Chemical Structure of Betaine:
Betaine is a naturally occurring compound with the chemical formula C₅H₁₁NO₂. Structurally, it is derived from the amino acid glycine and can be considered as a trimethylglycine. Its structure consists of a quaternary ammonium group (N⁺(CH₃)₃) attached to a carboxylate group (COO⁻), which gives betaine its zwitterionic nature (it has both positive and negative charges on different parts of the molecule).
- IUPAC name: Trimethylglycine
- Molecular formula: C₅H₁₁NO₂
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
- Structural formula:
H₃C
|
H₃C-N⁺-CH₂-COO⁻
|
H₃C
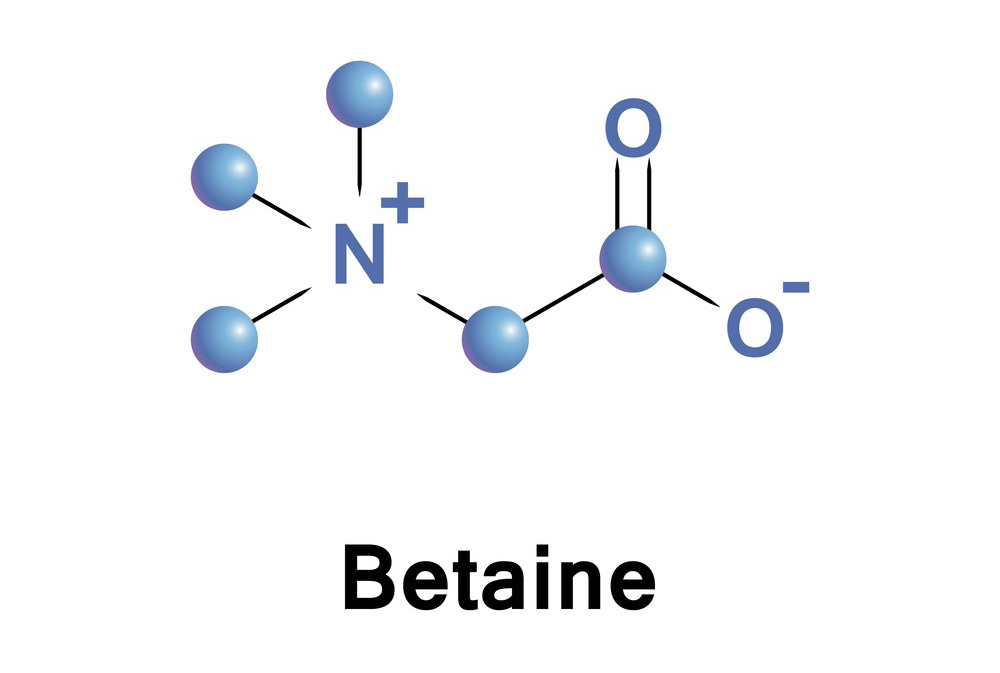
This structure shows that betaine is a methylated derivative of glycine (trimethyl glycine), where the nitrogen is bonded to three methyl groups and the carboxyl group is ionized.
Physical Properties of Betaine:
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Betaine is highly soluble in water. It also dissolves in ethanol and other polar solvents but is less soluble in non-polar solvents like chloroform or hexane.
- Melting Point: Approximately 301°C (decomposes)
- Density: 1.00 g/cm³ (in solid form)
- Boiling Point: Betaine does not have a clear boiling point as it decomposes upon heating.
- pKa: The carboxyl group has a pKa of around 2.3, but since betaine is a zwitterion, it exists primarily in its neutral form in solution across a wide pH range.
- Hygroscopicity: Betaine is hygroscopic, meaning it tends to absorb moisture from the air.

Special Characteristics:
- Zwitterionic nature: As a zwitterion, betaine is electrically neutral but has both a positive charge on the nitrogen atom (due to the quaternary ammonium group) and a negative charge on the carboxyl group.
- Osmoprotectant: Betaine is known for its role as an osmoprotectant, helping cells manage osmotic stress, and it is used in cosmetics, health supplements, and agriculture for its water retention properties.
Would you like more information about its applications or any specific aspect of its chemistry?
