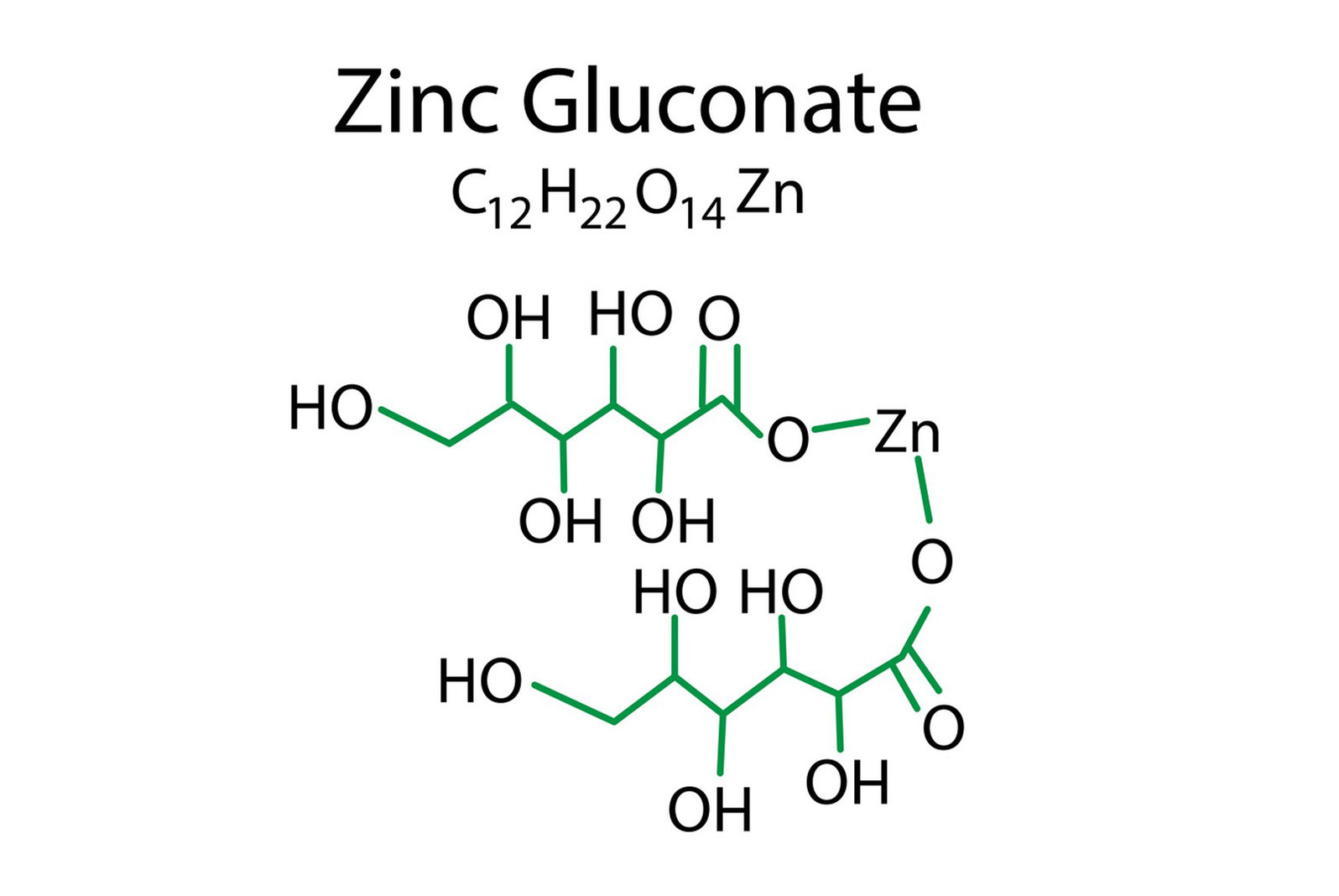
Zinc gluconate is a chemical compound that consists of the essential mineral zinc and the organic molecule gluconic acid. Its chemical formula is C12H22O14Zn. Here’s a breakdown of its chemical structure and some of its physical properties:
Chemical Structure of Zinc Gluconate:
Zinc gluconate is derived from the reaction between zinc oxide or zinc carbonate and gluconic acid. The structure can be represented as follows:
The zinc ion (Zn^2+) is coordinated with the oxygen atoms from the gluconate molecule.
Physical Properties of Zinc Gluconate:
1.Color and Appearance:
Zinc gluconate is typically a white to slightly yellowish powder or granules.
2.Solubility:
It is soluble in water, which makes it suitable for use in various oral zinc supplements.
3.Molecular Weight:
The molecular weight of zinc gluconate is approximately 455.68 g/mol.
4.Melting Point:
The compound may not have a distinct melting point as it may decompose before reaching a specific temperature. However, it is stable at typical storage conditions.
5.Odor and Taste:
Zinc gluconate is generally odorless and has a slightly astringent taste.
6.pH:
Solutions of zinc gluconate are mildly acidic. The pH of a solution will depend on the concentration.
7.Stability:
Zinc gluconate is stable under normal storage conditions. However, it may be sensitive to heat and moisture, and exposure to these conditions can lead to degradation.

8.Usage:
Zinc gluconate is commonly used as a zinc supplement in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and syrups. It is chosen for its water solubility and bioavailability.
9.Bioavailability:
The gluconate form of zinc is known to have good bioavailability, meaning that the body can absorb and utilize the zinc efficiently.
10.Health Considerations:
Zinc is an essential trace element required for numerous biological functions, including immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. Zinc gluconate is often used to address zinc deficiencies.
It’s important to note that the properties mentioned here can vary based on factors such as purity, crystalline form, and specific manufacturing processes. If you are using zinc gluconate for specific applications, it’s recommended to refer to the product specifications provided by the manufacturer. Additionally, for any medical or nutritional concerns, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.
