Dutasteride is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. It is primarily used to treat conditions related to the prostate gland, specifically benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and androgenetic alopecia (male-pattern baldness). The drug works by inhibiting the action of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into its more potent form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Here’s how Dutasteride works and its effects:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
BPH is a common condition in aging men where the prostate gland enlarges, leading to urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak stream, and difficulty starting and stopping urination. DHT is believed to contribute to the growth of the prostate gland. By inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to DHT, Dutasteride helps reduce the size of the prostate gland over time, relieving urinary symptoms and improving urine flow.
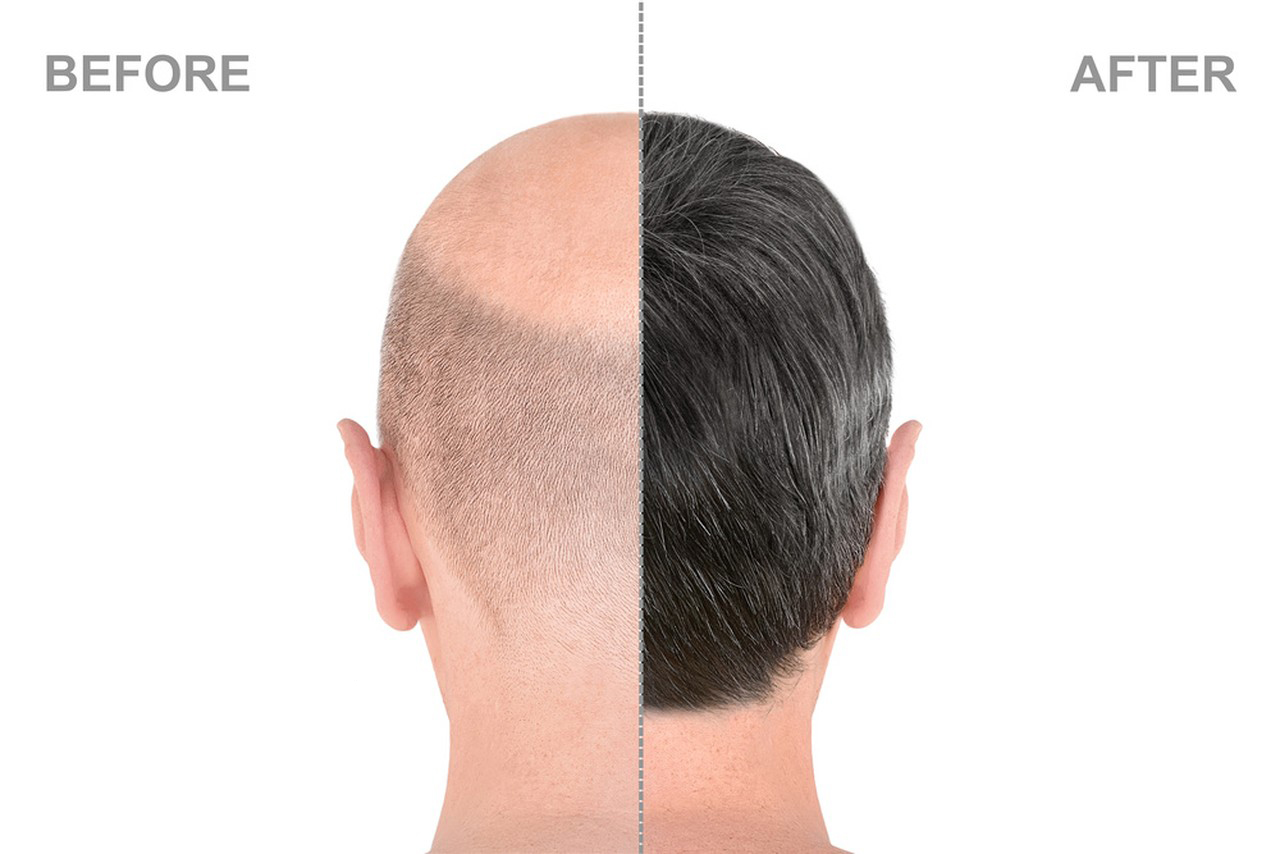
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male-Pattern Baldness):
Androgenetic alopecia is a hereditary condition characterized by gradual hair loss and thinning in men. DHT is known to contribute to hair follicle miniaturization, leading to the gradual loss of hair. By reducing DHT levels, Dutasteride may help slow down or even reverse hair loss in some individuals. However, its use for this purpose is generally off-label and controversial due to potential side effects and long-term consequences.
Effects and Considerations:
- Prostate Health: Dutasteride can effectively alleviate symptoms of BPH, improve urinary flow, and reduce the size of the prostate gland. It may take several months of consistent use to observe noticeable improvements.
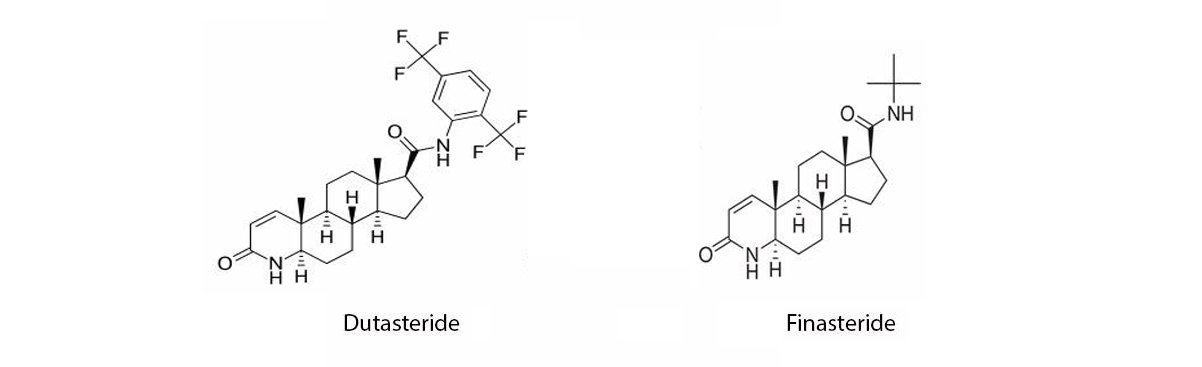
- Hair Loss: While some studies suggest that Dutasteride might be more effective than the more commonly used finasteride for treating male-pattern baldness, it’s important to note that its use for this purpose is not approved by regulatory agencies like the FDA in the United States. Additionally, Dutasteride has a longer half-life and stronger impact on DHT compared to finasteride, which could lead to more significant hormonal changes and potential side effects.
Side Effects and Risks:
Dutasteride, like any medication, can have side effects. Common side effects include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and decreased ejaculate volume. There are also concerns about potential long-term impacts on hormonal balance, sexual function, and fertility.
It’s important to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives with a medical professional before starting Dutasteride, especially if considering its off-label use for hair loss. The decision to use Dutasteride should be based on a thorough evaluation of your medical history, current health status, and individual needs.
Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance, and do not stop or modify any medication without consulting a qualified medical professional.
Adverse effects of Dutasteride
Dutasteride is a medication primarily used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition in which the prostate gland becomes enlarged, and also to treat male pattern baldness. Like any medication, dutasteride can have potential adverse effects. It’s important to note that not everyone will experience these side effects, and some individuals may experience only mild or no side effects at all. Common adverse effects of dutasteride may include:
Sexual Side Effects: Dutasteride can impact sexual function in some individuals. This can include a decreased sex drive, difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection (erectile dysfunction), and a decrease in semen volume during ejaculation.
Breast Enlargement and Tenderness: Some men taking dutasteride might experience breast enlargement (gynecomastia) and breast tenderness.
Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to dutasteride are rare, but they can occur. Symptoms of an allergic reaction might include rash, itching, swelling (especially of the face, tongue, or throat), severe dizziness, and difficulty breathing.
Testosterone Suppression: Dutasteride is known to lower levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone related to testosterone. This can lead to a reduction in testosterone levels, which might have implications for energy levels, mood, and muscle mass.
Mood Changes: Some individuals may experience mood changes, including depression and anxiety, while taking dutasteride.
Decreased Ejaculatory Volume: Alongside its effect on sexual function, dutasteride might also lead to a decrease in the volume of ejaculated semen.
Urinary Tract Symptoms: While dutasteride is often used to alleviate urinary symptoms associated with BPH, it can initially cause some worsening of urinary symptoms in some individuals.
Headache: Headaches are a possible side effect of dutasteride, though they are generally not very common.
Digestive Disturbances: Some people might experience digestive issues like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Liver Enzyme Abnormalities: In some cases, dutasteride can cause changes in liver enzyme levels. Regular monitoring of liver function might be recommended by healthcare providers.
It’s important to remember that you should not discontinue or adjust your medication without consulting a healthcare professional. If you are experiencing any side effects or concerns while taking dutasteride, it’s best to discuss them with your doctor. They can provide guidance on managing side effects and determine if the benefits of the medication outweigh the potential risks in your individual case.
