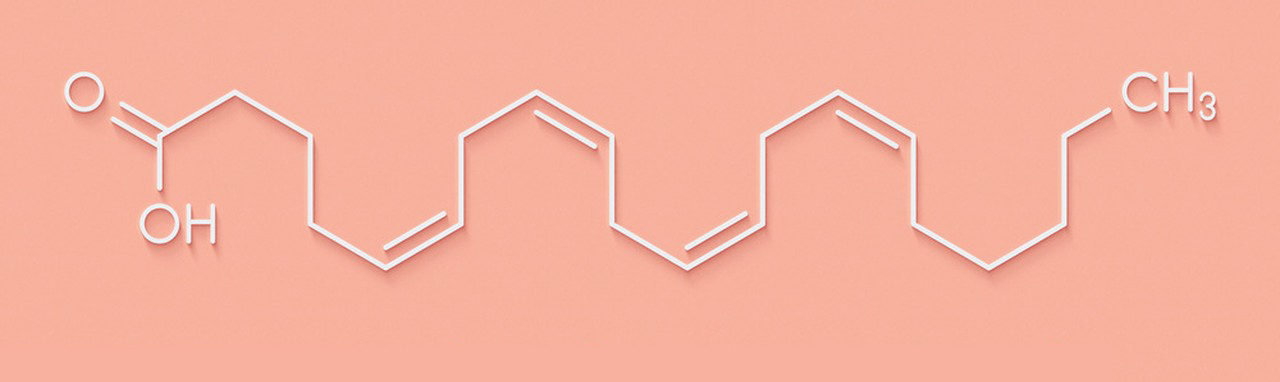
- Structure: It has a carbon chain of 20 carbons with four double bonds, making it highly unsaturated.
- Biological Significance: Arachidonic acid is a key component of phospholipids in cell membranes, contributing to membrane fluidity and signaling.
- Metabolism: It can be metabolized into various bioactive lipid mediators, including prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, which play crucial roles in inflammation, immunity, and vascular function.
- Role in Inflammation: Arachidonic acid is involved in inflammatory responses; its metabolites can promote or resolve inflammation, depending on the context.
- Dietary Sources: It is primarily obtained from animal products, such as meat, eggs, and dairy, as well as some fish oils.
- Health Implications: Imbalances in arachidonic acid levels can be associated with various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and other inflammatory disorders.
- Interactions with Other Fatty Acids: The balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in the diet is crucial for maintaining health, as they can compete for the same metabolic pathways.
Understanding these properties is essential for studying lipid biochemistry, nutrition, and various physiological processes.
