Liposomal Vitamin C combines Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) with liposomes to enhance its stability and absorption. Here’s a breakdown of the chemical structure and physical properties of the key components:
1. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Chemical Structure:
- Molecular Formula: C₆H₈O₇
- Structure: Ascorbic acid is a water-soluble vitamin with a structure featuring a six-carbon sugar acid with enediol groups. Its structure includes:
- Two hydroxyl groups (-OH) on each of the first two carbon atoms.
- A lactone ring (a cyclic ester) that is integral to its antioxidant properties.
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: White to slightly yellow crystalline powder.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water.
- Stability: Sensitive to heat, light, and air; prone to oxidation, which can reduce its effectiveness.
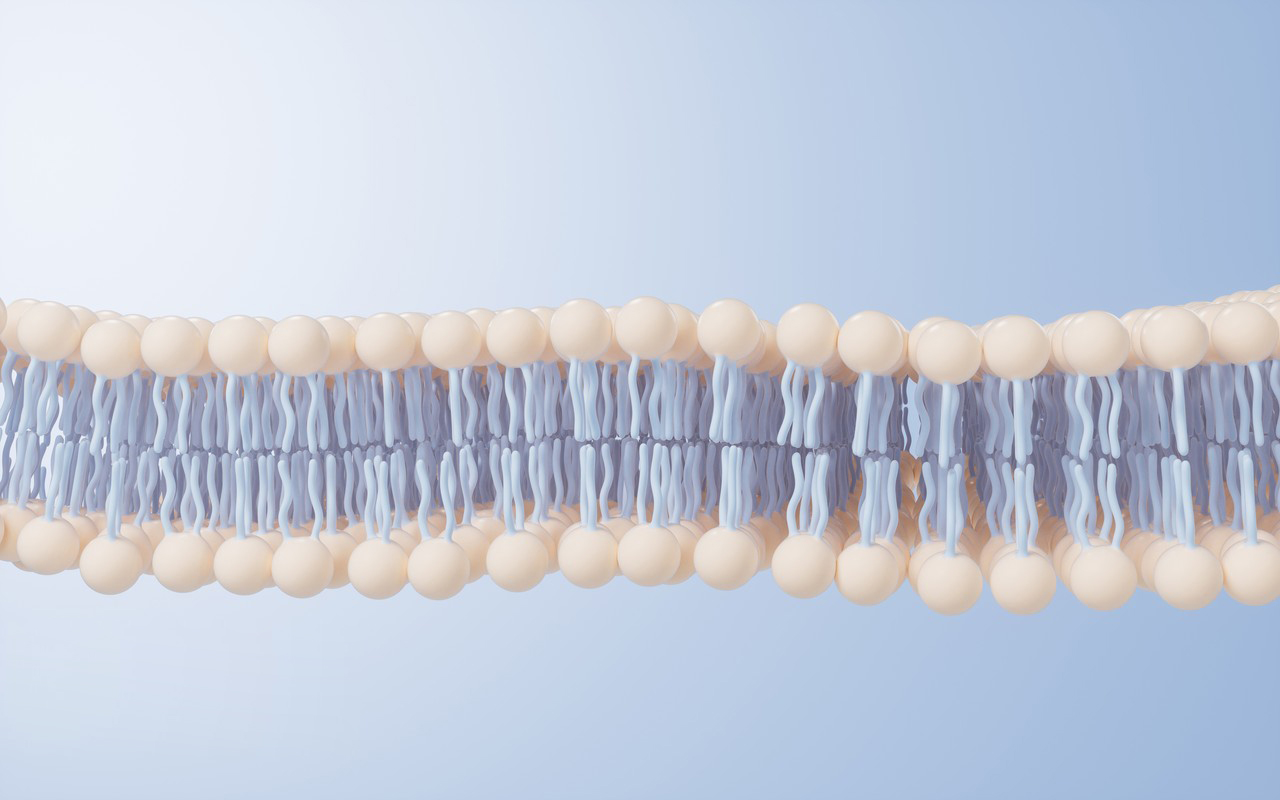
2. Liposomes
Chemical Structure:
- Phospholipids: The primary component of liposomes. Phospholipids typically have a structure consisting of:
- Hydrophilic Head: A phosphate group attached to a glycerol molecule.
- Hydrophobic Tails: Two fatty acid chains that are repellent to water.
- Liposome Structure: Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of one or more phospholipid bilayers. The hydrophilic heads face outward toward the aqueous environment, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, forming the lipid bilayer. The Vitamin C is encapsulated within the aqueous core of these vesicles.
Physical Properties:
- Size: Typically range from 50 nanometers to several micrometers in diameter.
- Appearance: Liposomal formulations are usually clear to slightly opaque liquids.
- Stability: More stable than free Vitamin C due to encapsulation; however, stability can still be affected by factors such as temperature and light exposure.
- Solubility: Liposomes are dispersible in water, which allows them to carry both hydrophilic (Vitamin C) and lipophilic substances.

Combination of Vitamin C with Liposomes:
Encapsulation:
- Mechanism: Vitamin C is encapsulated within the liposomes, which protect it from oxidation and degradation. The liposomal structure allows for better absorption and delivery of Vitamin C to cells.
Overall Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Liposomal Vitamin C formulations are usually in liquid or gel form and may appear milky or translucent.
- Stability: Enhanced compared to non-liposomal Vitamin C due to the protective liposomal layers. However, the formulation needs to be stored properly to maintain efficacy.
Liposomal Vitamin C aims to leverage the stability and delivery advantages of liposomes to improve the efficacy of Vitamin C supplementation.
