Bacillus megaterium is a versatile bacterium with several economic uses across various industries:
- Agriculture: Bacillus megaterium is used as a biofertilizer. It helps in the solubilization of phosphate, making it more available to plants. This can enhance plant growth and crop yields.
- Bioremediation: It has the capability to degrade various pollutants, including heavy metals and hydrocarbons, making it useful in cleaning up contaminated environments.
- Enzyme Production: Bacillus megaterium is used in the production of enzymes such as amylases, proteases, and cellulases. These enzymes have applications in food processing, textiles, and detergents.
- Pharmaceuticals: It is involved in the production of antibiotics and other bioactive compounds, contributing to the pharmaceutical industry.
- Probiotics: Some formulations include Bacillus megaterium as a probiotic, which can benefit gut health in animals and potentially humans.
- Food Industry: It can be used in fermentation processes and as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties.

Overall, Bacillus megaterium’s ability to produce enzymes and its role in nutrient cycling make it an important organism in sustainable practices across various sectors.
Introduction to Bacillus Megaterium
Bacillus megaterium is a gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the genus Bacillus. It is one of the largest known bacteria, with a length of up to 1–3 micrometers and a diameter of about 0.5–1 micrometer. Here are some key points about Bacillus megaterium:
Characteristics:
- Shape and Size: Rod-shaped and larger than many other bacteria.
- Gram Stain: Positive, indicating a thick peptidoglycan layer in its cell wall.
- Spores: Forms endospores, allowing it to survive in harsh conditions.
Habitat:
- Found in various environments, including soil, water, and plant surfaces.
- Can also be present in the gut flora of some animals.
Metabolism:
- Primarily aerobic, but can also grow anaerobically.
- Utilizes a wide range of organic compounds for energy.
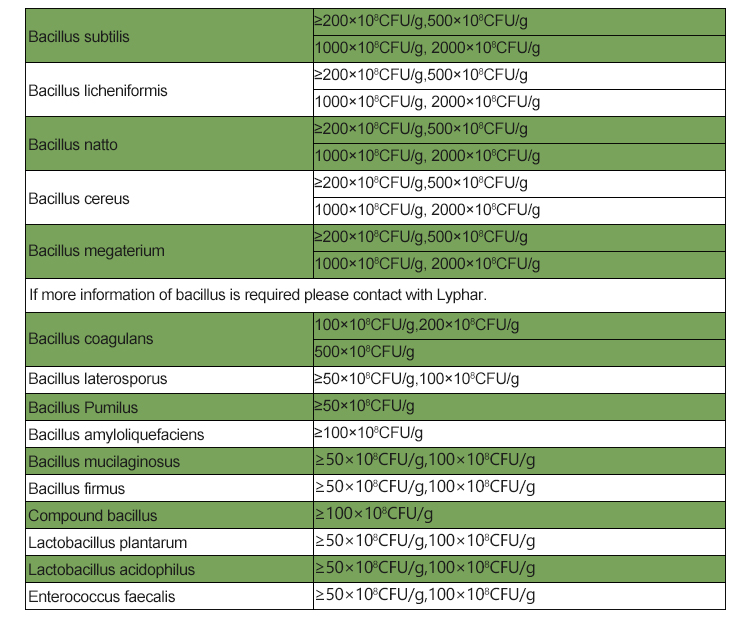
Industrial Applications:
- Biotechnology: Used in the production of enzymes, antibiotics, and vitamins.
- Bioremediation: Can degrade environmental pollutants.
- Research: Serves as a model organism in studies of cellular processes and genetics.
Pathogenicity:
- Generally considered non-pathogenic; however, some strains can be opportunistic pathogens in immunocompromised individuals.
Bacillus megaterium is significant in both ecological and industrial contexts due to its versatility and resilience.
