Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a cosmetic ingredient, particularly used in anti-aging skincare products. It’s a derivative of retinoic acid, known for its efficacy in skin rejuvenation, but with potentially less irritation compared to traditional retinoids.
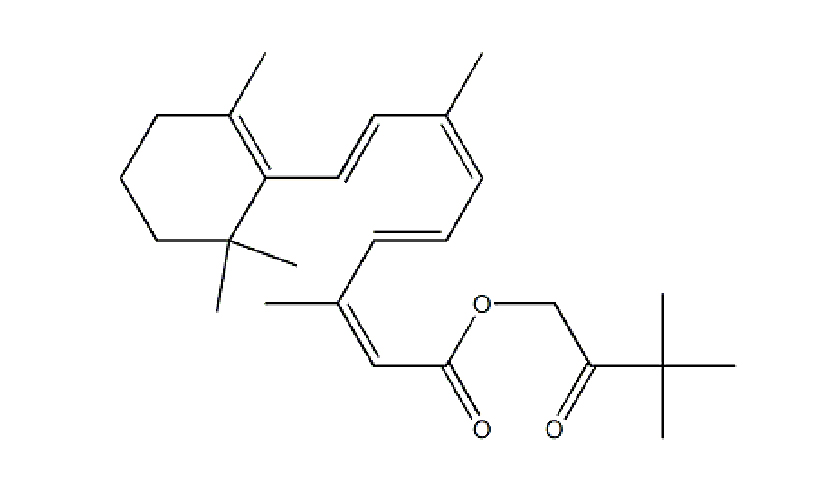
Chemical Structure of Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR)
IUPAC Name: 3,3-Dimethyl-1-oxobutyl 4-[(1E,3E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-4-carboxylate
Molecular Formula: C26H38O3
Molecular Weight: 398.58 g/mol
The structure features:
A retinoic acid backbone with modifications.
An ester linkage to a hydroxypinacolone moiety, which stabilizes the retinoid structure and increases its lipophilicity.
Physical Properties of Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR)
Appearance: Yellow to orange crystalline powder.
Solubility: Soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, methanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); slightly soluble in water.
Melting Point: Approximately 70-75°C (158-167°F).
Functional Properties
Stability: Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is more stable than retinol and other retinoids due to its esterified form.
Skin Penetration: Better skin penetration due to its lipophilic nature, allowing for effective delivery of the active retinoic acid to the skin.
Efficacy: Promotes skin cell turnover, improves skin texture, reduces fine lines and wrinkles, and helps with acne management.
Irritation Potential: Lower irritation potential compared to retinoic acid, making it suitable for sensitive skin.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is popular in skincare formulations due to its effective anti-aging benefits while minimizing the typical side effects associated with retinoids.
Potential benefits of Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR)
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a newer form of retinoid that has gained attention for its potential benefits in skincare. Here are some of its advantages:
Gentler on the Skin: Compared to traditional retinoids like retinol or tretinoin, Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is generally considered to be less irritating. This makes it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin who may not tolerate other forms of retinoids well.
Effective at Lower Concentrations: Studies suggest that Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) can be effective at lower concentrations compared to other retinoids. This means it can deliver similar results with potentially less risk of irritation.
Stable Formulation: Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is more stable than some other forms of retinoids, which can be prone to degradation when exposed to light and air. This stability allows for longer shelf life and more consistent efficacy in skincare products.
Enhanced Collagen Production: Like other retinoids, Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) has been shown to stimulate collagen production in the skin. This can help improve skin firmness and elasticity, leading to a more youthful appearance over time.
Reduced Appearance of Wrinkles and Fine Lines: By promoting cell turnover and collagen synthesis, Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) can help minimize the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of aging.

Improvement in Skin Tone and Texture: Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) can also help improve skin tone and texture by promoting exfoliation and reducing hyperpigmentation, resulting in smoother, more even-looking skin.
Potential for Acne Treatment: Retinoids are known for their ability to unclog pores and regulate oil production, making them effective in the treatment of acne. While more research is needed, Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) shows promise in this area as well.
Sun Damage Repair: Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) may also help repair sun damage by promoting the turnover of damaged skin cells and stimulating the production of new, healthy cells.
It’s important to note that individual responses to Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) may vary, and some people may still experience mild irritation or other side effects. As with any skincare ingredient, it’s best to start with a lower concentration and gradually increase usage to minimize the risk of adverse reactions. Additionally, sunscreen should always be used during the day when using retinoids to protect the skin from sun damage.
