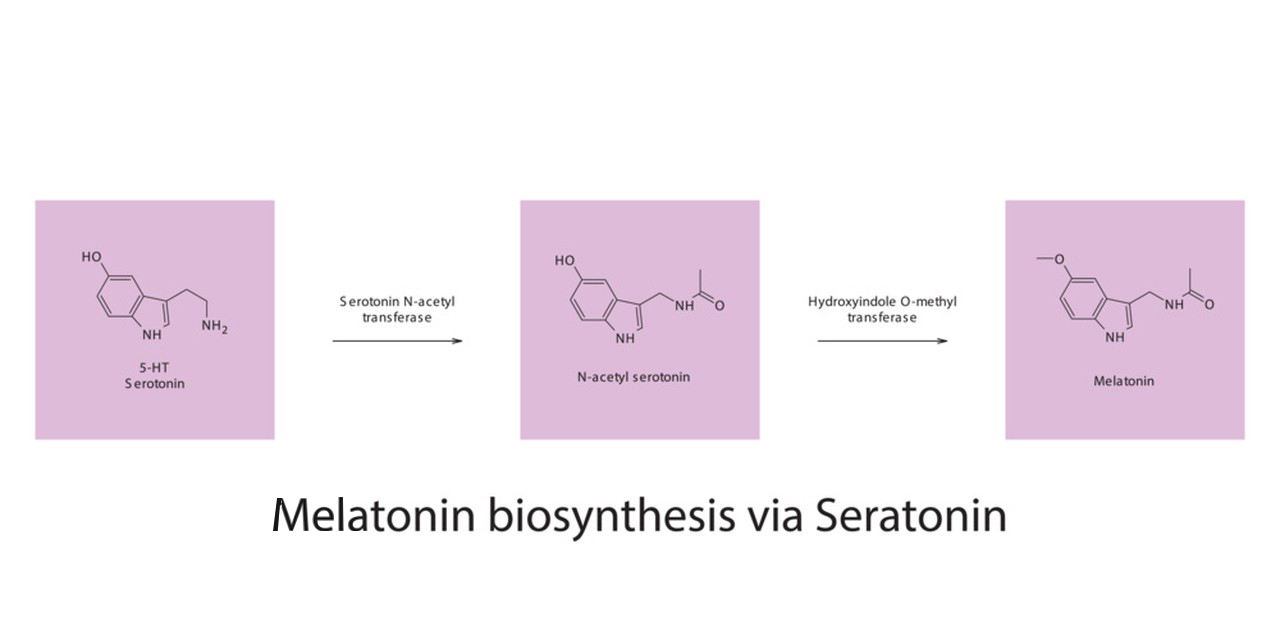
Melatonin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the pineal gland in the brain and plays a key role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. It is often referred to as the “sleep hormone” because it helps to signal to the body that it’s time to sleep. Melatonin supplements are available over the counter and are sometimes used to help treat insomnia or sleep-related issues.
Melatonin supplements can be effective for certain types of insomnia, particularly for people who have difficulty falling asleep due to circadian rhythm disturbances or jet lag. For example, if you have recently traveled to a different time zone and are experiencing jet lag, taking melatonin at the appropriate time can help your body adjust to the new schedule and facilitate better sleep.
However, melatonin may not be as effective for other types of insomnia, such as insomnia related to chronic stress, anxiety, or other underlying medical conditions. In such cases, addressing the root causes of insomnia and adopting good sleep hygiene practices are often more effective approaches.

It’s important to use melatonin supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as the appropriate dosage and timing can vary from person to person. Additionally, it’s generally recommended for short-term use and not as a long-term solution for chronic insomnia. If you’re struggling with persistent insomnia, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying causes and explore appropriate treatments, which may include behavioral therapy, lifestyle changes, or prescription medications.
How about the effect of Melatonin on insomnia?
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in the brain, and it plays a key role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. It is often used as a supplement to help manage sleep problems, particularly insomnia. Here are some key points about the effects of melatonin on insomnia:
Melatonin and Circadian Rhythm: Melatonin is involved in regulating the body’s internal clock, which helps govern the sleep-wake cycle. The pineal gland releases melatonin in response to darkness, making us feel sleepy. Taking melatonin supplements can help adjust this cycle, making it easier to fall asleep, especially in cases of jet lag or shift work-related sleep disturbances.
Types of Insomnia: Melatonin may be more effective for certain types of insomnia. It is particularly useful for people with delayed sleep phase syndrome, which causes difficulty falling asleep at a typical bedtime. Melatonin can help advance the sleep-wake cycle in such cases.
Short-Term Use: Melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use, and it can be used to help with occasional sleep problems. For example, taking melatonin before bedtime may be helpful for dealing with temporary sleep disruptions, like those caused by travel or certain medications.
Efficacy Varies: The effectiveness of melatonin can vary from person to person. While it works well for some individuals, it may not be as effective for others. It’s not a guaranteed solution for everyone with insomnia.
Timing and Dosage: The timing and dosage of melatonin are crucial. It is typically taken 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime. The appropriate dose varies, but lower doses (around 0.5 to 3 mg) are often more effective than higher doses. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on the right dose and timing for your specific needs.
Considerations and Precautions: Melatonin supplements are available over the counter, but it’s important to use them with caution. Consult a healthcare provider before starting melatonin, especially if you have underlying health conditions, are taking other medications, are pregnant or nursing, or are giving it to a child.
Not a Cure-All: Melatonin is not a cure-all for all types of insomnia. If you have chronic or severe insomnia, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional who can help identify and address the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments.
In summary, melatonin can be a helpful tool for managing insomnia, particularly in situations where the sleep-wake cycle needs adjustment. However, it may not be a suitable or effective solution for everyone with insomnia, and its use should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the right approach for your specific circumstances.
