Liposomal glutathione is a form of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant, that is encapsulated in liposomes. Liposomes are tiny spherical vesicles made from phospholipids, similar to the membranes that surround cells. This delivery system is designed to improve the absorption and bioavailability of glutathione when taken as a supplement.
Chemical Structure of Liposomal Glutathione:
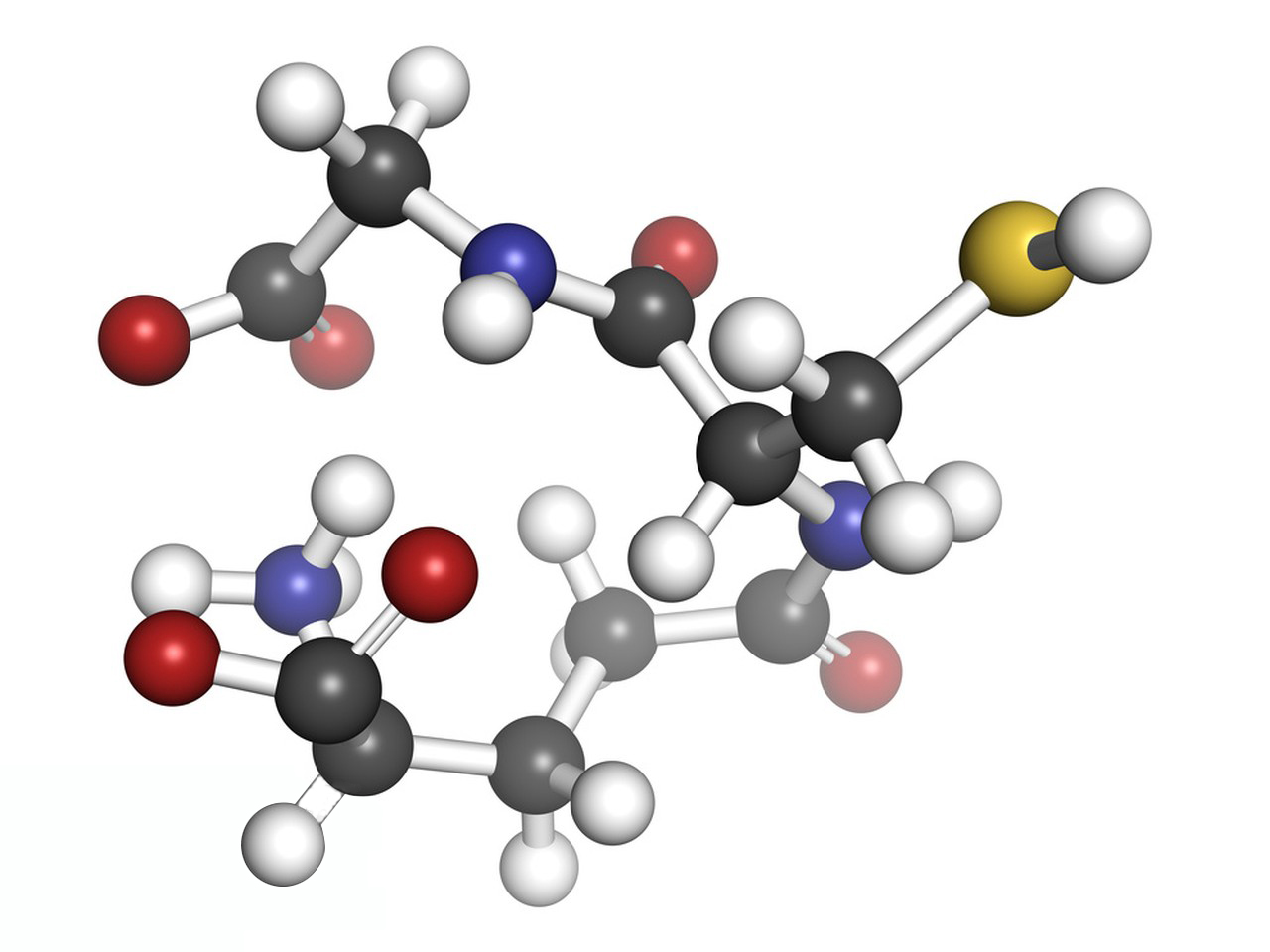
1.Glutathione (GSH):
Chemical formula: C₁₀H₁₇N₃O₆S
Structure: Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids: glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. The unique feature of glutathione is the presence of a thiol (-SH) group in cysteine, which plays a central role in its antioxidant properties.
Glutamate is linked to cysteine via a gamma-glutamyl bond (unusual in peptides).
Cysteine provides the reactive thiol group.
Glycine is attached to the carboxyl group of cysteine.
2.Liposomal Delivery System:
Liposomal glutathione is glutathione encapsulated within a liposome.
Liposome: A spherical vesicle with a phospholipid bilayer.
Phospholipids: Amphiphilic molecules that form the bilayer, where the hydrophilic heads face outwards, and the hydrophobic tails face inwards, creating a protective layer around the glutathione.
Common phospholipids used include phosphatidylcholine (C₄₂H₈₄NO₈P), which enhances glutathione’s stability and bioavailability.
Physical Properties of Liposomal Glutathione:
1.Molecular Weight:
Glutathione: 307.32 g/mol
Phosphatidylcholine (for the liposome): 734.04 g/mol (varies with the type of phospholipids).
2.Solubility:
Glutathione: Water-soluble.
Liposomal Glutathione: The liposomal structure makes it soluble in aqueous environments while protecting glutathione from degradation.
3.Appearance:
The glutathione powder is typically white or off-white.
Liposomal glutathione appears as a milky, liquid suspension due to the encapsulation of glutathione within the liposomal vesicles.
4.Stability:
Free glutathione is highly prone to oxidation, which reduces its effectiveness.
Encapsulation within liposomes increases its stability, protecting it from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and oxidation.

5.Bioavailability:
Liposomal encapsulation enhances the absorption of glutathione, allowing more of it to reach the bloodstream when taken orally.
6.pH Stability:
Glutathione is relatively stable at neutral or slightly alkaline pH but is more prone to degradation in acidic environments. Liposomal encapsulation helps protect it from the acidic conditions of the stomach.
This combination of glutathione’s antioxidant power and the liposomal delivery system provides improved therapeutic benefits due to increased absorption and protection from degradation.
