Melatonin is a hormone produced by the body’s endocrine system, mainly responsible for regulating the biological clock and sleep. In addition to being used as a drug to treat sleep disorders and regulate the biological clock, melatonin has also been studied for its potential to treat other diseases, but there is still controversy.
Some studies have shown that melatonin may have therapeutic effects on certain diseases, such as:
Antioxidant effects: Melatonin has strong antioxidant properties and can remove free radicals in the body, preventing oxidative stress. Therefore, research has explored the potential of melatonin to prevent and treat diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Immunomodulatory effects: Melatonin can regulate the function of the immune system, enhance immunity, and help prevent infections and autoimmune diseases. Therefore, research has explored the potential of melatonin to treat autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
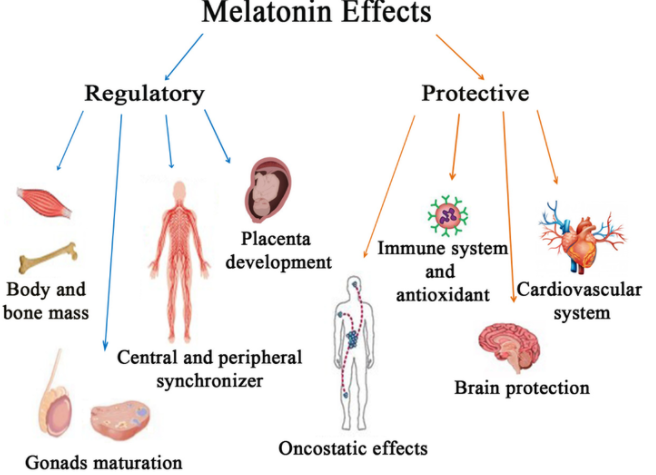
Although these studies suggest that melatonin may have therapeutic effects on some diseases, these conclusions need to be further validated through more research. In addition, melatonin as a drug also has its side effects and contraindications, so it should be used under the guidance of a doctor.
Melatonin is a hormone synthesized in the body and animals, mainly produced by the pineal gland located in the brain. Melatonin plays an important role in regulating the biological clock, promoting sleep, and antioxidant effects. The following is a brief overview of the mechanism of action of melatonin:
Biological clock regulation: Melatonin secretion is influenced by the light-dark cycle. When it is dark, the pineal gland secretes melatonin at a faster rate, while when it is bright, melatonin secretion decreases. This secretion pattern helps synchronize the biological clock, enabling the body to adapt to the rhythm of day and night. Melatonin secretion is higher at night in humans, promoting sleep.
Sleep promotion: Melatonin can affect neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby regulating the activity of the nervous system. When melatonin levels rise, the body feels sleepy, promoting sleep. When melatonin levels decrease, the body gradually wakes up. Therefore, melatonin plays a key role in regulating and promoting sleep.
Antioxidant effects: Melatonin has antioxidant properties, can remove free radicals, and protect cells from oxidative stress damage.
