Dutasteride is a medication primarily used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate) and androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness). It belongs to a class of drugs known as 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. The chemical structure and physical properties of dutasteride are as follows:
Chemical Structure of Dutasteride:
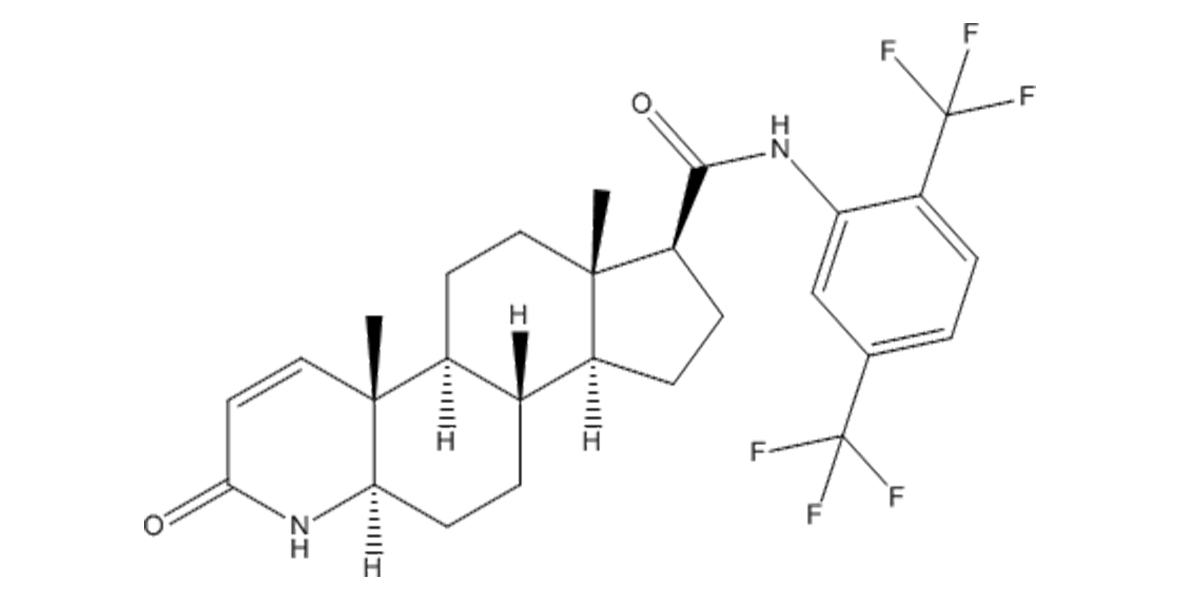
Dutasteride’s chemical structure is characterized by its molecular formula and arrangement of atoms. Its systematic name is (5α,17β)-N-{2,5 bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}-3-oxo-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide. The structural formula can be described as follows:
Physical Properties of Dutasteride:
Dutasteride’s physical properties include its appearance, solubility, melting point, and other relevant characteristics:
- Appearance: Dutasteride is a white to pale yellow powder.
- Melting Point: The melting point of dutasteride is approximately 242-250°C (468-482°F).
- Solubility: Dutasteride is practically insoluble in water. It is soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, methanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of dutasteride is approximately 528.5 g/mol.
- Lipophilicity: Dutasteride’s lipophilicity contributes to its ability to be absorbed by fatty tissues.
It’s important to note that while these properties provide a general understanding of dutasteride, its behavior can vary in different environments and formulations. As with any medication, you should consult a healthcare professional or pharmacist for accurate and up-to-date information about dutasteride or any other drug.
The clinical application of Dutasteride
Dutasteride is a medication that is primarily used for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland in men. It belongs to a class of drugs known as 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. Dutasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to prostate enlargement.
Here are some clinical applications of dutasteride:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Treatment: Dutasteride is FDA-approved for the treatment of BPH, a condition that commonly occurs as men age. By reducing DHT levels, dutasteride helps to shrink the prostate gland, relieving symptoms like urinary hesitancy, weak urine stream, frequent urination, and incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Combination Therapy: Dutasteride can be used as a monotherapy or in combination with another class of BPH medications called alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin) to provide more effective symptom relief. Combination therapy addresses both the size of the prostate gland and the relaxation of muscles around the bladder neck, improving urine flow.
Male Pattern Baldness (Off-Label Use): While not approved by the FDA for this purpose, dutasteride has been explored off-label for the treatment of male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). It works similarly to its use in BPH, by reducing DHT levels which are associated with hair loss. However, finasteride is more commonly used for this indication due to its selective inhibition of the Type II isoform of 5-alpha-reductase.

Prostate Cancer Prevention (Off-Label Use): Dutasteride has been studied for its potential role in preventing prostate cancer. It can decrease DHT levels, which might help reduce the risk of developing certain types of prostate cancer. However, the use of dutasteride for prostate cancer prevention is not a widely accepted practice due to potential side effects and concerns about the detection of high-grade prostate cancer.
It’s important to note that dutasteride, like any medication, can have side effects and risks. Some common side effects include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, breast tenderness or enlargement, and decreased ejaculate volume. Before considering dutasteride or any medication, individuals should consult a healthcare professional who can provide personalized advice based on their medical history and current health status.
