Melatonin is a hormone that is naturally produced in the pineal gland of the brain and plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm. Its chemical structure and physical properties are as follows:
Chemical Structure of Melatonin:
Melatonin has a relatively simple chemical structure. It is a derivative of the amino acid tryptophan. Its chemical formula is C13H16N2O2, and its systematic name is N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine. The structure consists of a tryptophan core with an acetyl group and a methoxy group attached to it. The chemical structure can be represented as:
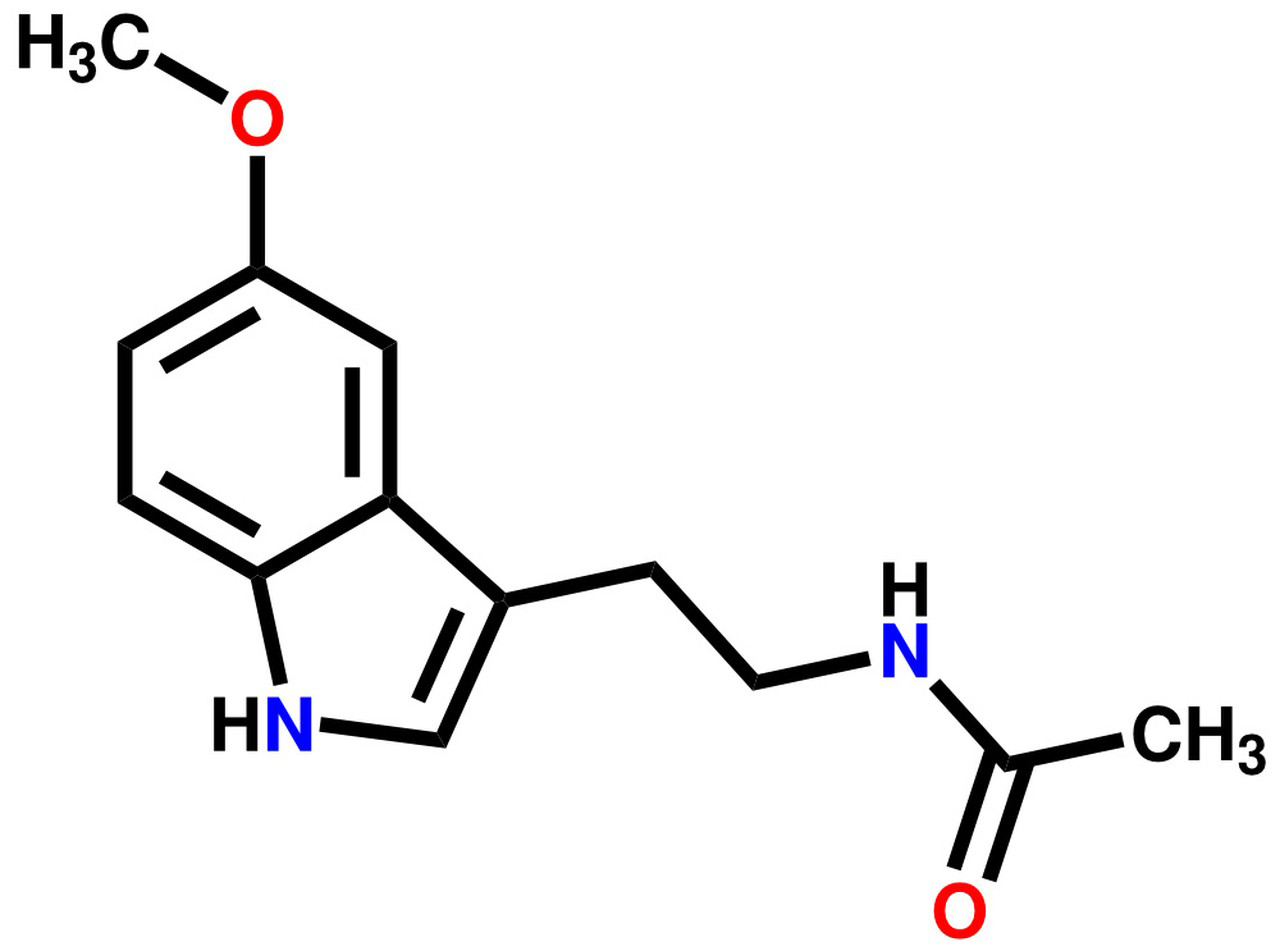
Physical Properties of Melatonin:
Melatonin is a white to off-white crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water. Here are some of its physical properties:
- Melting Point: Melatonin melts at around 116-117°C (241-243°F).
- Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water but more soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and methanol.
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of melatonin is approximately 232.3 g/mol.
- **Melatonin has a low partition coefficient (log P) value, which means it has a higher affinity for lipid-based substances.
- **It is stable at room temperature but can degrade in the presence of light and oxygen, so it should be stored in a dark, cool, and dry place to maintain its stability.
Melatonin is also known for its role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, and its levels in the body typically rise in the evening, helping to promote sleep, and decrease in the morning, allowing for wakefulness. Melatonin supplements are sometimes used to help with sleep disorders and jet lag, among other things.
Application of Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain that plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm) in humans and other animals. It is also available in supplement form and has a range of potential applications. Here are some common uses and applications of melatonin:
Sleep Aid: Melatonin supplements are commonly used to help people with sleep disorders or those who have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. It can be particularly useful for individuals with jet lag, shift work sleep disorder, or insomnia.
Jet Lag: Melatonin is often used to alleviate the symptoms of jet lag, such as sleep disturbances, fatigue, and difficulty adjusting to new time zones. Taking melatonin supplements at the right time can help synchronize your internal clock with the new time zone.
Shift Work: People who work irregular or night shifts may use melatonin to help regulate their sleep-wake patterns and improve sleep quality.
Insomnia: Melatonin supplements may be used as a short-term solution for those with insomnia. It is typically recommended for short-term use and in conjunction with other lifestyle changes to address the underlying causes of insomnia.
Circadian Rhythm Disorders: Melatonin is sometimes prescribed to individuals with circadian rhythm sleep disorders, such as delayed sleep phase disorder or advanced sleep phase disorder. It can help reset the body’s internal clock.
Sleep Disorders in Children: Some children with sleep disorders, such as autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), may benefit from melatonin supplements to improve sleep quality.
Light Sensitivity: Melatonin can be used to alleviate symptoms of certain light-sensitive conditions, such as seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Aging: As people age, their natural melatonin production may decrease. Melatonin supplements are sometimes used by older adults to help improve sleep and manage age-related sleep disturbances.
Antioxidant Properties: Melatonin is also known for its antioxidant properties and its potential role in protecting cells from oxidative stress. Some research suggests it may have a protective effect against certain diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders and cardiovascular diseases.
Migraine Prevention: There is limited evidence to suggest that melatonin may help reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines in some individuals.
It’s important to note that while melatonin is available over the counter as a dietary supplement in many countries, it is not regulated as strictly as pharmaceutical drugs. Therefore, it’s essential to use melatonin supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to follow recommended dosages and guidelines. Potential side effects and interactions with other medications should also be considered. Melatonin is not a suitable treatment for all sleep-related problems, and its use should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine if it is appropriate for your specific situation.
