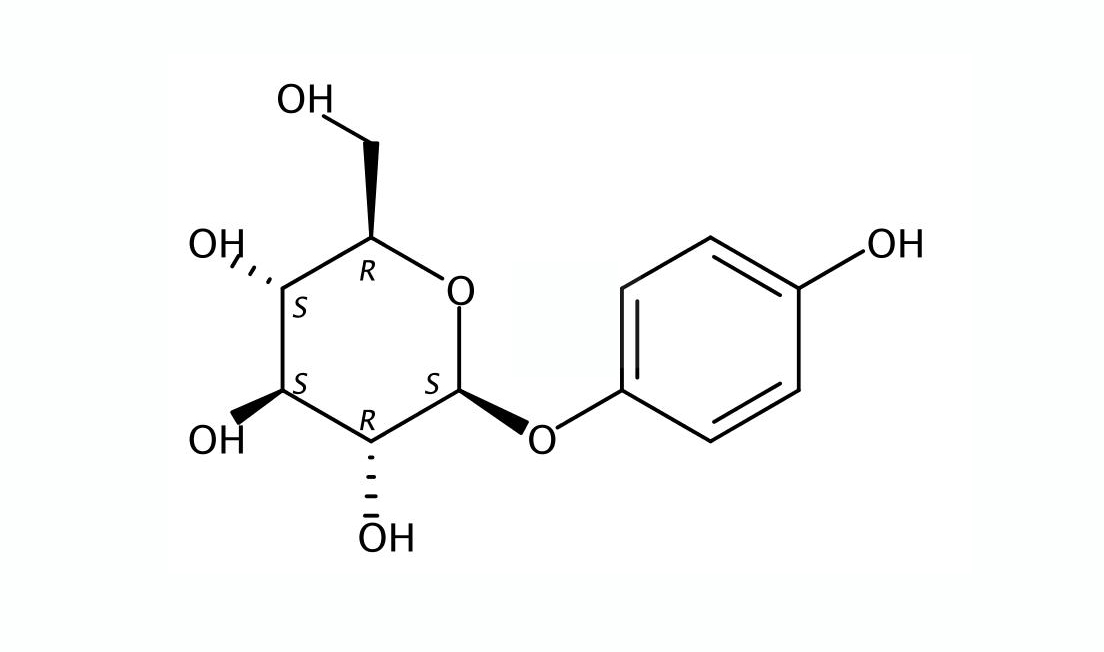
Beta arbutin, also known as 4-hydroxyphenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside, is a glycosylated hydroquinone commonly used in skincare products for its skin-brightening properties. Here are its chemical structure and physical properties:
Chemical Structure of Beta Arbutin
- IUPAC Name: 4-Hydroxyphenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Molecular Formula: C12H16O7
- Molecular Weight: 272.25 g/mol
- Structure: Beta arbutin consists of a hydroquinone moiety (4-hydroxyphenol) attached to a glucose molecule. The glycosidic bond forms between the phenolic hydroxyl group and the glucose, which is in the beta configuration.
Physical Properties of Beta Arbutin
- Appearance: Beta arbutin typically appears as a white to off-white powder.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water and ethanol but less soluble in organic solvents like hexane.
- Melting Point: It generally has a melting point around 180-185 °C, but this can vary slightly based on purity.
- Stability: Beta arbutin is more stable than alpha arbutin, especially in formulations exposed to light and heat.
Biological Propertiesof Beta Arbutin
Beta arbutin is known for its skin-lightening effects, working by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. It is often used in cosmetics for its ability to reduce hyperpigmentation and improve skin tone.
Applications of Beta Arbutin
Beta arbutin is often used in cosmetic formulations for its ability to inhibit melanin production, making it popular for brightening skin and treating hyperpigmentation.
If you need more specific information or have any other questions, feel free to ask!
