L-Arginine is an amino acid that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes in the human body. It’s considered semi-essential, which means the body can produce it, but under certain conditions, supplementation may be necessary. Here are some of the effects and uses of L-Arginine:
1. Nitric Oxide Production: L-Arginine is a precursor to nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that plays a key role in blood vessel dilation (vasodilation). This effect can help improve blood flow, which is important for cardiovascular health and can have potential benefits for conditions like hypertension and erectile dysfunction.
2. Cardiovascular Health: Due to its role in promoting vasodilation and improving blood flow, L-Arginine is often used as a supplement to support cardiovascular health. It may help reduce blood pressure and improve overall heart function.
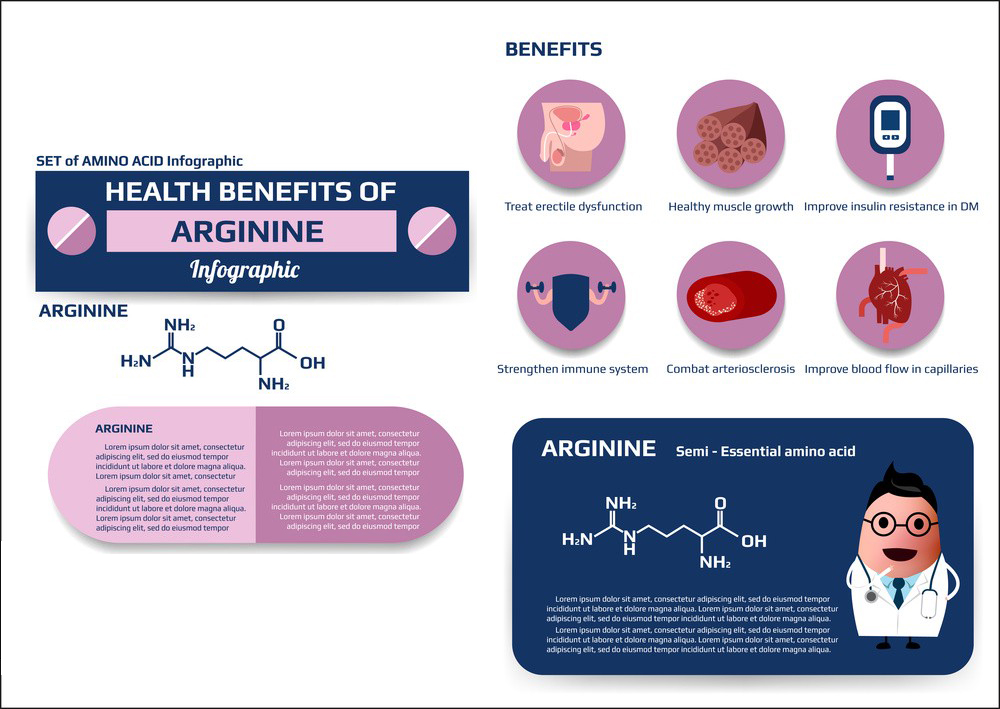
3. Exercise Performance: L-Arginine is sometimes used by athletes and bodybuilders to enhance exercise performance. It’s believed that increased blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscles can improve endurance and muscle recovery.
4. Erectile Dysfunction: Because of its role in promoting blood flow, L-Arginine has been explored as a potential natural remedy for erectile dysfunction. However, its effectiveness in this regard is still a subject of debate, and other treatments like PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra) are more commonly prescribed.
5. Immune Function: L-Arginine is involved in immune system function and wound healing. It may support the body’s defense mechanisms and help with tissue repair.
6. Growth Hormone Production: L-Arginine is sometimes used in conjunction with other amino acids to stimulate the release of growth hormone. This application is more common in the bodybuilding and fitness community.
7. Wound Healing: L-Arginine’s role in promoting tissue repair and collagen production makes it relevant for wound healing and recovery from surgery.
8. Cognitive Function: Some research suggests that L-Arginine may have a role in improving cognitive function, particularly in conditions where blood flow to the brain is compromised, such as vascular dementia. However, more research is needed in this area.
9. Immune System Modulation: L-Arginine is also involved in regulating the immune system. It can modulate the production of immune cells and cytokines, potentially affecting the body’s ability to respond to infections and inflammatory conditions.
10. Potential Side Effects: While L-Arginine is generally considered safe when taken at recommended doses, it can cause side effects in some individuals, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, diarrhea, and nausea. High doses may lead to more severe side effects, including low blood pressure, allergic reactions, and exacerbation of certain health conditions like herpes outbreaks.
It’s important to note that the effects of L-Arginine can vary from person to person, and its use should be discussed with a healthcare provider, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking medications, as it can interact with certain drugs. As with any supplement, it’s crucial to use it responsibly and in accordance with medical advice.
