NMNH (Reduced Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), is an important compound in the study of cellular metabolism and aging. It is the reduced form of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), a precursor to NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), which plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes.
Overview of NMNH
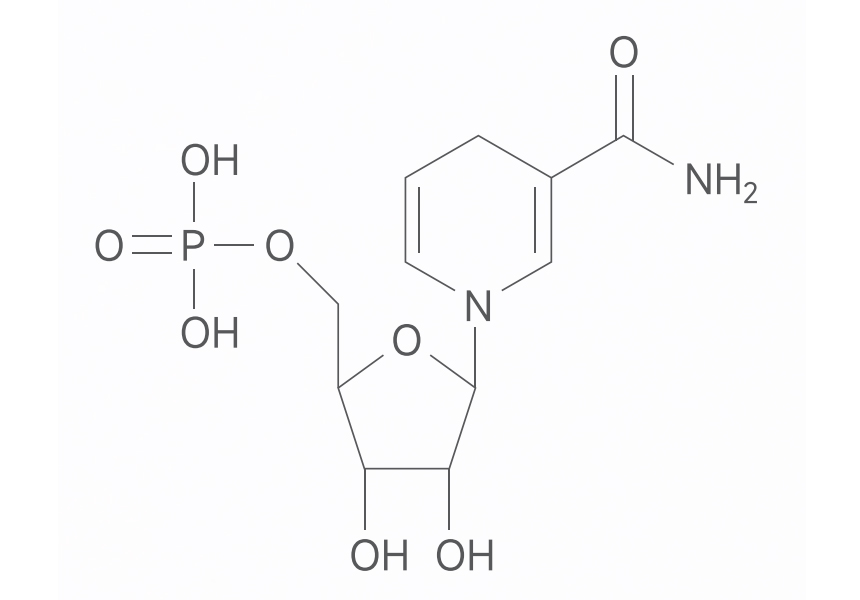
1. Chemical Structure and Properties:
- Chemical Formula: C11H16N2O7P
- Molecular Weight: 318.23 g/mol
- NMNH is the reduced form of NMN, with an additional hydrogen atom on the nicotinamide ring, changing the oxidation state of the molecule.
2. Role in NAD+ Biosynthesis:
- NAD+ is a vital coenzyme in redox reactions, DNA repair, and signaling. It exists in two forms: NAD+ (oxidized) and NADH (reduced).
- NMN is a direct precursor to NAD+, and NMNH serves as the reduced form of NMN.
- The presence of NMNH suggests a potential pathway where NMN can exist in both oxidized and reduced states, impacting NAD+ biosynthesis and cellular redox balance.

3. Biological Significance:
- Energy Metabolism: NMNH is involved in the maintenance of NAD+ levels, which is essential for cellular energy production through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
- Aging and Longevity: NAD+ levels decline with age, and its replenishment has been linked to extended lifespan and improved healthspan. NMNH, as a precursor to NAD+, could play a role in mitigating age-related decline.
- Cellular Health and Repair: NAD+ is crucial for the activity of sirtuins, enzymes involved in DNA repair and cellular stress resistance. NMNH may contribute to maintaining NAD+ levels, thereby supporting cellular repair mechanisms.
4. Research and Therapeutic Potential:
- Aging and Neurodegeneration: Studies suggest that NMN supplementation can improve cognitive function and delay neurodegenerative processes in animal models. NMNH, as a related compound, may offer similar benefits.
- Metabolic Disorders: By influencing NAD+ levels, NMNH could be beneficial in conditions like obesity, diabetes, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
- Cardiovascular Health: NAD+ is critical for the function of vascular endothelial cells. NMNH could potentially support cardiovascular health by sustaining NAD+ levels.
5. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability:
- Research into NMNH’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion is still limited compared to NMN.
- Oral bioavailability and stability in vivo are crucial considerations for its potential as a therapeutic agent.
6. Current Research and Future Directions:
- Studies are ongoing to better understand NMNH’s role in cellular metabolism and its impact on NAD+ homeostasis.
- Investigations into NMNH as a dietary supplement or therapeutic intervention for age-related conditions are in their early stages.
Conclusion
NMNH, as a reduced form of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, is an intriguing compound with significant implications for cellular metabolism, aging, and disease. While research is still in its infancy compared to its counterpart NMN, it holds potential for therapeutic development in areas such as neurodegeneration, metabolic health, and longevity.
If you have more specific aspects or studies on NMNH you’d like to explore, feel free to ask!
