Extraction process of L-Tryptophan (an essential amino acid) from natural sources involves several steps, which vary depending on the raw material and the method chosen. Here’s a general overview of the process:
1. Raw Material Selection
L-Tryptophan can be extracted from natural sources such as plant proteins (e.g., soy, corn), microbial fermentation, or animal-based proteins. Microbial fermentation is commonly used for industrial-scale production, while plant-based sources are used less frequently.
2. Hydrolysis of Protein Source (if applicable)
- If plant or animal proteins are being used as the raw material, hydrolysis is the first step. The proteins are broken down into their constituent amino acids, including L-Tryptophan.
- Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Enzymes like proteases are used to break down the proteins into peptides and amino acids.
- Acid or Alkali Hydrolysis: Strong acids (e.g., hydrochloric acid) or alkalis (e.g., sodium hydroxide) may also be used for hydrolysis.

3. Fermentation (in the case of microbial production)
- Industrial-scale L-Tryptophan production is often carried out through microbial fermentation, using genetically engineered microorganisms such as Escherichia coli or Corynebacterium glutamicum.
- In this process, the microorganism is cultured in a medium containing a carbon source (like glucose or starch) and other nutrients. The microorganisms synthesize L-Tryptophan as a metabolic byproduct.
- The culture medium is usually monitored for optimal growth conditions such as pH, temperature, and oxygen levels to maximize the yield of L-Tryptophan.
4. Separation of L-Tryptophan
After hydrolysis or fermentation, the L-Tryptophan is separated from other compounds in the mixture. This can be achieved using:
- Filtration: To remove insoluble impurities.
- Centrifugation: If fermentation is used, this step helps separate the biomass (cells and cell debris) from the broth.
- Precipitation: Certain chemicals (like acids or salts) can be added to precipitate L-Tryptophan out of the solution.
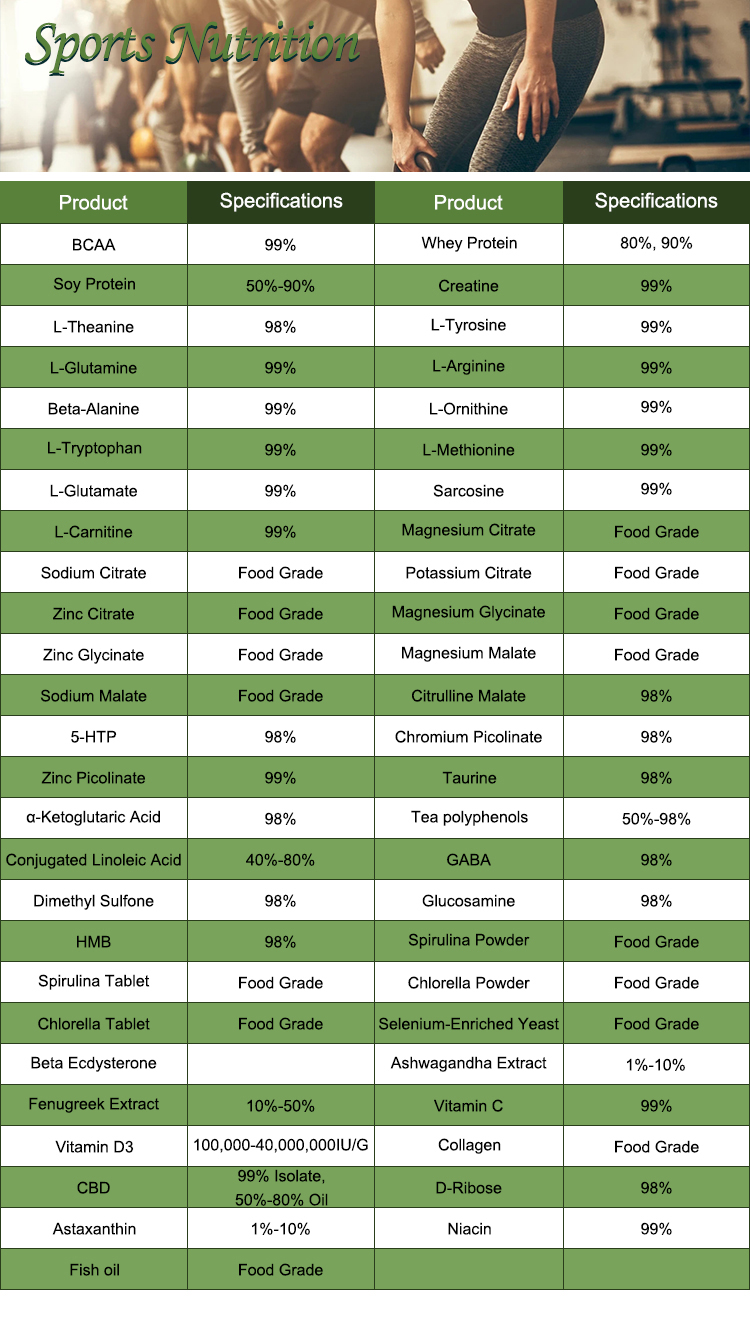
5. Purification
L-Tryptophan, after being isolated, often needs further purification to obtain the desired purity for pharmaceutical or food-grade applications. Methods used for purification include:
- Ion Exchange Chromatography: This separates L-Tryptophan based on its charge, allowing for higher purity.
- Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): A common technique to separate amino acids based on their polarity and affinity to a stationary phase.
- Crystallization: L-Tryptophan can be crystallized from the solution, followed by filtration to isolate the crystals.
6. Drying and Final Processing
After purification, L-Tryptophan is often dried to remove residual solvents or water. This can be done through methods such as:
- Spray Drying
- Freeze Drying
- The final product may be further processed into a powder or tablet form depending on its intended use.
7. Quality Control and Testing
The final product is subjected to various quality control tests to ensure it meets the required standards for purity, strength, and safety. These tests typically include:
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis to check purity.
- UV spectrophotometry to measure the concentration of L-Tryptophan.
- Microbial testing for contamination.
Summary of Methods
- Microbial fermentation is the most common industrial method for L-Tryptophan production.
- Hydrolysis is used when extracting from plant or animal protein sources.
- Purification techniques like chromatography and crystallization are employed to obtain high-purity L-Tryptophan.
Let me know if you need further details or a specific focus on any step!
