Retinoic acid, also known as vitamin A acid or tretinoin, is a biologically active form of vitamin A. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including embryonic development, vision, immune function, and skin health. Here is some information about the chemical structure and physical properties of retinoic acid:
Chemical Structure of Retinoic Acid:
Retinoic acid belongs to the class of compounds known as retinoids, which are derivatives of vitamin A.
The chemical formula of retinoic acid is C20H28O2.
Its systematic name is (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid.
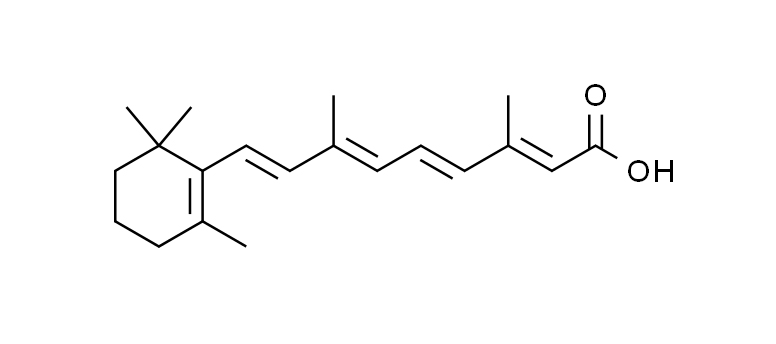
Chemical Structure Visualization:
H H O
| | //
H–C==C–C==C–C==C–COOH
| | \
H H CH3
Physical Properties of Retinoic Acid:
Appearance: Retinoic acid is a yellow to light-orange crystalline powder.
Melting Point: The melting point of retinoic acid is approximately 180-182°C.
Solubility: It is practically insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as acetone, chloroform, and methanol.
Stability: It is sensitive to light and air, and its stability can be affected by exposure to these factors.
Biological Activity of Retinoic Acid:
Retinoic acid is a biologically active compound and serves as a signaling molecule in the regulation of gene expression.
It is widely used in dermatology for the treatment of acne and certain skin conditions, as it helps regulate skin cell growth and differentiation.
Note: Retinoic acid is different from retinol, another form of vitamin A, which is commonly used in skincare products. Retinol is converted into retinoic acid in the skin and then exerts its biological effects.
It’s important to note that while retinoic acid has beneficial effects, it can also be irritating to the skin, and its use should be carefully monitored. If considering the use of retinoic acid for skincare or any medical purpose, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.
