Collagen extraction and detection are crucial techniques in various research fields, including biochemistry, biotechnology, and medical diagnostics. Collagen is a major structural protein in connective tissues like skin, tendons, cartilage, and bones. Below is an outline of common methods for extraction and detection of collagen:
1. Collagen Extraction
Extraction of collagen typically involves isolating it from tissues where it is abundant, such as skin, bone, or tendons. The general approach is to denature other proteins and extract collagen in a form that can be analyzed.
A. Solubilization of Collagen
Tissue Preparation:
- Tissues such as skin or tendons are typically dissected and washed to remove impurities (e.g., blood, fat).
- Freeze-drying or homogenization can also be used to prepare the tissue.

Collagen Solubilization:
Collagen can be solubilized from tissues by using acidic or enzymatic methods.
- Acid Extraction: Typically involves using acetic acid (0.5 M to 1 M) to solubilize collagen from tissues, which helps break down the extracellular matrix and release collagen fibers.
- Enzymatic Digestion: Collagenase or pepsin can be used to digest non-collagenous proteins and release collagen in a soluble form. Pepsin digestion is common, especially for extracting type I collagen.
B. Purification
After solubilizing collagen, it often requires further purification:
- Ultracentrifugation: To remove non-collagenous proteins and impurities.
- Dialysis: To remove excess salts and other small molecules.
- Chromatography (e.g., ion-exchange chromatography, size exclusion chromatography): Can be used for more refined purification.
2. Collagen Detection Methods
Several techniques are used to identify and quantify collagen, based on its unique structure, amino acid composition, or physical properties.
A. Biochemical Assays
- Hydroxyproline Assay: Hydroxyproline is an amino acid found in collagen, and its quantification is commonly used as an indirect method to determine collagen content in tissues.
- Method: Tissues or extracted collagen are hydrolyzed to release free hydroxyproline, which is then reacted with a colorimetric reagent (e.g., chloramine-T) to produce a color that can be quantified using spectrophotometry.
- Collagenase Digestion Assay: The digestion of collagen by collagenase can be used as a functional assay to assess the integrity of collagen and its solubility after extraction.

B. Molecular Biology Techniques
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR can be used to detect collagen mRNA expression (e.g., types I, II, III, etc.) from RNA extracted from cells or tissues.
- Western Blotting: Detection of specific collagen types can be done using antibodies that bind to specific collagen isoforms (e.g., anti-collagen I, II, III).
- ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay): Commercial kits are available to quantify specific collagen types in biological samples using monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies.
C. Histological and Microscopic Techniques
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): Antibodies specific to collagen can be used in tissue sections to localize and visualize collagen distribution and expression patterns.
- Mass Spectrometry: Advanced techniques such as matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) or liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) can be used to identify collagen peptides and determine collagen subtypes.
D. Spectroscopic Methods
- Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): Collagen has a characteristic absorption in the infrared range, which can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
- Second Harmonic Generation (SHG) Microscopy: Collagen fibers exhibit SHG signal due to their ordered structure, and this method is highly sensitive for collagen detection in tissues.
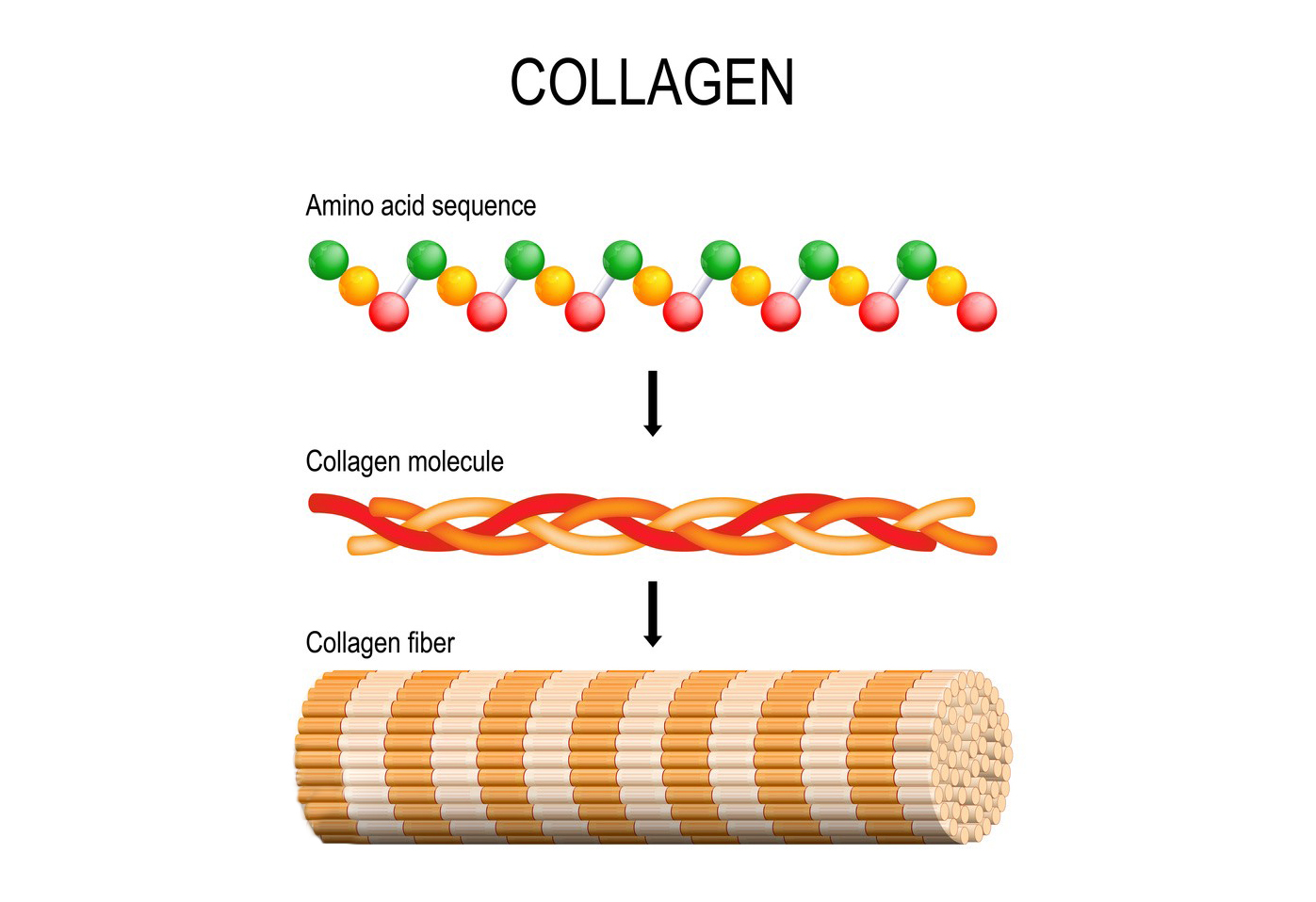
3. Applications of Collagen Extraction and Detection
- Tissue Engineering: Collagen is often used as a scaffold material for growing tissues in vitro.
- Biomarker Discovery: Collagen biomarkers are important for diagnosing diseases such as fibrosis, osteoarthritis, and cancer.
- Wound Healing: Collagen’s role in wound healing is studied in both basic and clinical research.
- Cosmetic Industry: Collagen is also used in anti-aging products, and its detection is critical in quality control and formulations.
Would you like more details on any specific extraction or detection method?
