Tranexamic acid is a synthetic compound that belongs to the class of antifibrinolytic medications. It is used to treat or prevent excessive bleeding in various medical conditions. Here’s some information about its chemical structure and physical properties:
Chemical Structure of Tranexamic Acid:
Chemical Formula: C8H15NO2
Systematic Name: trans-4-(Aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Molecular Weight: 157.21 g/mol
CAS Number: 1197-18-8
Tranexamic acid has a simple chemical structure consisting of a cyclohexane ring with an amino group and a carboxylic acid group attached. The chemical structure is:
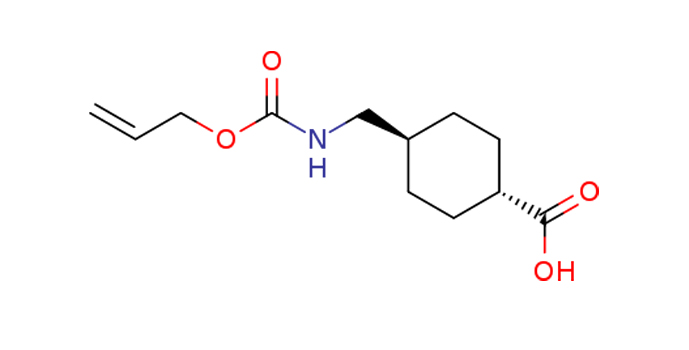
Physical Properties of Tranexamic Acid:
Physical Form: Tranexamic acid is typically found as a white or almost white crystalline powder.
Melting Point: The melting point of tranexamic acid is approximately 300-305°C (572-581°F).
Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water and ethanol but more soluble in methanol. Its solubility in water is about 1.9 g/100 mL at 25°C.
Stability: Tranexamic acid is stable under normal storage conditions. It should be protected from moisture and light.
Odor and Taste: It is odorless and has a slightly bitter taste.
Density: The density of tranexamic acid is about 1.5 g/cm³.
pKa: The pKa (acid dissociation constant) of tranexamic acid is around 3.6.
These physical properties are important in pharmaceutical formulations and for understanding how tranexamic acid behaves in various medical and chemical contexts. It is commonly available in the form of oral tablets, injections, or topical preparations for medical use.
Treatment of Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid is a medication that is used to treat or prevent excessive bleeding or hemorrhage in various medical conditions. It works by helping to prevent blood clots from breaking down too quickly. Here’s a general overview of how tranexamic acid is used in medical treatment:
Trauma and Surgery: Tranexamic acid is often used in surgical and trauma settings to reduce bleeding during and after procedures. It can be given intravenously (IV) before and during surgery to help control bleeding.
Menstrual Bleeding: Tranexamic acid can be prescribed to women with heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia) to help reduce the amount of blood loss during their periods. It is typically taken orally, as tablets, for a few days during the menstrual cycle.
Hemophilia: In some cases, tranexamic acid may be used to manage bleeding in individuals with hemophilia, a genetic bleeding disorder. It can be given intravenously in a hospital setting.
Nosebleeds: Tranexamic acid may be used as a topical treatment for recurrent nosebleeds. It can be applied as a nasal spray or soaked in cotton pledgets and inserted into the nostrils.
Dental Procedures: Dentists may use tranexamic acid as a mouthwash after oral surgery to help control bleeding and reduce the risk of complications.
It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations and dosage instructions when using tranexamic acid, as the appropriate dosage and administration method can vary depending on the specific condition being treated. Also, inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Tranexamic acid is generally considered safe when used as directed, but like any medication, it may have side effects. Common side effects can include gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and diarrhea. In rare cases, severe allergic reactions can occur, so it’s important to be aware of any unusual or severe side effects and seek medical attention if they occur.
This information is intended to provide a general overview of tranexamic acid’s uses and treatments. Always consult with a healthcare professional for specific guidance on its use and any potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
