Vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine (SMM), is not technically classified as a vitamin, though it is sometimes referred to as one due to its health benefits. It is a compound derived from the amino acid methionine and is found in foods like cabbage, particularly in cabbage juice, and in certain vegetables.
Key Benefits of Vitamin U:
- Gastrointestinal Health: Vitamin U is primarily known for its ability to help protect the stomach lining and promote healing, particularly in cases of ulcers and gastritis. It is believed to help stimulate the healing of stomach and intestinal ulcers by enhancing mucous production.
- Liver Health: Some studies suggest it may support liver function and protect it from damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Its potential anti-inflammatory properties can help in reducing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.

Similar Products or Compounds to Compare Vitamin U With:
1. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
- Similarities: Both are antioxidants and have a role in supporting the immune system and reducing inflammation. Vitamin C also aids in collagen production, which is important for skin and tissue repair.
- Differences: Vitamin C is more widely recognized for its role in immune function and skin health, while Vitamin U is more specialized in gastrointestinal and liver health.
2. L-Glutamine
- Similarities: Both have benefits related to gut health. L-Glutamine is an amino acid that supports the healing of the intestinal lining and can help manage conditions like leaky gut syndrome.
- Differences: L-Glutamine is more directly involved in maintaining the integrity of the gut lining, while Vitamin U focuses more on ulcer healing and protecting the stomach lining.
3. L-Arginine
- Similarities: L-Arginine, like Vitamin U, may have a role in gastrointestinal health and support blood circulation, as it is a precursor to nitric oxide, which helps dilate blood vessels.
- Differences: L-Arginine’s main functions focus on nitric oxide production and cardiovascular health, whereas Vitamin U’s main use is for stomach health, particularly healing ulcers.
4. Probiotics
- Similarities: Both Vitamin U and probiotics have benefits for the digestive system. Probiotics promote a healthy gut microbiome, which aids in digestion and overall gut function.
- Differences: Vitamin U directly targets the mucous lining of the stomach and intestines, whereas probiotics focus on balancing gut bacteria to maintain gut health.
5. Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice (DGL)
- Similarities: Both Vitamin U and Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice have been traditionally used to treat gastrointestinal issues such as ulcers and gastritis. DGL helps soothe the stomach lining and promote healing.
- Differences: Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice is a herbal product that works by enhancing mucus production and soothing the stomach, while Vitamin U is a compound derived from methionine that has similar protective effects.
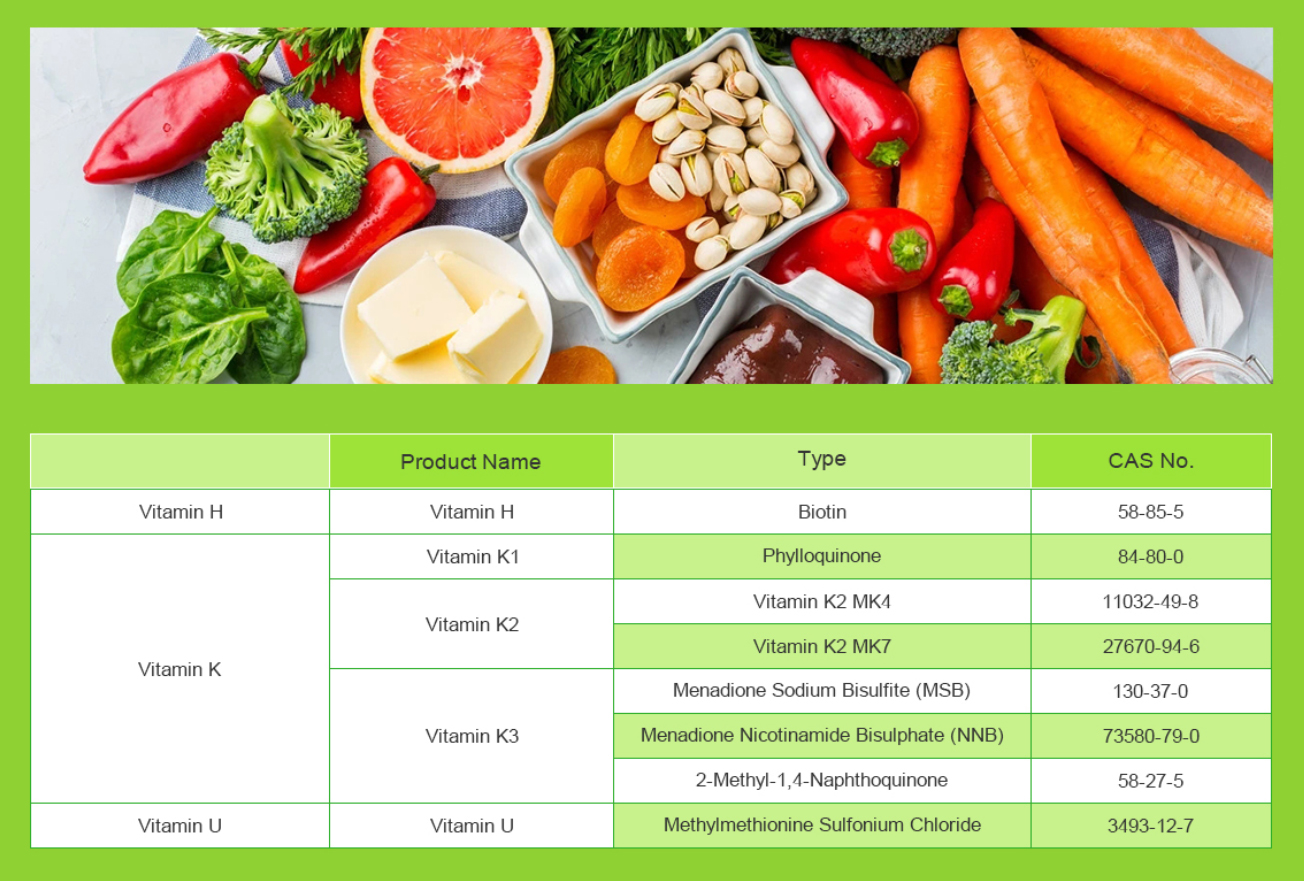
Conclusion:
Vitamin U is unique in its ability to directly support the healing of ulcers and protect the stomach lining, which distinguishes it from other nutrients and supplements that generally support gut health, immune function, or liver health. When compared with similar products, its specific use in gastrointestinal and ulcer-related conditions sets it apart, although there are other compounds like L-Glutamine, DGL, and probiotics that may also aid in digestive health but via different mechanisms.
