Mandelic acid is an aromatic alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) derived from bitter almonds. It’s commonly used in dermatology and cosmetic formulations for its exfoliating, antibacterial, and anti-aging properties.
Chemical Structure of Mandelic Acid
Molecular Formula: C₈H₈O₃
Molecular Weight: 152.15 g/mol
IUPAC Name: 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid
Structure:
- Functional Groups: Mandelic acid contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the alpha carbon, a carboxylic acid group (-COOH), and a phenyl ring (C₆H₅).
- Stereochemistry: Mandelic acid has a chiral center at the alpha carbon, meaning it exists in two enantiomeric forms: (R)-mandelic acid and (S)-mandelic acid.
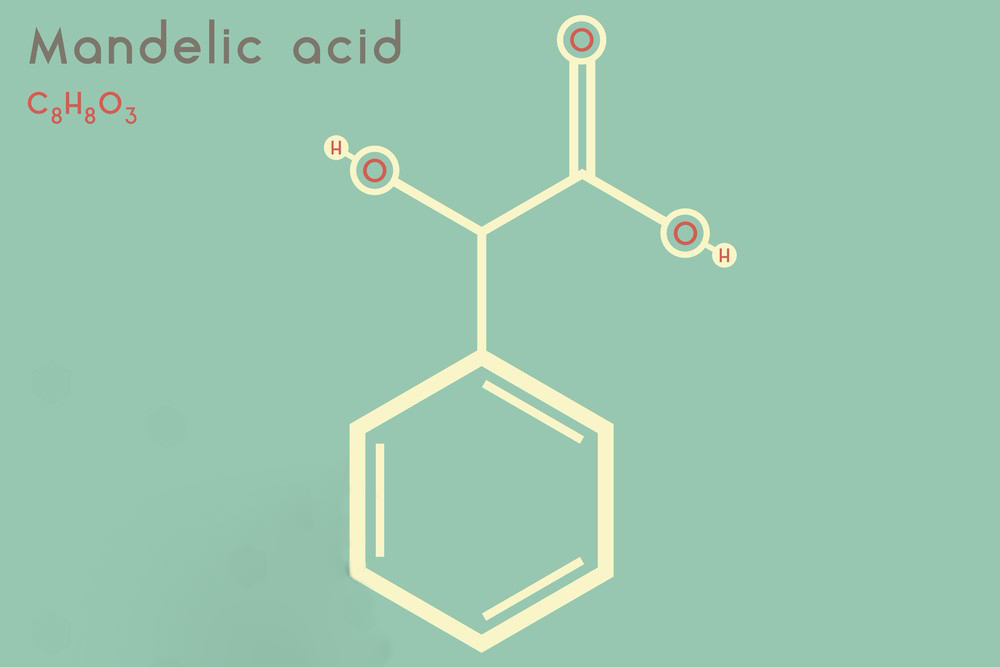
Structure Formula:
OH
|
C6H5—C—COOH
|
H
Physical Properties of Mandelic Acid
- Appearance: White crystalline powder.
- Melting Point: 118–121°C
- Solubility:
- Water: Moderately soluble (~1.4 g/100 mL at 25°C).
- Organic solvents: Soluble in ethanol and acetone.
- pKa: 3.85 (for the carboxylic acid group, indicating weak acidity).
- Boiling Point: Mandelic acid decomposes before reaching a boiling point.
- Density: 1.3 g/cm³ at 25°C.
- Optical Rotation: Depending on the enantiomer, it can be either dextrorotatory (+) or levorotatory (-).

Additional Characteristics:
- Hygroscopic: Absorbs moisture from the air.
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions but can degrade in the presence of strong acids or bases.
- Toxicity: Generally considered safe at low concentrations, commonly used in dermatological formulations.
Mandelic acid is primarily used for its exfoliating and antibacterial properties in skincare, particularly for treating acne and hyperpigmentation.
