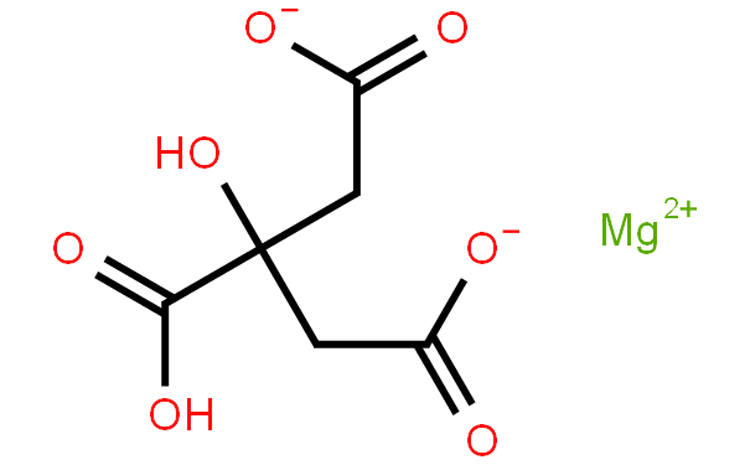
Magnesium citrate capsules typically contain two main ingredients: magnesium citrate and the capsule material itself. Magnesium citrate is a chemical compound with the formula Mg3(C6H5O7)2. It is a magnesium salt of citric acid. The compound is commonly used as a dietary supplement due to its high bioavailability of magnesium. Magnesium citrate is often found in various forms including capsules, tablets, and solutions. Here is a general overview of its chemical structure and physical properties:
Chemical Structure of Magnesium Citrate Capsules:
Chemical Formula: Mg3(C6H5O7)2
Molecular Weight: Approximately 451.1 g/mol
It is composed of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and citrate ions derived from citric acid.
Physical Properties of Magnesium Citrate Capsules:
Appearance: Magnesium citrate capsules typically contain a white to off-white powder or granules.
Solubility: Magnesium citrate is highly soluble in water.
Taste: It generally has a sour or slightly tart taste due to the presence of citric acid.
Odor: It is usually odorless or has a faint odor.
Stability: Magnesium citrate is stable under normal conditions but may degrade over time in the presence of moisture or at elevated temperatures.
Density: The density of magnesium citrate varies depending on its form (capsule, powder, solution) and any additional excipients used in the formulation.
Melting Point: Magnesium citrate does not have a distinct melting point, but it decomposes upon heating.
Use in Supplements:
Dietary Supplement: Magnesium citrate is commonly used as a dietary supplement to provide magnesium, which is an essential mineral involved in various physiological processes in the body, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone health.
Laxative: In higher doses, magnesium citrate can act as a laxative, helping to relieve constipation by drawing water into the intestines and promoting bowel movements.
Dosage and Administration:
The dosage of magnesium citrate capsules may vary depending on the intended use and individual factors such as age, sex, and health status.
It is typically taken orally with water, preferably on an empty stomach, but can also be taken with food if gastrointestinal discomfort occurs.
It is essential to follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by healthcare professionals or indicated on the product label to avoid overdose or adverse effects.

Safety Considerations:
Magnesium citrate is generally considered safe for most people when taken at recommended doses. However, excessive intake may lead to magnesium toxicity, which can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping.
Individuals with certain medical conditions (e.g., kidney disease, heart disease) or those taking certain medications should consult with a healthcare professional before using magnesium citrate supplements to avoid potential interactions or complications.
Overall, magnesium citrate capsules are widely used as a convenient and effective way to supplement magnesium intake and promote overall health and well-being. However, it is essential to use them responsibly and as directed to ensure safety and efficacy.
