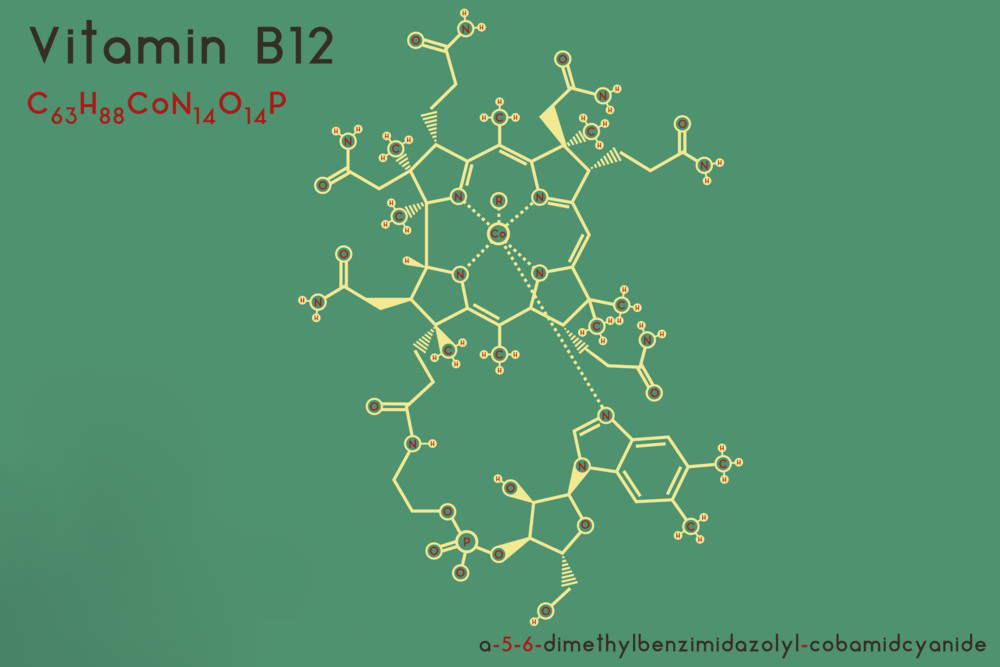
Mecobalamin (Methylcobalamin)
Chemical Structure of Mecobalamin:
IUPAC Name: Cobinamide, Co-methyl-, 5′-phosphate (ester)
Molecular Formula: C63H91CoN13O14P
Molecular Weight: 1344.38 g/mol
Mecobalamin is a cobalamin, a form of vitamin B12. The structure of mecobalamin is similar to other cobalamins, with a central cobalt atom coordinated in a corrin ring. In mecobalamin, the cobalt atom is bonded to a methyl group.
Structure Description of Mecobalamin:
Central Cobalt Atom: The cobalt atom is in the +3 oxidation state.
Corrin Ring: A macrocyclic structure with four pyrrole rings connected by methylene bridges.
Axial Ligands: One of the axial ligands is a methyl group (–CH3), distinguishing it from other cobalamins where different groups occupy this position. The other axial ligand is a nucleotide (5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole).
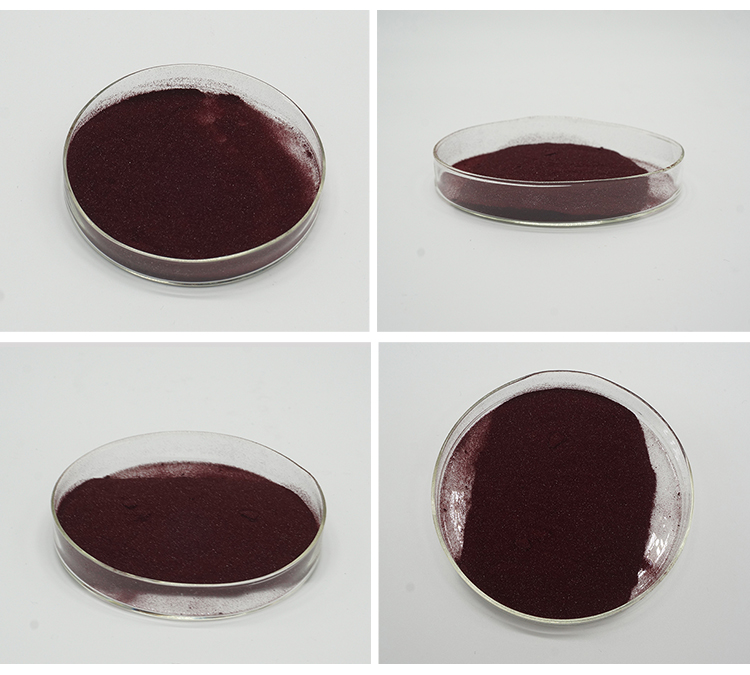
Physical Properties of Mecobalamin:
1.Appearance:
Form: Crystalline powder
Color: Dark red to reddish-brown
2.Solubility:
Water: Soluble
Ethanol: Slightly soluble
Methanol: Soluble
Chloroform: Insoluble
3.Melting Point: Decomposes before melting, generally around 300°C.
4.Stability:
Mecobalamin is light-sensitive and should be protected from light.
It is relatively stable at room temperature but should be stored in a cool, dry place.
5.Optical Rotation: Typically shows optical activity, but specific rotation values depend on the solvent and concentration.
Biological Role:
Mecobalamin plays a crucial role in the human body, including:
DNA Synthesis: It is involved in the formation of red blood cells and maintenance of the nervous system.
Methylation Reactions: Acts as a coenzyme in the methylation of homocysteine to methionine.
Neurological Function: Supports healthy nerve cells and the production of nucleic acids.

Medical Uses:
Mecobalamin is often used to treat:
Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Especially in individuals with pernicious anemia.
Neuropathies: Such as diabetic neuropathy or peripheral neuropathy.
Anemia: Due to its role in red blood cell production.
Summary:
Mecobalamin is a biologically active form of vitamin B12 with a unique chemical structure that includes a central cobalt atom bonded to a methyl group. Its physical properties include solubility in water and light sensitivity. It is crucial for DNA synthesis, neurological function, and various metabolic processes.
