Chemical Structure of S-Acetyl-L-Glutathione
S-Acetyl-L-Glutathione is a derivative of glutathione, where an acetyl group is attached to the sulfur atom of the cysteine residue. This modification is intended to enhance the stability and bioavailability of glutathione. Here is the detailed information:
IUPAC Name: N-(N-L-γ-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)glycine, S-(acetyloxy)-
Molecular Formula: C12H19N3O7S
Molecular Weight: 349.36 g/mol
Chemical Structure
The structure can be described in segments:
Glutathione structure: γ-Glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine
Acetyl group attached to the sulfur atom of the cysteine residue
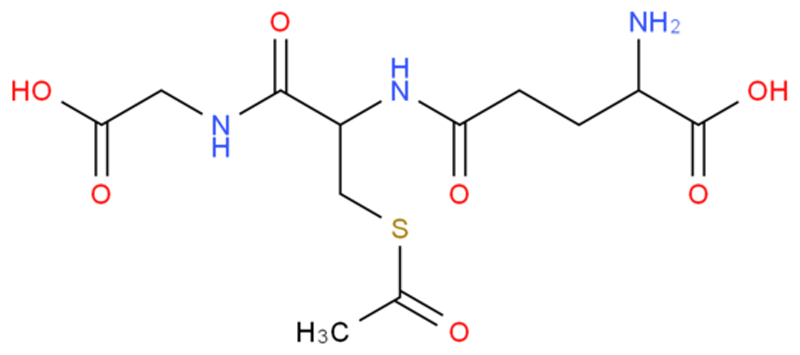
The structure can be represented as follows:
O
||
H3C – C – S – CH2 – CH – COOH
|
NH – CH – CO – NH – CH2 – COOH
|
CH2 – CH2 – COOH
Here, the acetyl group (CH3-CO) is attached to the sulfur (S) of the cysteine part of glutathione.
Physical Properties of S-Acetyl-L-Glutathione
1.Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder.
2.Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol.
3.Melting Point: Typically around 195-200°C.
4.Stability: More stable than reduced glutathione (GSH) due to the acetyl group, which protects it from oxidation and degradation in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing better systemic absorption.
5.Taste: Slightly bitter.

Functional Benefits
S-Acetyl-L-Glutathione is used as a dietary supplement for its antioxidant properties. The acetylation increases its stability in the digestive system, allowing more glutathione to be absorbed and utilized by the body. It helps in:
Reducing oxidative stress
Supporting immune function
Detoxifying harmful substances
Protecting cells from damage
These attributes make it popular in nutraceuticals and health supplements.
